
The value of \[\cos {{25}^{o}}\cos {{20}^{o}}+\sin {{25}^{o}}\sin {{20}^{o}}\text{ is:}\]
(a) \[\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\]
(b) 2
(c) \[\cos {{5}^{o}}\]
(d) \[\sin {{5}^{o}}\]
Answer
604.5k+ views
Hint: First try to prove the formula of cos (A – B). By this, you will have an equation for the expression in the question. By applying this formula, you can directly convert the whole expression into a single cosine term, which is the required result in the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given expression in the question can be written as follows:
\[\cos {{25}^{o}}\cos {{20}^{o}}+\sin {{25}^{o}}\sin {{20}^{o}}\]
Assume, a combination of 2 right-angled triangles namely ABC, CBD. Both are right-angled at vertex B.
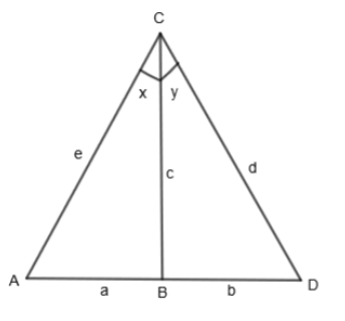
Let us assume the side AB as variable a, CB as variable c, BD as variable b, AC as variable e, DC as variable d. By basic trigonometry, we can say that in the right-angled triangle,
\[\sin A=\dfrac{\text{Opposite side}}{\text{Hypotenuse}},\cos A=\dfrac{\text{Adjacent side}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}\]
By applying this to triangle ABC, we get the equations as:
\[\begin{align}
& \sin x=\dfrac{a}{e}....\left( i \right) \\
& \cos x=\dfrac{c}{e}....\left( ii \right) \\
\end{align}\]
By applying this to triangle CBD, we get the equation as:
\[\begin{align}
& \sin y=\dfrac{b}{d}....\left( iii \right) \\
& \cos y=\dfrac{c}{d}....\left( iv \right) \\
\end{align}\]
By basic knowledge of properties of the triangle, for a triangle ACD, cosine rule is:
\[\cos C=\dfrac{A{{C}^{2}}+C{{D}^{2}}-{{\left( AD \right)}^{2}}}{2\left( AC \right)\left( CD \right)}\]
By substituting the values, we get as follows:
\[\cos \left( x+y \right)=\dfrac{{{e}^{2}}+{{d}^{2}}-{{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}}{2ed}=\dfrac{{{e}^{2}}+{{d}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}-2ab-{{b}^{2}}}{2ed}\]
By Pythagoras theorem, we know that,
\[{{a}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}={{e}^{2}};{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}={{d}^{2}}\]
By substituting these, we can write the equation as,
\[\cos \left( x+y \right)=\dfrac{{{c}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-2ab}{2ed}\]
By canceling 2 and separating the fraction, we can write:
\[\cos \left( x+y \right)=\dfrac{{{c}^{2}}}{ed}-\dfrac{ab}{ed}=\dfrac{c}{e}.\dfrac{c}{d}-\dfrac{a}{e}.\dfrac{b}{d}\]
By substituting equation (i), (ii), (iii), and (iv), we get,
\[\cos \left( x+y \right)=\cos x\cos y-\sin x\sin y\]
Substituting y = – y, we get it as,
\[\cos \left( x-y \right)=\cos x\cos y+\sin x\sin y\]
As sin (– y) = – sin y, cos (– y) = + cos y, substitute x = 25, y = 20
\[\cos {{25}^{o}}\cos {{20}^{o}}+\sin {{25}^{o}}\sin {{20}^{o}}=\cos \left( {{25}^{o}}-{{20}^{o}} \right)\]
By simplifying, we get the equation in the form
\[\cos {{25}^{o}}\cos {{20}^{o}}+\sin {{25}^{o}}\sin {{20}^{o}}=\cos \left( {{5}^{o}} \right)\]
Therefore, option (c) is the right answer.
Note: Be careful with the variables as sides. Because we have to assume 5 sides, so we need 5 variables. Students get confused about these variables and write wrong expressions. So, write each and every step with utmost care to avoid those mistakes. Application of cosine rule is the key in getting cos(x+y) here.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given expression in the question can be written as follows:
\[\cos {{25}^{o}}\cos {{20}^{o}}+\sin {{25}^{o}}\sin {{20}^{o}}\]
Assume, a combination of 2 right-angled triangles namely ABC, CBD. Both are right-angled at vertex B.

Let us assume the side AB as variable a, CB as variable c, BD as variable b, AC as variable e, DC as variable d. By basic trigonometry, we can say that in the right-angled triangle,
\[\sin A=\dfrac{\text{Opposite side}}{\text{Hypotenuse}},\cos A=\dfrac{\text{Adjacent side}}{\text{Hypotenuse}}\]
By applying this to triangle ABC, we get the equations as:
\[\begin{align}
& \sin x=\dfrac{a}{e}....\left( i \right) \\
& \cos x=\dfrac{c}{e}....\left( ii \right) \\
\end{align}\]
By applying this to triangle CBD, we get the equation as:
\[\begin{align}
& \sin y=\dfrac{b}{d}....\left( iii \right) \\
& \cos y=\dfrac{c}{d}....\left( iv \right) \\
\end{align}\]
By basic knowledge of properties of the triangle, for a triangle ACD, cosine rule is:
\[\cos C=\dfrac{A{{C}^{2}}+C{{D}^{2}}-{{\left( AD \right)}^{2}}}{2\left( AC \right)\left( CD \right)}\]
By substituting the values, we get as follows:
\[\cos \left( x+y \right)=\dfrac{{{e}^{2}}+{{d}^{2}}-{{\left( a+b \right)}^{2}}}{2ed}=\dfrac{{{e}^{2}}+{{d}^{2}}-{{a}^{2}}-2ab-{{b}^{2}}}{2ed}\]
By Pythagoras theorem, we know that,
\[{{a}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}={{e}^{2}};{{b}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}={{d}^{2}}\]
By substituting these, we can write the equation as,
\[\cos \left( x+y \right)=\dfrac{{{c}^{2}}+{{c}^{2}}-2ab}{2ed}\]
By canceling 2 and separating the fraction, we can write:
\[\cos \left( x+y \right)=\dfrac{{{c}^{2}}}{ed}-\dfrac{ab}{ed}=\dfrac{c}{e}.\dfrac{c}{d}-\dfrac{a}{e}.\dfrac{b}{d}\]
By substituting equation (i), (ii), (iii), and (iv), we get,
\[\cos \left( x+y \right)=\cos x\cos y-\sin x\sin y\]
Substituting y = – y, we get it as,
\[\cos \left( x-y \right)=\cos x\cos y+\sin x\sin y\]
As sin (– y) = – sin y, cos (– y) = + cos y, substitute x = 25, y = 20
\[\cos {{25}^{o}}\cos {{20}^{o}}+\sin {{25}^{o}}\sin {{20}^{o}}=\cos \left( {{25}^{o}}-{{20}^{o}} \right)\]
By simplifying, we get the equation in the form
\[\cos {{25}^{o}}\cos {{20}^{o}}+\sin {{25}^{o}}\sin {{20}^{o}}=\cos \left( {{5}^{o}} \right)\]
Therefore, option (c) is the right answer.
Note: Be careful with the variables as sides. Because we have to assume 5 sides, so we need 5 variables. Students get confused about these variables and write wrong expressions. So, write each and every step with utmost care to avoid those mistakes. Application of cosine rule is the key in getting cos(x+y) here.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




