
The true statement for the acids of phosphorus, ${H_3}P{O_2},{H_3}P{O_3}$ and ${H_3}P{O_4}$ is
A. The order of their acidity is ${H_3}P{O_2} > {H_3}P{O_3} > {H_3}P{O_4}$
B. All of them are reducing in nature
C. All of them are tribasic acids
D. The geometry of phosphorus is tetrahedral in all the three.
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: Phosphorous acid, is the compound described by the formula${H_3}P{O_3}$. This acid is diprotic, not triprotic. Phosphorous acid is an intermediate in the preparation of other phosphorus compounds. Organic derivatives of phosphorous acid, compounds with the formula $RP{O_3}{H_2}$ are called phosphoric acids.
Complete step by step answer:
${H_3}P{O_2},{\text{ }}{{\text{H}}_3}P{O_3}$ and ${H_3}P{O_4}$ are monobasic, dibasic and tribasic acids. The order of their acidity increases as the number of oxygen atoms increases, phosphorus acid is reducing agent, and has less oxidation property as $ + 5 $ oxidation state of phosphorus is more stable than $ + 3$.
${H_3}P{O_2},{H_3}P{O_5}$ and ${H_3}P{O_4}$ contain one, two and three ionisable hydrogen atoms respectively
But there is very little difference in acidity
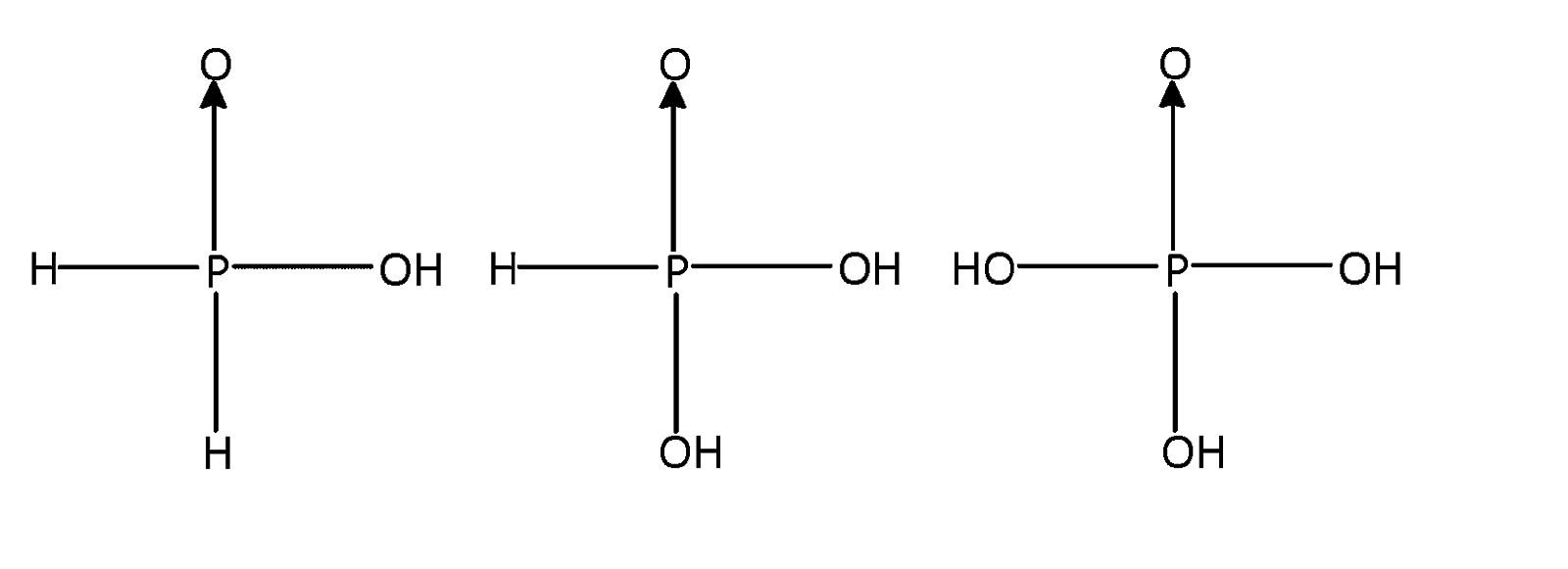
As $s{p^3}$ hybridised all the above three phosphorus acids are tetrahedral
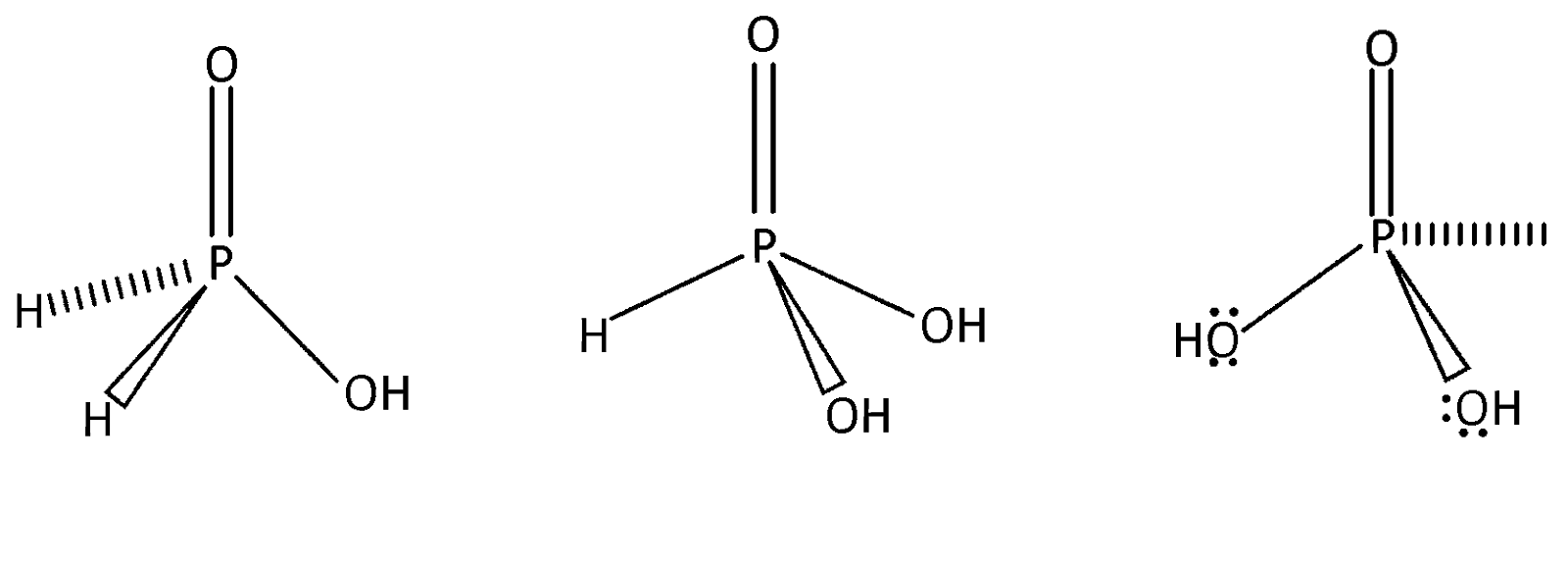
Phosphorus forms a number of oxoacids which differ in their structures and oxidation state of phosphorus atom liked tetrahedrally to four other atoms or groups each of them has at least one $P = 0$ or $P \to 0$ unit and one $P - OH$ unit. The OH group is ionisable but H – atom linked directly to P is non – ionisable structures of all the acids are considered to be derived either from phosphorus acid or phosphoric acid. The number of or $P = O$ and $P - O - H$ bonds in ${H_3}P{O_4}$ are $3$.
The correct option is (D), the geometry of phosphorus is tetrahedral in all the three.
Note:
