
The value of $1 + {\cot ^2}A$ is:
(A) ${\cos ^2}A$
(B) ${\sec ^2}A$
(C) ${\tan ^2}A$
(D) $\cos e{c^2}A$
Answer
497.4k+ views
Hint: The given question deals with basic simplification of trigonometric functions by using some of the simple trigonometric formulae such as the definition of the basic trigonometric functions like tangent and cotangent in terms of sides of a right angled triangle. Basic algebraic rules and trigonometric identities are to be kept in mind while simplifying the given problem and proving the result given to us.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given problem, we have to find the value of a trigonometric expression that can be further used in many questions and problems as a direct result and has wide ranging applications. For proving the desired result, we need to have a good grip over the basic trigonometric formulae and identities.
So, we have, $1 + {\cot ^2}A$
So, we know the definition of the trigonometric function cotangent in terms of the ratio of sides of a right angled triangle as $\dfrac{{{\text{Base}}}}{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}$.
So, substituting this, we get the value of expression as,
$ \Rightarrow 1 + {\left( {\dfrac{{{\text{Base}}}}{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}} \right)^2}$
Opening the whole square and taking LCM of the rational expressions, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicula}}{{\text{r}}^2} + {\text{Bas}}{{\text{e}}^2}}}{{{\text{Perpendicula}}{{\text{r}}^2}}}$
Now, we know the Pythagoras theorem of a right angled triangle. So, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Hypotenus}}{{\text{e}}^2}}}{{{\text{Perpendicula}}{{\text{r}}^2}}}$
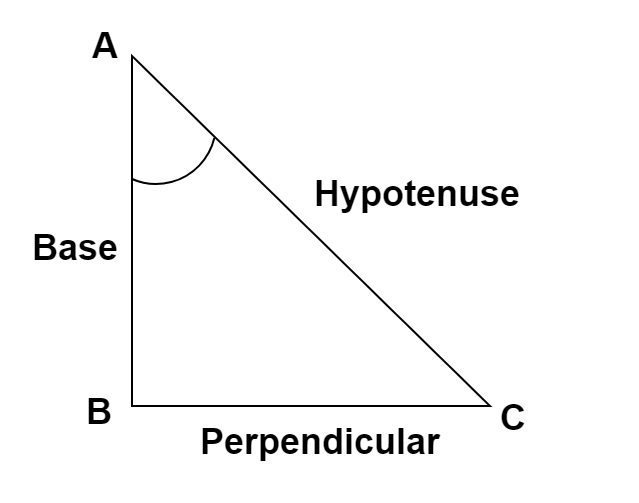
Now, we know the definition of the sine trigonometric function as $\dfrac{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}$. Hence, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{{\left( {\dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}} \right)}^2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{\text{si}}{{\text{n}}^2}A}}$
Now, we know that the sine and cosecant functions are the reciprocal of each other. So, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \cos e{c^2}A$
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
The definitions of the trigonometric functions such as tangent and cosecant must be known to attempt such problems. The answer of this problem can be used as a trigonometric identity in various other questions and problems as a direct result. A right angled triangle should be assumed and Pythagoras theorem should be applied keeping in mind the name of the right angled triangle.
Complete step by step answer:
In the given problem, we have to find the value of a trigonometric expression that can be further used in many questions and problems as a direct result and has wide ranging applications. For proving the desired result, we need to have a good grip over the basic trigonometric formulae and identities.
So, we have, $1 + {\cot ^2}A$
So, we know the definition of the trigonometric function cotangent in terms of the ratio of sides of a right angled triangle as $\dfrac{{{\text{Base}}}}{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}$.
So, substituting this, we get the value of expression as,
$ \Rightarrow 1 + {\left( {\dfrac{{{\text{Base}}}}{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}} \right)^2}$
Opening the whole square and taking LCM of the rational expressions, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicula}}{{\text{r}}^2} + {\text{Bas}}{{\text{e}}^2}}}{{{\text{Perpendicula}}{{\text{r}}^2}}}$
Now, we know the Pythagoras theorem of a right angled triangle. So, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{\text{Hypotenus}}{{\text{e}}^2}}}{{{\text{Perpendicula}}{{\text{r}}^2}}}$

Now, we know the definition of the sine trigonometric function as $\dfrac{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}$. Hence, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{{\left( {\dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}} \right)}^2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{\text{si}}{{\text{n}}^2}A}}$
Now, we know that the sine and cosecant functions are the reciprocal of each other. So, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \cos e{c^2}A$
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note:
The definitions of the trigonometric functions such as tangent and cosecant must be known to attempt such problems. The answer of this problem can be used as a trigonometric identity in various other questions and problems as a direct result. A right angled triangle should be assumed and Pythagoras theorem should be applied keeping in mind the name of the right angled triangle.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

The draft of the Preamble of the Indian Constitution class 10 social science CBSE

Who gave "Inqilab Zindabad" slogan?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

The Equation xxx + 2 is Satisfied when x is Equal to Class 10 Maths




