
The tetrahedral shape is.
A-\[s{p^2}\]
B-\[s{p^3}\]
C-\[ds{p^2}\]
D- None of the above.
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: We know that if a molecule has four bonds and no lone pairs around the central atom then the molecule has tetrahedral geometry and the bond angle is ${109.5^ \circ }$. Ammonium ion and the methane molecule are some of the examples of the tetrahedral molecule..
Complete step by step answer:
First, we discuss hybridization.
Hybridization means the mixing of two atomic orbitals of the same energy to give a new hybrid molecular orbital of the same energy. Based on the type of orbitals involved, hybridization is classified as $sp$,$s{p^2}$,$s{p^3}$,\[ds{p^2}\],\[ds{p^3}\] etc.
Let us discuss the shape and bond angle of given hybridization with examples.
A-\[s{p^2}\] Hybridization.
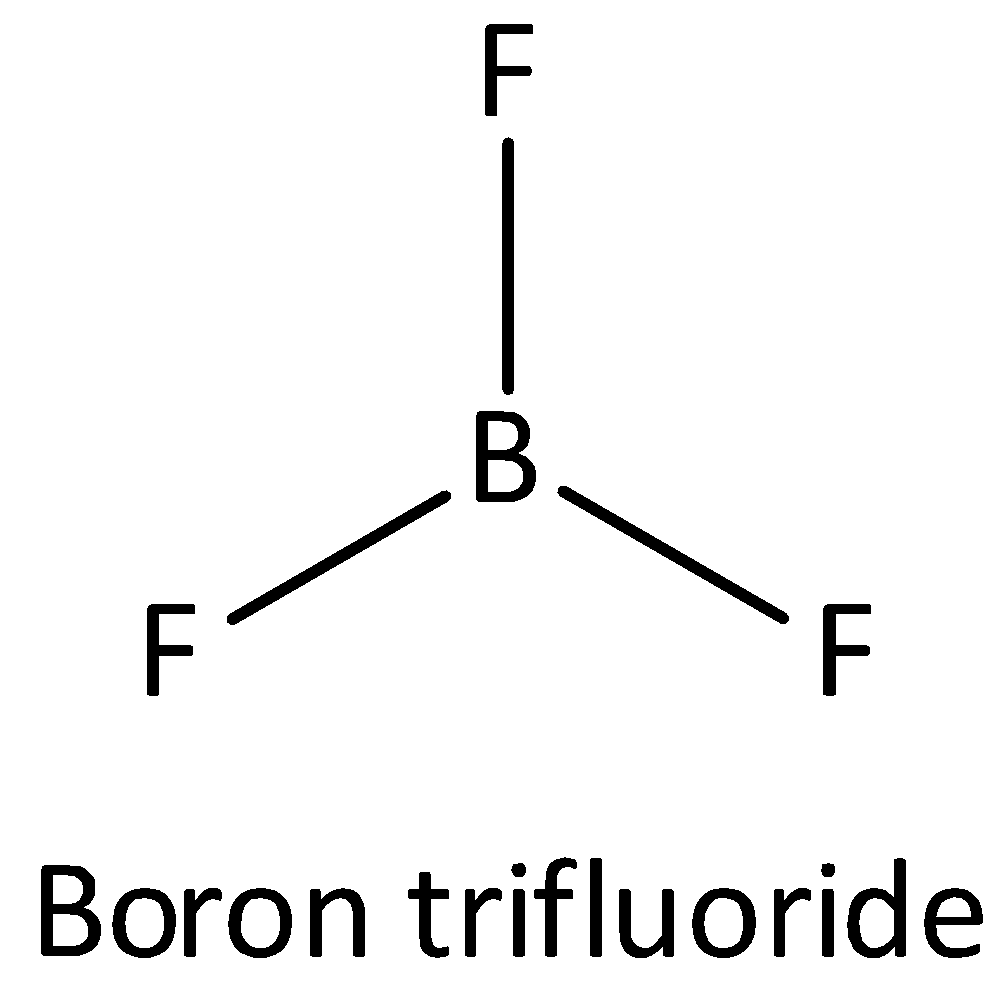
If one $s$ and two \[p\] orbitals having the same energy mixed to form three equivalent hybrid orbitals then the newly formed orbital is known as \[s{p^2}\] orbital. An example of \[s{p^2}\] hybridized molecule is Boron trifluoride. The bond angle of \[s{p^2}\] orbital is ${120^ \circ }$. The shape of \[s{p^2}\] hybridized molecule is a trigonal planar. Thus option (A) is incorrect.