Pure phosphoric acid is a white crystalline solid with melting point of $42.35^\circ C$. When it is less concentrated it is colourless, odourless, viscous liquid with a density of $1.885g/ml$. It is non – toxic and non – volatile. The most common phosphoric acid concentration is $85\% $ in water. Phosphoric acid is not considered toxic or hazardous. In low concentration it is safe on skin and even for consumption. However, at very high concentration it is corrosive and can cause skin burn.
Complete step by step answer:
${H_3}P{O_2},{\text{ }}{{\text{H}}_3}P{O_3}$ and ${H_3}P{O_4}$ are monobasic, dibasic and tribasic acids. The order of their acidity increases as the number of oxygen atoms increases, phosphorus acid is reducing agent, and has less oxidation property as $ + 5 $ oxidation state of phosphorus is more stable than $ + 3$.
${H_3}P{O_2},{H_3}P{O_5}$ and ${H_3}P{O_4}$ contain one, two and three ionisable hydrogen atoms respectively
But there is very little difference in acidity

As $s{p^3}$ hybridised all the above three phosphorus acids are tetrahedral

Phosphorus forms a number of oxoacids which differ in their structures and oxidation state of phosphorus atom liked tetrahedrally to four other atoms or groups each of them has at least one $P = 0$ or $P \to 0$ unit and one $P - OH$ unit. The OH group is ionisable but H – atom linked directly to P is non – ionisable structures of all the acids are considered to be derived either from phosphorus acid or phosphoric acid. The number of or $P = O$ and $P - O - H$ bonds in ${H_3}P{O_4}$ are $3$.
The correct option is (D), the geometry of phosphorus is tetrahedral in all the three.
Note:
Pure phosphoric acid is a white crystalline solid with melting point of $42.35^\circ C$. When it is less concentrated it is colourless, odourless, viscous liquid with a density of $1.885g/ml$. It is non – toxic and non – volatile. The most common phosphoric acid concentration is $85\% $ in water. Phosphoric acid is not considered toxic or hazardous. In low concentration it is safe on skin and even for consumption. However, at very high concentration it is corrosive and can cause skin burn.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




