
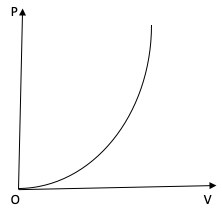
The variation of pressure P with volume V for an ideal diatomic gas is parabolic as shown in the figure. The molar specific heat of the gas during this process is?
A.$\dfrac{{9R}}{5}$
B.$\dfrac{{17R}}{6}$
C.$\dfrac{{3R}}{5}$
D.$\dfrac{{8R}}{5}$

Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: From the PV curve given in the question, we will find the relation between P and V, and then by comparing it with the relation for the polytropic process $(P{V^x} = const.)$ we can find the value of ‘x’. Then by using the below given formula, molar specific heat of the polytropic process can be found.
$C = \dfrac{{fR}}{2} + \dfrac{R}{{1 - x}}$
Complete step by step answer:
The PV curve of the diatomic gas is a parabola. Therefore, we can write
$P\alpha {V^2}$
$ \Rightarrow P{V^{ - 2}} = $ constant
For a polytropic process, the relation between P and V is $P{V^x} = $ constant. On comparing the two equations we get, $x = - 2$.
Now, in case of a diatomic gas, the degree of freedom is 5, that is, $f = 5$.
The molar specific heat of a gas undergoing polytropic process is given by,
$C = \dfrac{{fR}}{2} + \dfrac{R}{{1 - x}}$
Substituting the values of ‘f’ and ‘x’, we get,
$C = \dfrac{{5R}}{2} + \dfrac{R}{{1 - ( - 2)}}$
$ \Rightarrow C = \dfrac{{5R}}{2} + \dfrac{R}{{1 + 2}}$
$ \Rightarrow C = \dfrac{{5R}}{2} + \dfrac{R}{3}$
$ \Rightarrow C = \dfrac{{15R + 2R}}{6}$
$ \Rightarrow C = \dfrac{{17R}}{6}$
Thus, the molar specific heat of the given diatomic gas is $\dfrac{{17R}}{6}$.
Hence option B is correct.
Note:
The molar specific heat of gases is the amount of heat energy required by 1 mole of the gas to raise its temperature by 1 degree Celsius. There are two types of molar specific heats of gases. When measured at constant pressure, it is called the molar specific heat at constant pressure, denoted by ${C_p}$. When it is measured at constant volume, then it is called molar specific heat at constant volume, denoted by ${C_v}$. Both these quantities are related as ${C_p} = {C_v} + R$.
$C = \dfrac{{fR}}{2} + \dfrac{R}{{1 - x}}$
Complete step by step answer:
The PV curve of the diatomic gas is a parabola. Therefore, we can write
$P\alpha {V^2}$
$ \Rightarrow P{V^{ - 2}} = $ constant
For a polytropic process, the relation between P and V is $P{V^x} = $ constant. On comparing the two equations we get, $x = - 2$.
Now, in case of a diatomic gas, the degree of freedom is 5, that is, $f = 5$.
The molar specific heat of a gas undergoing polytropic process is given by,
$C = \dfrac{{fR}}{2} + \dfrac{R}{{1 - x}}$
Substituting the values of ‘f’ and ‘x’, we get,
$C = \dfrac{{5R}}{2} + \dfrac{R}{{1 - ( - 2)}}$
$ \Rightarrow C = \dfrac{{5R}}{2} + \dfrac{R}{{1 + 2}}$
$ \Rightarrow C = \dfrac{{5R}}{2} + \dfrac{R}{3}$
$ \Rightarrow C = \dfrac{{15R + 2R}}{6}$
$ \Rightarrow C = \dfrac{{17R}}{6}$
Thus, the molar specific heat of the given diatomic gas is $\dfrac{{17R}}{6}$.
Hence option B is correct.
Note:
The molar specific heat of gases is the amount of heat energy required by 1 mole of the gas to raise its temperature by 1 degree Celsius. There are two types of molar specific heats of gases. When measured at constant pressure, it is called the molar specific heat at constant pressure, denoted by ${C_p}$. When it is measured at constant volume, then it is called molar specific heat at constant volume, denoted by ${C_v}$. Both these quantities are related as ${C_p} = {C_v} + R$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