The structure of $B{F_3}$ is,
B-\[s{p^3}\] Hybridization.
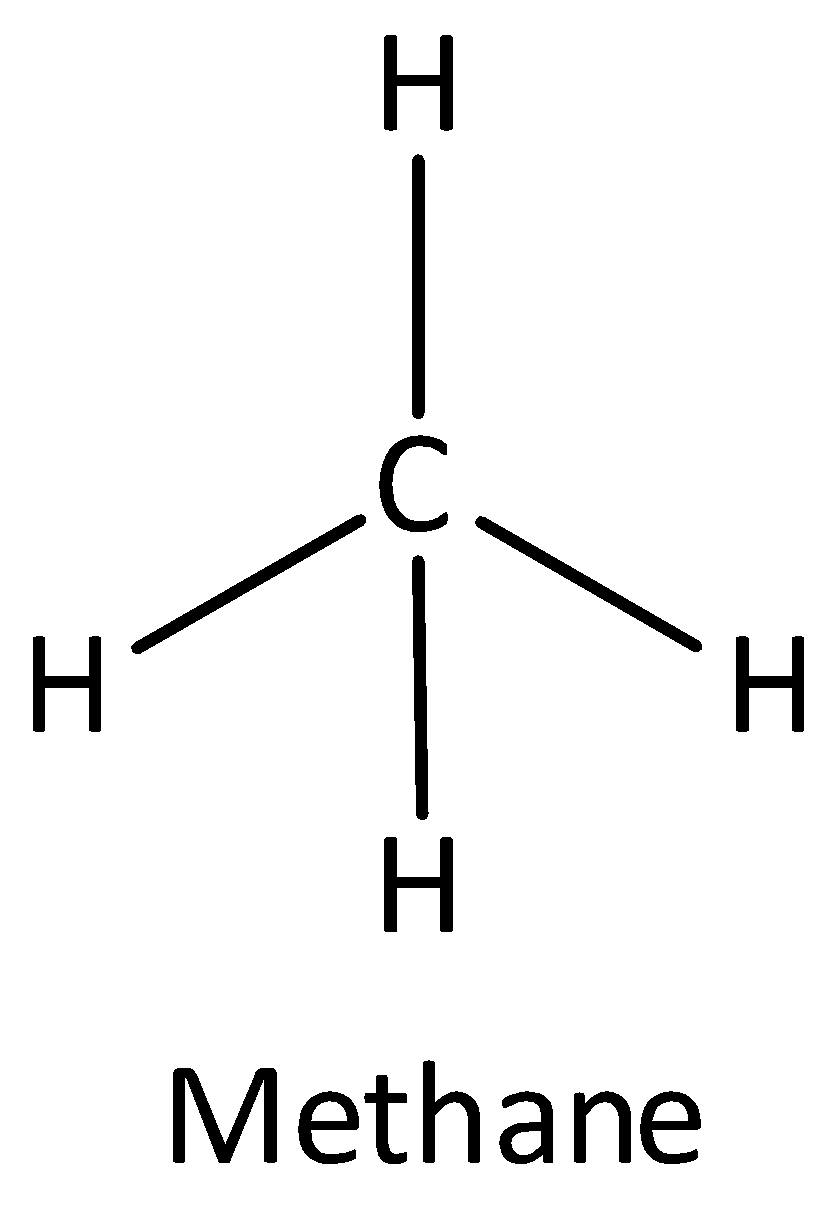
If one $s$ and three \[p\] orbitals having the same energy mixed to form four equivalent hybrid orbitals then the newly formed orbital is known as \[s{p^3}\] orbital. An example of \[s{p^3}\] hybridized molecule is methane. The bond angle of \[s{p^3}\]orbital is ${109.5^ \circ }$ . The shape of \[s{p^3}\] hybridized molecule is a tetrahedral. Thus option (B) is correct.
