
The structure of the compound formed, when nitrobenzene is reduced by lithium aluminium hydride $ \left( {{\text{LiAl}}{{\text{H}}_4}} \right) $ is=
A.
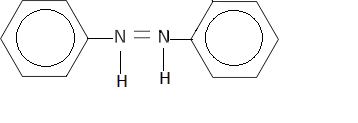
B.
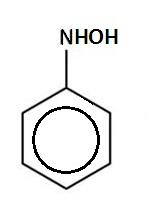
C.
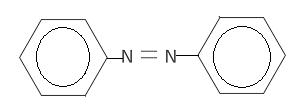
D.
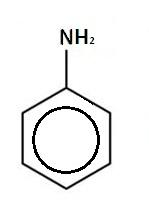




Answer
537.3k+ views
Hint :Lithium aluminum hydride is a strong reducing agent for polar double bonds. Since the nitro group contains polar double bonds, Lithium aluminum hydride reduces aromatic nitro compounds to azo products.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
In Lithium aluminum hydride, aluminum has low electro-negativity thus $ Al - H $ bond is strongly polarized with aluminum positive and hydrogen negative. This abnormal polarization for hydrogen results in high reactivity, especially with atoms that can accept electrons. This allows the hydrogen to become positive again. It reduces aldehyde, ketone, esters and carboxylic acids to alcohols.
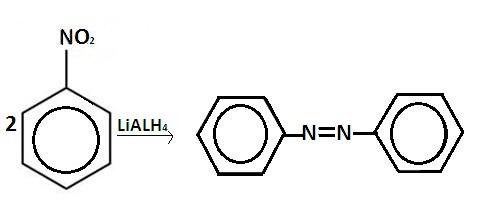
When nitrobenzene reacts with this reagent nitro group is reduced to form azobenzene. The reaction is as follows-
$ 2Ph - N{O_2}\xrightarrow{{LiAl{H_4}}}Ph - N = N - Ph $
Hence the correct option is ‘C’.
Additional Information:
Nitrobenzene is a yellow coloured aromatic compound with an almond like odor. It is slightly soluble in water and evaporates on reaction with air. It emits toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides upon combustion. Its applications are-
1. It is used in the manufacture of aniline.
2. It is also used in manufacture of lubricating oils, dyes, and drugs.
3. It is also used to make pesticides and synthetic rubber.
Note :
Azobenzene is the simplest aromatic azo compound. It is an orange-red crystal. It is soluble in organic solvents but slightly soluble in water. When it is strongly heated then it also emits toxic fumes. It uses-
It is used in production of benzidine and its salts.
It is used in manufacturing of insecticides and pyrazolone derivatives.
It is also used to manufacture dyes, rubber accelerators, fumigant in greenhouses against insects.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
In Lithium aluminum hydride, aluminum has low electro-negativity thus $ Al - H $ bond is strongly polarized with aluminum positive and hydrogen negative. This abnormal polarization for hydrogen results in high reactivity, especially with atoms that can accept electrons. This allows the hydrogen to become positive again. It reduces aldehyde, ketone, esters and carboxylic acids to alcohols.
When nitrobenzene reacts with this reagent nitro group is reduced to form azobenzene. The reaction is as follows-
$ 2Ph - N{O_2}\xrightarrow{{LiAl{H_4}}}Ph - N = N - Ph $

Hence the correct option is ‘C’.
Additional Information:
Nitrobenzene is a yellow coloured aromatic compound with an almond like odor. It is slightly soluble in water and evaporates on reaction with air. It emits toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides upon combustion. Its applications are-
1. It is used in the manufacture of aniline.
2. It is also used in manufacture of lubricating oils, dyes, and drugs.
3. It is also used to make pesticides and synthetic rubber.
Note :
Azobenzene is the simplest aromatic azo compound. It is an orange-red crystal. It is soluble in organic solvents but slightly soluble in water. When it is strongly heated then it also emits toxic fumes. It uses-
It is used in production of benzidine and its salts.
It is used in manufacturing of insecticides and pyrazolone derivatives.
It is also used to manufacture dyes, rubber accelerators, fumigant in greenhouses against insects.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




