
The total number of lone pairs of electrons in ${{N}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$.
Answer
568.8k+ views
Hint: There is no such formula that exists to calculate the number of lone pairs in a molecule. The only way to do this question is to draw the Lewis structure of the molecule given and then count the number of lone pairs.
Complete Solution :
The number of lone pairs in the structure can be predicted from the Lewis structure. The Lewis structure of an atom is represented by putting dots around the atom equal to the number of electrons in its valence shell. For example, in nitrogen five dots are drawn because there are five electrons in its valence shell and in oxygen six dots are drawn because there are six electrons in its valence shell. When a bond is formed between two atoms, one-one electron of each atom is used.
We are given the compound ${{N}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$.
We can draw the Lewis bond structure of this compound as:
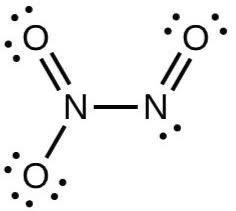
In this structure, there are two nitrogen and three oxygen atoms. One nitrogen atom is attached to other nitrogen by a single bond and also forms one double bond with oxygen. And we can also see that the other nitrogen is attached to one oxygen atom by a double bond and one oxygen atom with a single bond.
Now, let’s count the number of lone pairs present in this compound,
Total lone pairs = lone pairs on nitrogen atoms + lone pairs on oxygen atoms
Total lone pairs = 1 + 7 = 8
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is 8 lone pairs of electrons.
Note: Let’s discuss more about the structure of nitrogen trioxide. Dinitrogen trioxide has N–N bond length equal to 186 pm. Some other nitrogen oxides also possess long N–N bonds, including dinitrogen tetroxide (175 pm). The ${{N}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$ molecule is planar and exhibits symmetry.
Complete Solution :
The number of lone pairs in the structure can be predicted from the Lewis structure. The Lewis structure of an atom is represented by putting dots around the atom equal to the number of electrons in its valence shell. For example, in nitrogen five dots are drawn because there are five electrons in its valence shell and in oxygen six dots are drawn because there are six electrons in its valence shell. When a bond is formed between two atoms, one-one electron of each atom is used.
We are given the compound ${{N}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$.
We can draw the Lewis bond structure of this compound as:

In this structure, there are two nitrogen and three oxygen atoms. One nitrogen atom is attached to other nitrogen by a single bond and also forms one double bond with oxygen. And we can also see that the other nitrogen is attached to one oxygen atom by a double bond and one oxygen atom with a single bond.
Now, let’s count the number of lone pairs present in this compound,
Total lone pairs = lone pairs on nitrogen atoms + lone pairs on oxygen atoms
Total lone pairs = 1 + 7 = 8
Therefore, we can conclude that the correct answer to this question is 8 lone pairs of electrons.
Note: Let’s discuss more about the structure of nitrogen trioxide. Dinitrogen trioxide has N–N bond length equal to 186 pm. Some other nitrogen oxides also possess long N–N bonds, including dinitrogen tetroxide (175 pm). The ${{N}_{2}}{{O}_{3}}$ molecule is planar and exhibits symmetry.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




