
The valence electrons are involved in the formation of covalent bonds is/are called-
A.Non-bonding electrons
B.Lone pairs
C.Unshared pairs
D.None of these
Answer
581.4k+ views
Hint: The outermost shell of an atom is called the valence shell. Valence electrons are the electrons of the outermost shell of an atom. They determine the reactivity of the atom or tendency to form chemical bonds with other atoms.
Complete Step-by-Step Solution:
A covalent bond is formed by the sharing of valence electrons between atoms to form molecules.The valence electrons which are shared or which participate in the formation of covalent bonds are called bonding electrons. The pair of bonds which are not shared with another atom is called lone pair of electrons. They are also called non-bonding electrons or unshared pairs.
For example- When two chlorine atoms combine to form a molecule they form a covalent bond by sharing their valence electrons. This can be easily understood through the Lewis dot structure-
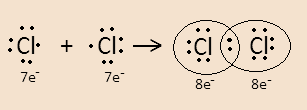
We know that Chlorine has atomic number \[17\] and its electronic configuration is $\left[ {{\text{Ne}}} \right]{\text{3}}{{\text{s}}^2}3{{\text{p}}^5}$ .
A chlorine atom has $7$ electrons in its valence shell so to complete its octet it needs one more electron. So when it combines with another chlorine atom both atoms share their one valence electron with the other. Here the dot represents electrons.
In the structure in the $C{l_2}$ molecule, the electrons that participate in forming covalent bonds are bonding electrons.
The $3$ electron pairs in each chlorine atom that do not participate in bond formation are lone pairs. So chlorine molecules have total $6$ lone pairs.
Answer-Hence the correct answer is D.
Note: Covalent bond and coordinate covalent bond are different from each other so don’t get confused between the two of them. The main difference between then is-
In a coordinate bond, both atoms contribute electrons to share and form the bond but in a coordinate covalent bond both electrons are from the same atom but shared by both atoms.
Also, the coordinate bond is represented by the $ \to $ symbol in which the arrow points towards the atom which shares both the electrons of another atom without contributing.
Complete Step-by-Step Solution:
A covalent bond is formed by the sharing of valence electrons between atoms to form molecules.The valence electrons which are shared or which participate in the formation of covalent bonds are called bonding electrons. The pair of bonds which are not shared with another atom is called lone pair of electrons. They are also called non-bonding electrons or unshared pairs.
For example- When two chlorine atoms combine to form a molecule they form a covalent bond by sharing their valence electrons. This can be easily understood through the Lewis dot structure-

We know that Chlorine has atomic number \[17\] and its electronic configuration is $\left[ {{\text{Ne}}} \right]{\text{3}}{{\text{s}}^2}3{{\text{p}}^5}$ .
A chlorine atom has $7$ electrons in its valence shell so to complete its octet it needs one more electron. So when it combines with another chlorine atom both atoms share their one valence electron with the other. Here the dot represents electrons.
In the structure in the $C{l_2}$ molecule, the electrons that participate in forming covalent bonds are bonding electrons.
The $3$ electron pairs in each chlorine atom that do not participate in bond formation are lone pairs. So chlorine molecules have total $6$ lone pairs.
Answer-Hence the correct answer is D.
Note: Covalent bond and coordinate covalent bond are different from each other so don’t get confused between the two of them. The main difference between then is-
In a coordinate bond, both atoms contribute electrons to share and form the bond but in a coordinate covalent bond both electrons are from the same atom but shared by both atoms.
Also, the coordinate bond is represented by the $ \to $ symbol in which the arrow points towards the atom which shares both the electrons of another atom without contributing.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




