
The two eukaryotic organelles responsible for cytoplasmic inheritance are
(a) Lysosome and mitochondria
(b) Chloroplasts and lysosomes
(c) Mitochondria and chloroplasts
(d) Mitochondria and Golgi complex
Answer
575.1k+ views
Hint: Cytoplasmic inheritance is the process of transfer of genes outside the nucleus. It occurs commonly in eukaryotic cellular parasites and organelles that are not the nucleus, but have genetic material.
Complete answer:
- Cytoplasmic inheritance is the extranuclear transmission of genes. It occurs in most eukaryotes, commonly occurring in cytoplasmic organelles such as chloroplast and mitochondria as well as cellular parasites such as bacteria and viruses.
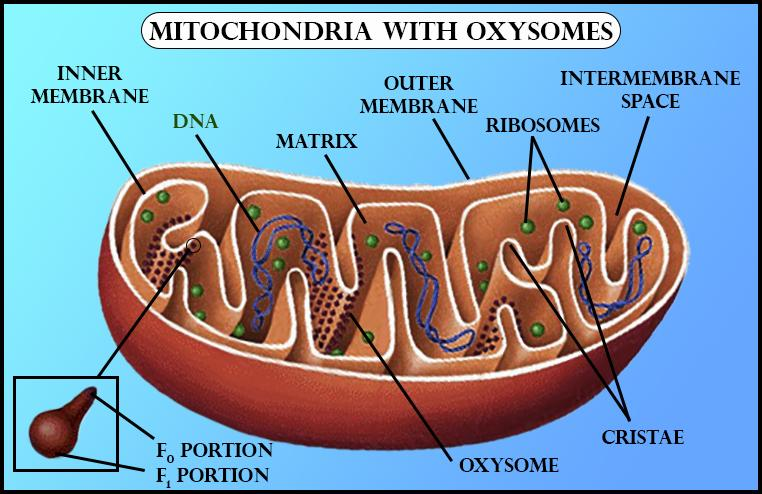
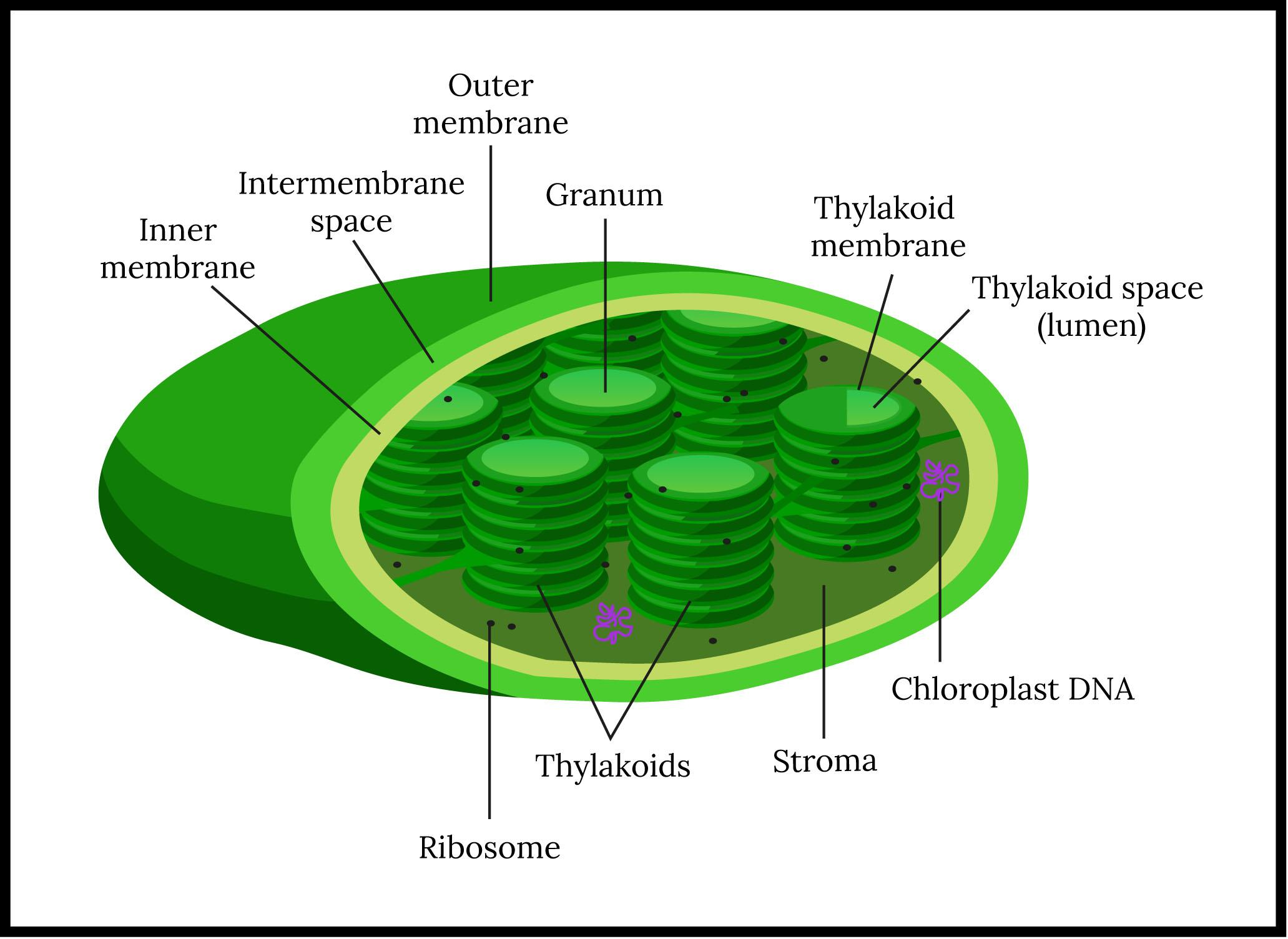
- Mitochondria are organelles that transform energy as a result of cellular respiration. Chloroplasts are organelles that produce sugars as food for plants and algae by photosynthesis.
- Cytoplasmic inheritance occurs in these two organelles because they have their own genetic material.
- The genes located in mitochondria and chloroplasts carry out proper cellular functions and the genomes replicate independently of the nuclear DNA which is typically arranged in chromosomes that only replicate once preceding cellular division.
Additional information:
- Cytoplasmic inheritance is also known as extranuclear inheritance.
- Lysosomes are organelles responsible for the digestion of worn-out organelles. The organelles contain digestive enzymes present in a highly acidic environment to digest a number of molecules.
- The Golgi bodies are responsible for post-synthesis modifications of lipids and proteins such as sorting, tagging, packaging, and distribution.
So, the correct answer is ‘(c) Mitochondria and chloroplasts’.
Note:
