
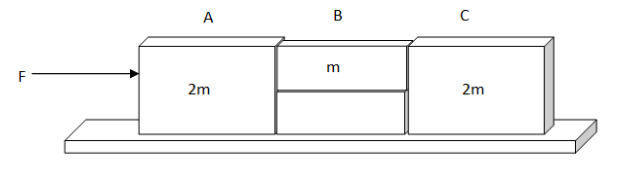
The system is pushed by a force F as shown in fig. All surfaces are smooth except between B and C. Friction coefficient between B and C is \[\mu \] . Minimum value of F to prevent block B from down ward slipping is:
\[
A.{\text{ }}\left( {\dfrac{3}{{2\mu }}} \right)mg \\
B.{\text{ }}\left( {\dfrac{5}{{2\mu }}} \right)mg \\
C.{\text{ }}\left( {\dfrac{5}{2}} \right)\mu mg \\
D.{\text{ }}\left( {\dfrac{3}{2}} \right)\mu mg \\
\]

Answer
617.4k+ views
Hint- In order to deal with this question we have to keep in mind that B will not slide down if frictional force is more than the weight of block B, so first we will find the normal forces by using the simple formula as product of mass and acceleration.
Formula used- $a = \dfrac{F}{M},N = M \times a,W = mg,{\text{frictional force}} = {\text{frictional coefficient}} \times {\text{normal force}}$.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given that there are three blocks having masses as 2m, m and 2m respectively.
Then horizontal acceleration of the system is
$
\because a = \dfrac{F}{M} \\
\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{F}{{2m + m + 2m}} \\
\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{F}{{5m}} \\
$
Now, we will calculate the normal force between B and C which will be calculated as
$
\because N = M \times a \\
\Rightarrow N = 2m \times \dfrac{F}{{5m}} \\
\Rightarrow N = \dfrac{{2F}}{5} \\
$
As we know that the frictional force is given as the product of frictional coefficient and the normal force.
As for this case as we know the frictional coefficient and the normal force so the frictional force is given as:
\[
{\text{frictional force}} = {\text{frictional coefficient}} \times {\text{normal force}} \\
\Rightarrow {F_f} = \mu \times N \\
\Rightarrow {F_f} = \mu \times \dfrac{{2F}}{5} \\
\]
From the figure it has been cleared that B will not slide down if frictional force is more than the weight mg of block B.
So, minimum value of F to prevent block B from down ward slipping is given by the inequality:
$
{F_f} \geqslant W \\
\Rightarrow \mu \dfrac{{2F}}{5} \geqslant mg \\
\Rightarrow F \geqslant \dfrac{5}{{2\mu }}mg \\
$
Hence, the minimum value of F to prevent block B from down ward slipping is $\dfrac{5}{{2\mu }}mg$
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note- Frictional Force refers to the force generated by two surfaces that contact and slide against each other. These forces are mainly influenced by the structure of the surface and the amount of force which needs them together. The object's angle and location affect the amount of frictional force.
Formula used- $a = \dfrac{F}{M},N = M \times a,W = mg,{\text{frictional force}} = {\text{frictional coefficient}} \times {\text{normal force}}$.
Complete step-by-step solution -
Given that there are three blocks having masses as 2m, m and 2m respectively.
Then horizontal acceleration of the system is
$
\because a = \dfrac{F}{M} \\
\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{F}{{2m + m + 2m}} \\
\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{F}{{5m}} \\
$
Now, we will calculate the normal force between B and C which will be calculated as
$
\because N = M \times a \\
\Rightarrow N = 2m \times \dfrac{F}{{5m}} \\
\Rightarrow N = \dfrac{{2F}}{5} \\
$
As we know that the frictional force is given as the product of frictional coefficient and the normal force.
As for this case as we know the frictional coefficient and the normal force so the frictional force is given as:
\[
{\text{frictional force}} = {\text{frictional coefficient}} \times {\text{normal force}} \\
\Rightarrow {F_f} = \mu \times N \\
\Rightarrow {F_f} = \mu \times \dfrac{{2F}}{5} \\
\]
From the figure it has been cleared that B will not slide down if frictional force is more than the weight mg of block B.
So, minimum value of F to prevent block B from down ward slipping is given by the inequality:
$
{F_f} \geqslant W \\
\Rightarrow \mu \dfrac{{2F}}{5} \geqslant mg \\
\Rightarrow F \geqslant \dfrac{5}{{2\mu }}mg \\
$
Hence, the minimum value of F to prevent block B from down ward slipping is $\dfrac{5}{{2\mu }}mg$
So, the correct answer is option B.
Note- Frictional Force refers to the force generated by two surfaces that contact and slide against each other. These forces are mainly influenced by the structure of the surface and the amount of force which needs them together. The object's angle and location affect the amount of frictional force.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

The largest wind power cluster is located in the state class 11 social science CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

Which among the following are examples of coming together class 11 social science CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




