
The structure of glucose and galactose are same except with regard to
A) First carbon atom
B) Second carbon atom
C) Third carbon atom
D) Fourth carbon atom
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint:Glucose and galactose both are the carbohydrates or sugars or disaccharides. Carbohydrates are the most abundant compounds on the earth. They are the nutrients that must be present in our diet. Glucose and galactose both are the monosaccharides (having only one sugar).
Complete answer:
Structure of glucose:
>Glucose is the main sugar which is metabolized by the body for energy.
> Glucose can either be metabolized in aerobic conditions as well as in anaerobic conditions.
> The breakdown of glucose molecule starts with glycolysis pathway.
> Plants and algae prepare glucose by the processs of photosynthesis (process by which plants make their own food using Sunlight, chlorophyll, water and carbondioxide).
>The molecule of glucose is made up of 6 carbons and an aldehyde group.
>As it contains 6 carbon and 1 aldehyde group that’s why it is called as aldohexose sugar.
>It exist in both cyclic and acyclic forms.
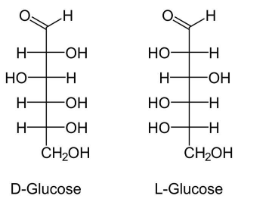
Structure of galactose:
Galactose is a type of sugar which can exist in cyclic form as well as in acyclic form.Charles Weissman oined the term glucose.It is a odourless white coloured solid.The molecule of galactose has 6 carbons and 1 aldehyde group.
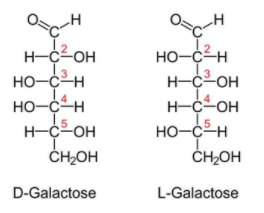
Difference between the structure of glucose and galactose:
Galactose is the isomer of glucose. They differ only in the organization of their atoms. Glucose and galactose are stereoisomers of each other. The main structural difference in between galactose and glucose is the orientation of the hydroxyl group (OH) at carbon 4.
Therefore it has been clear from the above discussion that the structure of glucose and galactose are the same except with regard to the fourth carbon atom.
Hence, the option D is the correct answer.
Note:Isomers are the molecules that have the same structural formula but they differ only in the orientation of their molecules. That’s why their physical and chemical properties may differ such as their boiling point, melting point, reactivity, etc.
Complete answer:
Structure of glucose:
>Glucose is the main sugar which is metabolized by the body for energy.
> Glucose can either be metabolized in aerobic conditions as well as in anaerobic conditions.
> The breakdown of glucose molecule starts with glycolysis pathway.
> Plants and algae prepare glucose by the processs of photosynthesis (process by which plants make their own food using Sunlight, chlorophyll, water and carbondioxide).
>The molecule of glucose is made up of 6 carbons and an aldehyde group.
>As it contains 6 carbon and 1 aldehyde group that’s why it is called as aldohexose sugar.
>It exist in both cyclic and acyclic forms.

Structure of galactose:
Galactose is a type of sugar which can exist in cyclic form as well as in acyclic form.Charles Weissman oined the term glucose.It is a odourless white coloured solid.The molecule of galactose has 6 carbons and 1 aldehyde group.

Difference between the structure of glucose and galactose:
Galactose is the isomer of glucose. They differ only in the organization of their atoms. Glucose and galactose are stereoisomers of each other. The main structural difference in between galactose and glucose is the orientation of the hydroxyl group (OH) at carbon 4.
Therefore it has been clear from the above discussion that the structure of glucose and galactose are the same except with regard to the fourth carbon atom.
Hence, the option D is the correct answer.
Note:Isomers are the molecules that have the same structural formula but they differ only in the orientation of their molecules. That’s why their physical and chemical properties may differ such as their boiling point, melting point, reactivity, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




