
The velocity time graph which represent a body moving with zero acceleration is
Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint:Velocity of a body is the rate of change of position of the body w.r.t a fixed reference frame. And the rate of change of velocity is known as the acceleration of the body. If a body moves with zero acceleration then its velocity doesn’t change i.e. it stays constant.
Formula used:
Velocity and time relationship of a body is given by:
$v(t) = u + a.t$ ……………………….(1)
Where,
$v(t)$is the velocity of the body at time t,
u is the initial velocity of the body at t=0,
a denotes acceleration of the body,
t denotes total elapsed time.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, eq.(1) gives the time dependence of velocity. You can clearly notice that velocity of a body is linearly dependent on the time when the acceleration is not time dependent. Now, compare eq.(1) with the equation of line i.e. $y = mx + c$ you’ll get the slope of the velocity time graph as a. For a body with zero acceleration we have a=0. Hence, the velocity time graph will be a straight line with slope 0 i.e. $v(t) = u$. Plotting this equation we get:
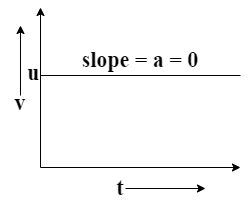
Here, the y-axis of the graph denotes the velocity of the graph while the x-axis denotes the timescale.
Note: At times some students have some misconception about this constant velocity concept. They might think that having a constant velocity means that the body will not move w.r.t time. Yes, for a body that is completely at rest has a constant velocity, but that is a very special case when that value of constant is zero i.e. according to the graph u=0. For most general cases, an un-accelerated object will move at a constant velocity forever.
Formula used:
Velocity and time relationship of a body is given by:
$v(t) = u + a.t$ ……………………….(1)
Where,
$v(t)$is the velocity of the body at time t,
u is the initial velocity of the body at t=0,
a denotes acceleration of the body,
t denotes total elapsed time.
Complete step by step answer:
Here, eq.(1) gives the time dependence of velocity. You can clearly notice that velocity of a body is linearly dependent on the time when the acceleration is not time dependent. Now, compare eq.(1) with the equation of line i.e. $y = mx + c$ you’ll get the slope of the velocity time graph as a. For a body with zero acceleration we have a=0. Hence, the velocity time graph will be a straight line with slope 0 i.e. $v(t) = u$. Plotting this equation we get:

Here, the y-axis of the graph denotes the velocity of the graph while the x-axis denotes the timescale.
Note: At times some students have some misconception about this constant velocity concept. They might think that having a constant velocity means that the body will not move w.r.t time. Yes, for a body that is completely at rest has a constant velocity, but that is a very special case when that value of constant is zero i.e. according to the graph u=0. For most general cases, an un-accelerated object will move at a constant velocity forever.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




