
The two diagonals of a rhombus are of length 55 cm and 48 cm. If p is the perpendicular height of the rhombus, then which one of the following is correct? \[\]
A. $ 36\text{ cm} < p <37\text{ cm} $ \[\]
B. $ 35\text{ cm}< p <36\text{ cm} $ \[\]
C. $ 34\text{ cm}< p < 35\text{ cm} $ \[\]
D. $ 33\text{ cm} < p < 34\text{ cm} $ \[\]
Answer
567.3k+ views
Hint: We name the given rhombus ABCD where $ \angle B,\angle D $ are obtuse angles and name the point of intersection of diagonals as O. The perpendicular from D on as DP. We use the fact that diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other perpendicularly and use the similarity of triangles AOB and DPB. We then use Pythagoras theorem to find $ p $ .\[\]
Complete step by step answer:
Let ABCD be the rhombus where the obtuse angles are $ \angle B,\angle D $ . Since the diagonal joining the vertices with acute angles will be the longest we can assign given length of the diagonals as
$ BD=\text{ 48 cm },AC=55\text{ cm} $
Let us denote the point of intersection of diagonals AC and BD as O. We know that diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other perpendicularly, we have
\[\begin{align}
& BO=DO=\dfrac{48}{12}=24\text{ cm} \\
& AO=CO=\dfrac{55}{2}=27.5\text{ cm} \\
\end{align}\]
Let P be the foot of the perpendicular dropped from D on AB. We are given the height of the perpendicular as $ p. $ So we have $ DP=p $ . We have the rough figure as;\[\]
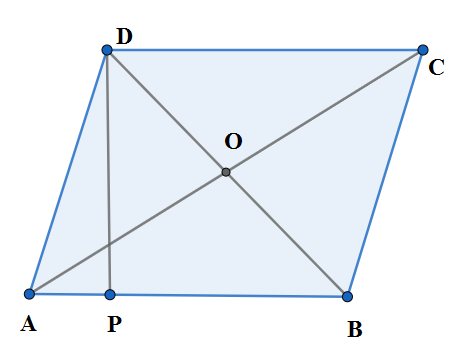
Let us observe the triangles AOB and DPB. We have the right angles of equal measure $ \angle AOB=\angle DPB={{90}^{\circ }} $ . We also have the common angle $ \angle OBA=\angle DBP $ . So by angle –angles similarity criterion we have;
\[\Delta AOB\sim \Delta DPB\]
We know that in similar triangles corresponding to opposite sides of equal angles are always in proportion. So we have;
\[\dfrac{AO}{DP}=\dfrac{OB}{PB}=\dfrac{AB}{BD}\]
Let us consider
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{AO}{DP}=\dfrac{AB}{BD} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{DP}{AO}=\dfrac{BB}{AB} \\
& \Rightarrow DP=\dfrac{BD}{AB}\times AO \\
& \Rightarrow p=\dfrac{BD}{AB}\times AO \\
\end{align}\]
Let us observe the right angled triangle AOB with hypotenuse AB. We use the Pythagoras theorem in triangle AOB to have;
\[\begin{align}
& A{{B}^{2}}=A{{O}^{2}}+B{{O}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{A{{O}^{2}}+B{{O}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{{{27.5}^{2}}+{{24}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{1336.25} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=36.5\text{ cm} \\
\end{align}\]
So the height of the perpendicular is
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow p=\dfrac{BD}{AB}\times AO \\
& \Rightarrow p=\dfrac{48}{36.5}\times 27.5=36.164\text{ cm}\left( \text{approximately} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
So the height of the perpendicular is in between 36 cm and 37 cm. So the correct option is A.\[\]
Note:
We note that we want to find the answer quickly we have to use an estimation of 36.5 cm to 36 cm. We also note that the length of the perpendicular dropped vertices will be equal since the length of the sides of the rhombus is equal and parallel. We can alternatively solve using the formula for the area of the rhombus as $ \dfrac{1}{2}\times AC\times BD $ and then equating this area another formula for area $ p\times b $ where $ b $ is one of the sides of the rhombus which can be obtained using Pythagoras theorem.
Complete step by step answer:
Let ABCD be the rhombus where the obtuse angles are $ \angle B,\angle D $ . Since the diagonal joining the vertices with acute angles will be the longest we can assign given length of the diagonals as
$ BD=\text{ 48 cm },AC=55\text{ cm} $
Let us denote the point of intersection of diagonals AC and BD as O. We know that diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other perpendicularly, we have
\[\begin{align}
& BO=DO=\dfrac{48}{12}=24\text{ cm} \\
& AO=CO=\dfrac{55}{2}=27.5\text{ cm} \\
\end{align}\]
Let P be the foot of the perpendicular dropped from D on AB. We are given the height of the perpendicular as $ p. $ So we have $ DP=p $ . We have the rough figure as;\[\]

Let us observe the triangles AOB and DPB. We have the right angles of equal measure $ \angle AOB=\angle DPB={{90}^{\circ }} $ . We also have the common angle $ \angle OBA=\angle DBP $ . So by angle –angles similarity criterion we have;
\[\Delta AOB\sim \Delta DPB\]
We know that in similar triangles corresponding to opposite sides of equal angles are always in proportion. So we have;
\[\dfrac{AO}{DP}=\dfrac{OB}{PB}=\dfrac{AB}{BD}\]
Let us consider
\[\begin{align}
& \dfrac{AO}{DP}=\dfrac{AB}{BD} \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{DP}{AO}=\dfrac{BB}{AB} \\
& \Rightarrow DP=\dfrac{BD}{AB}\times AO \\
& \Rightarrow p=\dfrac{BD}{AB}\times AO \\
\end{align}\]
Let us observe the right angled triangle AOB with hypotenuse AB. We use the Pythagoras theorem in triangle AOB to have;
\[\begin{align}
& A{{B}^{2}}=A{{O}^{2}}+B{{O}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{A{{O}^{2}}+B{{O}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{{{27.5}^{2}}+{{24}^{2}}} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=\sqrt{1336.25} \\
& \Rightarrow AB=36.5\text{ cm} \\
\end{align}\]
So the height of the perpendicular is
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow p=\dfrac{BD}{AB}\times AO \\
& \Rightarrow p=\dfrac{48}{36.5}\times 27.5=36.164\text{ cm}\left( \text{approximately} \right) \\
\end{align}\]
So the height of the perpendicular is in between 36 cm and 37 cm. So the correct option is A.\[\]
Note:
We note that we want to find the answer quickly we have to use an estimation of 36.5 cm to 36 cm. We also note that the length of the perpendicular dropped vertices will be equal since the length of the sides of the rhombus is equal and parallel. We can alternatively solve using the formula for the area of the rhombus as $ \dfrac{1}{2}\times AC\times BD $ and then equating this area another formula for area $ p\times b $ where $ b $ is one of the sides of the rhombus which can be obtained using Pythagoras theorem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