The structure of methane is,
C-\[ds{p^2}\] Hybridization.
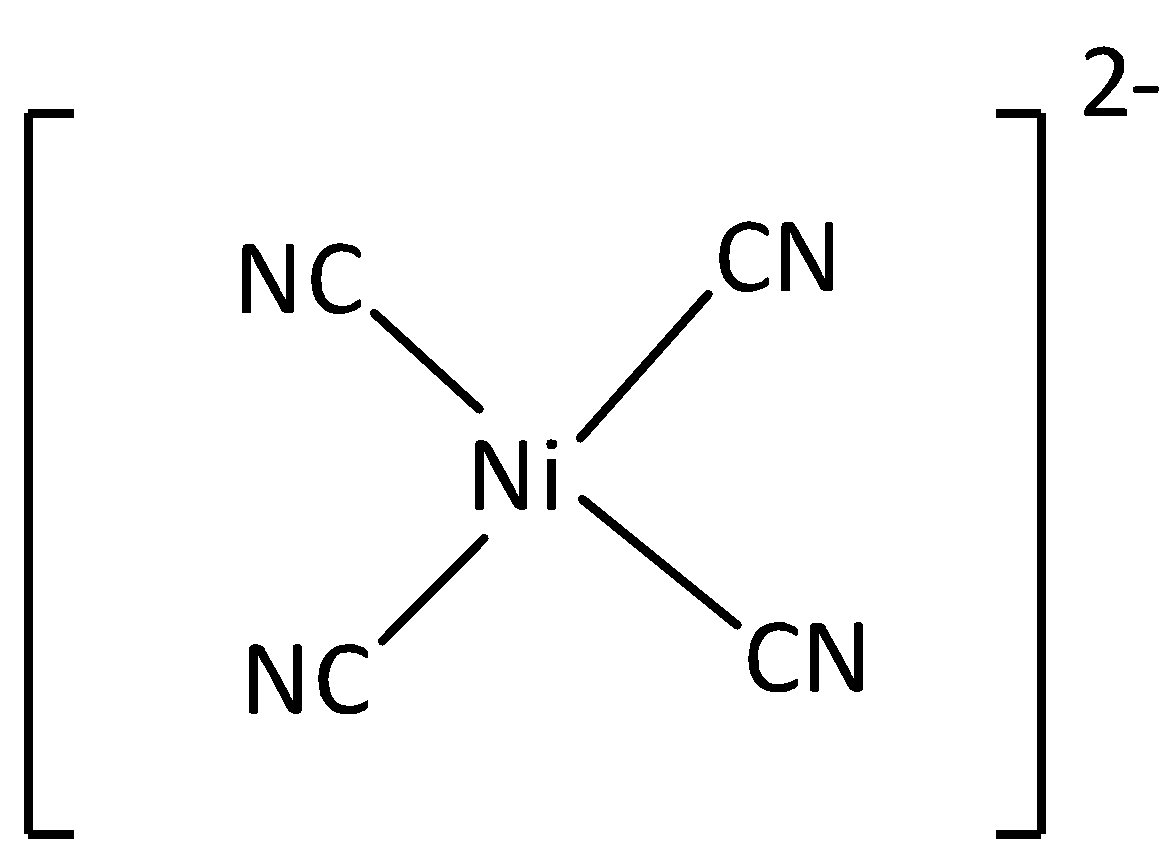
If one $d$ , one $s$ , and two \[p\] orbitals having the same energy mixed to form four equivalent hybrids orbital then the newly formed orbital is known as \[ds{p^2}\] orbital. An example of \[ds{p^2}\] hybridized molecule is nickel complex. The bond angle of \[ds{p^2}\]orbital is ${90^ \circ }$. The shape of \[ds{p^2}\] hybridized molecule is a square planar. Thus option (C) is incorrect.
