
The term glycocalyx is used for
(a) The cell wall of bacteria
(b) Bacterial cell wall glycoengineered to possess N-glycosylated proteins
(c) A layer surrounding the cell wall of bacteria
(d) A layer present between the cell wall and cell membrane
Answer
566.4k+ views
Hint: Bacterial cells with glycocalyx are almost invisible to the host immune system and also helps in the adhesion to the living tissue.
Complete answer:
A carbohydrate-protein layer that is covered on many of the eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells is called the glycocalyx. In prokaryotes particularly it is covered on the cell wall of bacteria. Many of the eukaryotic cells use glycocalyx to recognize the cell. To protect from the host factors bacterial cells are covered with glycocalyx. The glycocalyx in bacterial cells has the ability to establish an infection.
Additional information:
- In bacteria glycocalyx is of several forms: the glycocalyx is called capsule if it is attached tightly to the underlying cell wall in a condensed form. If the glycocalyx is loosely attached to the cell wall and easily removable, it is called the slime layer.
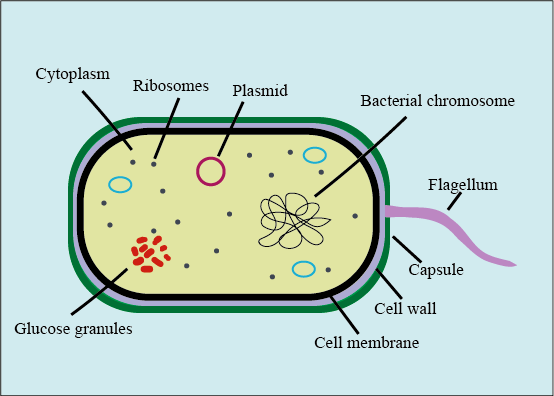
- The structure of glycocalyx varies from bacteria to bacteria depending on the availability of nutrients and growth conditions. Generally, it is made up of sugars called saccharides. If more than two sugars are present then the glycocalyx is said to be made up of polysaccharide. In some glycocalyx, proteins are also present.
So, the correct answer is ‘(c) A layer surrounding the cell wall of bacteria’.
Note: The two important functions of glycocalyx are:
- It covers the bacterial cell and hides them from the immune system of the host. Bacteria with glycocalyx are almost invisible to the bacteria.
- Biofilms are formed by the bacterial cell to promote adhesion of the bacterial cells to the living tissue.
Complete answer:
A carbohydrate-protein layer that is covered on many of the eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells is called the glycocalyx. In prokaryotes particularly it is covered on the cell wall of bacteria. Many of the eukaryotic cells use glycocalyx to recognize the cell. To protect from the host factors bacterial cells are covered with glycocalyx. The glycocalyx in bacterial cells has the ability to establish an infection.
Additional information:
- In bacteria glycocalyx is of several forms: the glycocalyx is called capsule if it is attached tightly to the underlying cell wall in a condensed form. If the glycocalyx is loosely attached to the cell wall and easily removable, it is called the slime layer.

- The structure of glycocalyx varies from bacteria to bacteria depending on the availability of nutrients and growth conditions. Generally, it is made up of sugars called saccharides. If more than two sugars are present then the glycocalyx is said to be made up of polysaccharide. In some glycocalyx, proteins are also present.
So, the correct answer is ‘(c) A layer surrounding the cell wall of bacteria’.
Note: The two important functions of glycocalyx are:
- It covers the bacterial cell and hides them from the immune system of the host. Bacteria with glycocalyx are almost invisible to the bacteria.
- Biofilms are formed by the bacterial cell to promote adhesion of the bacterial cells to the living tissue.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