- The nucleus of the cell houses the DNA responsible for the physiological functioning of the entire cell. The DNA is stored in the form of chromatin and produces ribosomes and proteins.
- There are three types of cytoplasmic inheritance: vegetative segregation, uniparental inheritance, and biparental inheritance.
Complete answer:
- Cytoplasmic inheritance is the extranuclear transmission of genes. It occurs in most eukaryotes, commonly occurring in cytoplasmic organelles such as chloroplast and mitochondria as well as cellular parasites such as bacteria and viruses.


- Mitochondria are organelles that transform energy as a result of cellular respiration. Chloroplasts are organelles that produce sugars as food for plants and algae by photosynthesis.
- Cytoplasmic inheritance occurs in these two organelles because they have their own genetic material.
- The genes located in mitochondria and chloroplasts carry out proper cellular functions and the genomes replicate independently of the nuclear DNA which is typically arranged in chromosomes that only replicate once preceding cellular division.
Additional information:
- Cytoplasmic inheritance is also known as extranuclear inheritance.
- Lysosomes are organelles responsible for the digestion of worn-out organelles. The organelles contain digestive enzymes present in a highly acidic environment to digest a number of molecules.
- The Golgi bodies are responsible for post-synthesis modifications of lipids and proteins such as sorting, tagging, packaging, and distribution.
So, the correct answer is ‘(c) Mitochondria and chloroplasts’.
Note:
- The nucleus of the cell houses the DNA responsible for the physiological functioning of the entire cell. The DNA is stored in the form of chromatin and produces ribosomes and proteins.
- There are three types of cytoplasmic inheritance: vegetative segregation, uniparental inheritance, and biparental inheritance.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE




