
The value of quantity ‘G’ in the law of gravitation:
$\left( A \right)$ Depends on the mass of the earth only.
$\left( B \right)$ Depends on the radius of the earth only.
$\left( C \right)$ Depends on both the mass and the radius of the earth only.
$\left( D \right)$ Is independent of the mass and the radius of the earth.
Answer
608.7k+ views
Hint: For this question using the principle that scientist Newton gives gravitational law that each particle attracts any other particle in the universe with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the distance square between their centers, so use this definition to arrive at the solution of the problem.
Complete step-by-step solution -
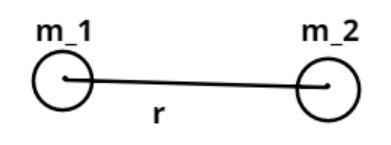
As we know that every object is the universe attracts every other object with a force (${F_g}$) directed along the line of centers for the two objects which is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of separation between the two bodies.
$ \Rightarrow {F_g} \propto \dfrac{{{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$, where ${m_1} = $ Mass of first object
${m_2} = $ Mass of second object
$r = $ Separation between two objects.
Now when we apply the proportionality constant it is become,
$ \Rightarrow {F_g} = G\dfrac{{{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$, where G = universal gravitational constant.
Now as we know that any constant term is simply a constant value which is not dependent on the other parameters, such as Planck’s constant (h), Boltzmann constant (K) etc.
So the quantity G in the law of gravitation does not depend on any parameter.
So this is the required answer.
Hence option (D) is the correct answer.
Note – Whenever we face such types of question always remember that all the constants in any equation does not dependent on the other parameters, such as Planck’s constant (h), Boltzmann constant (K), universal gravitational constant (G) etc. these are the derived constant values by our scientist such as G = $6.674 \times {10^{ - 11}}\dfrac{{{m^3}}}{{kg.{s^2}}}$.
Complete step-by-step solution -

As we know that every object is the universe attracts every other object with a force (${F_g}$) directed along the line of centers for the two objects which is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of separation between the two bodies.
$ \Rightarrow {F_g} \propto \dfrac{{{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$, where ${m_1} = $ Mass of first object
${m_2} = $ Mass of second object
$r = $ Separation between two objects.
Now when we apply the proportionality constant it is become,
$ \Rightarrow {F_g} = G\dfrac{{{m_1}{m_2}}}{{{r^2}}}$, where G = universal gravitational constant.
Now as we know that any constant term is simply a constant value which is not dependent on the other parameters, such as Planck’s constant (h), Boltzmann constant (K) etc.
So the quantity G in the law of gravitation does not depend on any parameter.
So this is the required answer.
Hence option (D) is the correct answer.
Note – Whenever we face such types of question always remember that all the constants in any equation does not dependent on the other parameters, such as Planck’s constant (h), Boltzmann constant (K), universal gravitational constant (G) etc. these are the derived constant values by our scientist such as G = $6.674 \times {10^{ - 11}}\dfrac{{{m^3}}}{{kg.{s^2}}}$.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




