
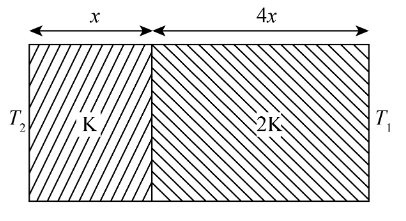
The temperature of the two outer surfaces of a composite slab, consisting of two materials having coefficients of thermal conductivity K and 2K and thickness x and 4x, respectively are \[{T_2}\] and \[{T_1}\left( {{T_2} > {T_1}} \right)\]. The rate of heat transfer through the slab, in a steady state is
\[\left( {\dfrac{{A\left( {{T_2} - {T_1}} \right)K}}{x}} \right)f\], with f equals to

Answer
586.8k+ views
Hint:The above problem can be resolved by using the concepts and applications of the thermal energy transfer. The various terms like thermal conductivity, thermal resistance, and the heat transfer coefficient also need to be considered. When the two blocks are considered for the analysis, they are exposed at some temperature difference range. This difference relates to the thermal resistance for each block, and the total resistance can be obtained utilizing the addition of the two resistances of respective blocks. Moreover, the thermal current expression is also needed to be remembered to get the desired result.
Complete step by step answer:
We know the thermal resistance of the two blocks is,
\[{R_1} = \dfrac{x}{{kA}}\]
\[{R_2} = \dfrac{{4x}}{{2kA}}\]
Here, in the above expressions, the variables A represents the area of slab and k is the value of thermal conductivity.
Then, the total resistance is given as,
\[R = {R_1} + {R_2}\]
On substitute the value as,
\[\begin{array}{l}
R = \dfrac{x}{{kA}} + \dfrac{{4x}}{{2kA}}\\
R = \dfrac{x}{{kA}} + \dfrac{{2x}}{{kA}}\\
R = \dfrac{{3x}}{{kA}}
\end{array}\] ……..(1)
The magnitude of heat current will be,
\[I = \dfrac{{{T_2} - {T_1}}}{R}\]
Here, \[{T_1}\] and \[{T_2}\] are the temperatures of block A and block B respectively.
On substituting the values in the above expression, we get,
\[\begin{array}{l}
I = \dfrac{{{T_2} - {T_1}}}{{\left( {\dfrac{{3x}}{{kA}}} \right)}}\\
I = \dfrac{1}{3}\left( {\dfrac{{KA\left( {{T_2} - {T_1}} \right)}}{x}} \right)
\end{array}\]
Therefore, the value of f on comparing the given equation is 1/3.
Note: Try to understand the various modes of heat transfer to resolve such conditions. There are three modes of heat transfer, namely conduction, convection, and radiation. Out of these three, the conduction mode of heat transfer is that mode of heat transfer in which the energy is being transmitted from one region to the other through molecular vibrations rather, there is no movement of atoms and molecules.
Complete step by step answer:
We know the thermal resistance of the two blocks is,
\[{R_1} = \dfrac{x}{{kA}}\]
\[{R_2} = \dfrac{{4x}}{{2kA}}\]
Here, in the above expressions, the variables A represents the area of slab and k is the value of thermal conductivity.
Then, the total resistance is given as,
\[R = {R_1} + {R_2}\]
On substitute the value as,
\[\begin{array}{l}
R = \dfrac{x}{{kA}} + \dfrac{{4x}}{{2kA}}\\
R = \dfrac{x}{{kA}} + \dfrac{{2x}}{{kA}}\\
R = \dfrac{{3x}}{{kA}}
\end{array}\] ……..(1)
The magnitude of heat current will be,
\[I = \dfrac{{{T_2} - {T_1}}}{R}\]
Here, \[{T_1}\] and \[{T_2}\] are the temperatures of block A and block B respectively.
On substituting the values in the above expression, we get,
\[\begin{array}{l}
I = \dfrac{{{T_2} - {T_1}}}{{\left( {\dfrac{{3x}}{{kA}}} \right)}}\\
I = \dfrac{1}{3}\left( {\dfrac{{KA\left( {{T_2} - {T_1}} \right)}}{x}} \right)
\end{array}\]
Therefore, the value of f on comparing the given equation is 1/3.
Note: Try to understand the various modes of heat transfer to resolve such conditions. There are three modes of heat transfer, namely conduction, convection, and radiation. Out of these three, the conduction mode of heat transfer is that mode of heat transfer in which the energy is being transmitted from one region to the other through molecular vibrations rather, there is no movement of atoms and molecules.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