The structure of ${\left[ {Ni{{\left( {CN} \right)}_4}} \right]^{2 - }}$ is,
Option B is the correct answer for this question.
Note:
We must know that the shape of a molecule can be identified by calculating the steric number. The total number of bonded and lone pairs of electrons in a molecule is called a steric number. It can be calculated using the formula,
$Steric\,number = \dfrac{{Valence\,electrons\,of\,the\,central\,atom\, + number\,of\,Bonded\,atom}}{2}$
Let us calculate the steric number of methane. Using the formula,
$Steric\,number = \dfrac{{4\, + 4}}{2} = 4$
The steric number of methane is four. Thus it has four bonded atoms and no lone pair around the central atom. Thus it is \[s{p^3}\] hybridized tetrahedral molecule.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we discuss hybridization.
Hybridization means the mixing of two atomic orbitals of the same energy to give a new hybrid molecular orbital of the same energy. Based on the type of orbitals involved, hybridization is classified as $sp$,$s{p^2}$,$s{p^3}$,\[ds{p^2}\],\[ds{p^3}\] etc.
Let us discuss the shape and bond angle of given hybridization with examples.
A-\[s{p^2}\] Hybridization.
If one $s$ and two \[p\] orbitals having the same energy mixed to form three equivalent hybrid orbitals then the newly formed orbital is known as \[s{p^2}\] orbital. An example of \[s{p^2}\] hybridized molecule is Boron trifluoride. The bond angle of \[s{p^2}\] orbital is ${120^ \circ }$. The shape of \[s{p^2}\] hybridized molecule is a trigonal planar. Thus option (A) is incorrect.
The structure of $B{F_3}$ is,

B-\[s{p^3}\] Hybridization.
If one $s$ and three \[p\] orbitals having the same energy mixed to form four equivalent hybrid orbitals then the newly formed orbital is known as \[s{p^3}\] orbital. An example of \[s{p^3}\] hybridized molecule is methane. The bond angle of \[s{p^3}\]orbital is ${109.5^ \circ }$ . The shape of \[s{p^3}\] hybridized molecule is a tetrahedral. Thus option (B) is correct.
The structure of methane is,

C-\[ds{p^2}\] Hybridization.
If one $d$ , one $s$ , and two \[p\] orbitals having the same energy mixed to form four equivalent hybrids orbital then the newly formed orbital is known as \[ds{p^2}\] orbital. An example of \[ds{p^2}\] hybridized molecule is nickel complex. The bond angle of \[ds{p^2}\]orbital is ${90^ \circ }$. The shape of \[ds{p^2}\] hybridized molecule is a square planar. Thus option (C) is incorrect.
The structure of ${\left[ {Ni{{\left( {CN} \right)}_4}} \right]^{2 - }}$ is,

Option B is the correct answer for this question.
Note:
We must know that the shape of a molecule can be identified by calculating the steric number. The total number of bonded and lone pairs of electrons in a molecule is called a steric number. It can be calculated using the formula,
$Steric\,number = \dfrac{{Valence\,electrons\,of\,the\,central\,atom\, + number\,of\,Bonded\,atom}}{2}$
Let us calculate the steric number of methane. Using the formula,
$Steric\,number = \dfrac{{4\, + 4}}{2} = 4$
The steric number of methane is four. Thus it has four bonded atoms and no lone pair around the central atom. Thus it is \[s{p^3}\] hybridized tetrahedral molecule.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




