
The top of a hill observed from the top and bottom of a building of height h is at angles of elevation p and q respectively. The height of the hill.
\[
A.{\text{ }}\dfrac{{h\cot q}}{{\cot a - \cot q}} \\
B.{\text{ }}\dfrac{{h\cot p}}{{\cot p - \cot q}} \\
C.{\text{ }}\dfrac{{h\tan p}}{{\tan p - \tan q}} \\
D.{\text{ }}None{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}these \\
\]
Answer
602.7k+ views
Hint: This problem is based on the application of trigonometry. Start with assuming the height of the hill and the distance between the hill and the building as different variables H and x. Analyse the situation with a diagram and use trigonometric identity \[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}}\] for two different triangles. Finally compare both the results and simplify it further to find the height of the hill.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let the height of the hill is equal to H.
And the distance between the base of the building and the hill is equal to x.
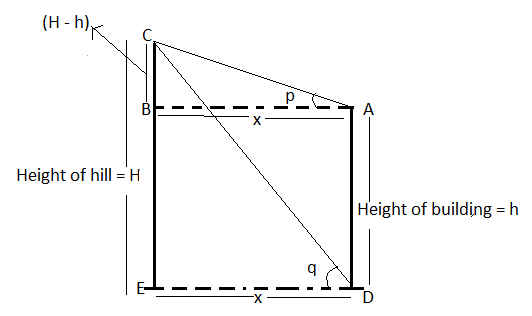
Now as we can see from the above figure that the length of BC is equal to (H – h) and the distance between building and hill (i.e. BA and ED) is equal to x.
So, now according trigonometric formula \[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}}\]
\[\tan p = \dfrac{{BC}}{{BA}} = \dfrac{{H - h}}{x}\] (1)
\[\tan q = \dfrac{{CE}}{{ED}} = \dfrac{H}{x}\] (2)
Now solving equation 2 to find the value of x. We get,
\[x = \dfrac{H}{{\tan q}}\]
Now putting the value of x in equation 1. We get,
\[\tan p = \dfrac{{\left( {H - h} \right)\tan q}}{H}\]
Now cross multiplying the above equation. We get,
\[
H\tan p = H\tan q - h\tan q \\
H\tan q - H\tan p = h\tan q \\
\]
\[H = \dfrac{{h\tan q}}{{\tan q - \tan p}}\] (3)
Now as we know that \[\tan \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\cot \theta }}\]
So, now replacing \[\tan p\] and \[\tan q\] in equation 3 with \[\cot p\] and \[\cot q\]. We get,
\[H = \dfrac{{\dfrac{h}{{\cot q}}}}{{\dfrac{1}{{\cot q}} - \dfrac{1}{{\cot p}}}}\]
Now taking LCM in the denominator of RHS of the above equation and then solving. We get,
\[H = \dfrac{{\dfrac{h}{{\cot q}}}}{{\dfrac{{\cot p - \cot q}}{{\left( {\cot q} \right)\left( {\cot p} \right)}}}} = \dfrac{{h\cot p}}{{\cot p - \cot q}}\]
So, the height of the hill must be equal to \[\dfrac{{h\cot p}}{{\cot p - \cot q}}\]
Hence, the correct option will be B.
Note:- Whenever we come up this type of problem then first, we had to find equations for \[\tan p\] and \[\tan q\] and then using substitution method we can find the value of x (distance between hill and building) using one equation and then put that value of x in other equation to find the value of H. Now if the height of hill is in terms of \[\tan p\] and \[\tan q\] then we can change \[\tan p\] to \[\cot p\] and \[\tan q\] to \[\cot q\] using formula \[\tan \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\cot \theta }}\]. This will be the easiest and efficient way to find the solution of the problem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let the height of the hill is equal to H.
And the distance between the base of the building and the hill is equal to x.

Now as we can see from the above figure that the length of BC is equal to (H – h) and the distance between building and hill (i.e. BA and ED) is equal to x.
So, now according trigonometric formula \[\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}}\]
\[\tan p = \dfrac{{BC}}{{BA}} = \dfrac{{H - h}}{x}\] (1)
\[\tan q = \dfrac{{CE}}{{ED}} = \dfrac{H}{x}\] (2)
Now solving equation 2 to find the value of x. We get,
\[x = \dfrac{H}{{\tan q}}\]
Now putting the value of x in equation 1. We get,
\[\tan p = \dfrac{{\left( {H - h} \right)\tan q}}{H}\]
Now cross multiplying the above equation. We get,
\[
H\tan p = H\tan q - h\tan q \\
H\tan q - H\tan p = h\tan q \\
\]
\[H = \dfrac{{h\tan q}}{{\tan q - \tan p}}\] (3)
Now as we know that \[\tan \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\cot \theta }}\]
So, now replacing \[\tan p\] and \[\tan q\] in equation 3 with \[\cot p\] and \[\cot q\]. We get,
\[H = \dfrac{{\dfrac{h}{{\cot q}}}}{{\dfrac{1}{{\cot q}} - \dfrac{1}{{\cot p}}}}\]
Now taking LCM in the denominator of RHS of the above equation and then solving. We get,
\[H = \dfrac{{\dfrac{h}{{\cot q}}}}{{\dfrac{{\cot p - \cot q}}{{\left( {\cot q} \right)\left( {\cot p} \right)}}}} = \dfrac{{h\cot p}}{{\cot p - \cot q}}\]
So, the height of the hill must be equal to \[\dfrac{{h\cot p}}{{\cot p - \cot q}}\]
Hence, the correct option will be B.
Note:- Whenever we come up this type of problem then first, we had to find equations for \[\tan p\] and \[\tan q\] and then using substitution method we can find the value of x (distance between hill and building) using one equation and then put that value of x in other equation to find the value of H. Now if the height of hill is in terms of \[\tan p\] and \[\tan q\] then we can change \[\tan p\] to \[\cot p\] and \[\tan q\] to \[\cot q\] using formula \[\tan \theta = \dfrac{1}{{\cot \theta }}\]. This will be the easiest and efficient way to find the solution of the problem.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




