
The structure of $P{F_5}$ molecule is.
A) Square planar.
B) Tetrahedral.
C) Trigonal bipyramidal.
D) Pentagonal Bipyramidal.
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: We can find the geometry of a molecule by finding the steric number of a molecule. The steric number of molecule is calculated using the formula,
\[Steric\,number = \dfrac{{valence\,electron\,of\,central\,atom + no.of.bonded\,atom}}{2}\]
Complete step by step answer:
Let us see what hybridization is.
Hybridization:
Hybridization is the idea that atomic orbitals combine to form new hybridized orbitals which in turn, influences molecular geometry and bonding properties.
We know that the electrons which are present at the outermost shell of an atom are called valence electrons and valency of an electron is the number of electrons in which atom accepts or donate to form a bond.
We know that the valence electrons of phosphorus is five and there are five fluoride bonds to the central metal atom.
The steric number of $P{F_5}$ can be calculated as,
\[Steric\,number = \dfrac{{valence\,electron\,of\,central\,atom + no.of.bonded\,atom}}{2}\]
In $P{F_5}$ molecule, valence electron of central atom is $5$ and phosphorus is surrounded by $5$ fluorine atoms so the no. of bonded atom in $P{F_5}$ is $5$. Substituting the values in formula we get,
\[Steric\,number = \dfrac{{5 + 5}}{2} = 5\]
The steric number of $P{F_5}$ is five.
The structure of $P{F_5}$ is,
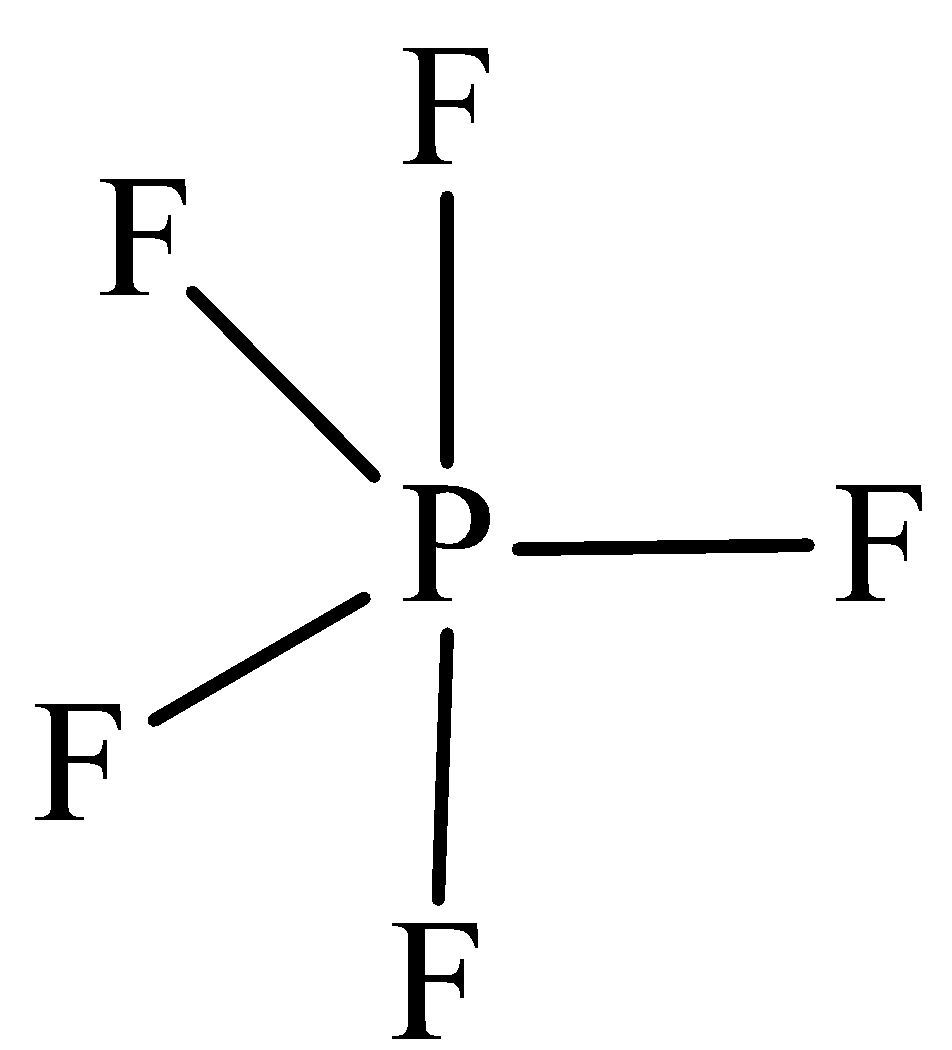
In $P{F_5}$ the central atom is phosphorus has five bonding domains. The hybridization of $PC{l_5}$ is ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{d}}$. The molecular geometry is trigonal bipyramidal.
The ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{d}}$ hybridization:
The combination of $1s$,$3p$ and $1d$ orbital result in the formation of ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{d}}$ orbital in which three lobes are oriented towards the corners of a triangle and the other lie perpendicular to them to minimize the repulsions.
So, the correct answer is Option C .
Note:
We can also calculate the steric number as follow,
The steric number is a sum of the number of ligands and lone pairs surrounding the central atom.
${\text{steric}}\,{\text{number}}\,{\text{ = (m + n)}}$
Where m is the number of ligands and n is the number of lone pairs.
\[Steric\,number = \dfrac{{valence\,electron\,of\,central\,atom + no.of.bonded\,atom}}{2}\]
Complete step by step answer:
Let us see what hybridization is.
Hybridization:
Hybridization is the idea that atomic orbitals combine to form new hybridized orbitals which in turn, influences molecular geometry and bonding properties.
We know that the electrons which are present at the outermost shell of an atom are called valence electrons and valency of an electron is the number of electrons in which atom accepts or donate to form a bond.
We know that the valence electrons of phosphorus is five and there are five fluoride bonds to the central metal atom.
The steric number of $P{F_5}$ can be calculated as,
\[Steric\,number = \dfrac{{valence\,electron\,of\,central\,atom + no.of.bonded\,atom}}{2}\]
In $P{F_5}$ molecule, valence electron of central atom is $5$ and phosphorus is surrounded by $5$ fluorine atoms so the no. of bonded atom in $P{F_5}$ is $5$. Substituting the values in formula we get,
\[Steric\,number = \dfrac{{5 + 5}}{2} = 5\]
The steric number of $P{F_5}$ is five.
The structure of $P{F_5}$ is,

In $P{F_5}$ the central atom is phosphorus has five bonding domains. The hybridization of $PC{l_5}$ is ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{d}}$. The molecular geometry is trigonal bipyramidal.
The ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{d}}$ hybridization:
The combination of $1s$,$3p$ and $1d$ orbital result in the formation of ${\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^{\text{3}}}{\text{d}}$ orbital in which three lobes are oriented towards the corners of a triangle and the other lie perpendicular to them to minimize the repulsions.
So, the correct answer is Option C .
Note:
We can also calculate the steric number as follow,
The steric number is a sum of the number of ligands and lone pairs surrounding the central atom.
${\text{steric}}\,{\text{number}}\,{\text{ = (m + n)}}$
Where m is the number of ligands and n is the number of lone pairs.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




