
The structural formula of monomer of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is:
a) $ C{H_2} = CHCOOC{H_3} $
b) $ C{H_2} = C(C{H_3}) - COOC{H_3} $
c) $ C{H_3}COOCH = C{H_2} $
d) $ C{H_3}COOC(C{H_3}) = C{H_2} $
Answer
547.8k+ views
Hint: Polymethyl methacrylate is a polymer with monomer methyl methacrylate. It is also known as the acrylic glass or acrylics. It is a synthetic resin produced from the polymerisation of methyl methacrylate. It appeared as transparent and rigid plastic.
Complete step by step solution:
Acrylic polymers are the set of polymers noted for their transparency, resistance to breakage and elasticity. They are very popularly known as acrylics or polyacrylates.
For e.g. Polyacrylic acid, of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), polyacrylonitrile etc.
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) can be prepared by emulsion polymerisation, solution polymerisation and bulk polymerisation.
Generally we use radical initiation methods but anionic polymerisation, another important method can also be performed.
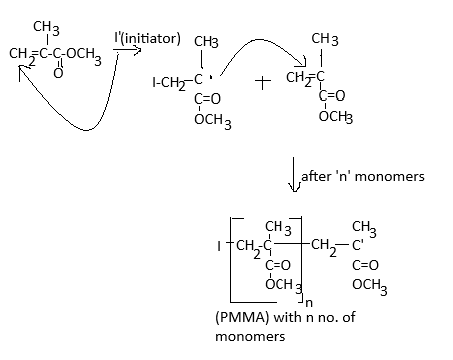
Polymers are colourless, transparent plastic with an excellent outdoor life period and very good strength. It is an amorphous polymer in nature which is mainly due to the presence of bulky side groups in the parent chain.
It is used in remote control or heat sensors as they allow specific I.R wavelengths to pass through blocking visible light. When it is burnt, it gives $ CO,C{O_2},{H_2}O $ and low molecular weight compounds including formaldehyde.
As from the above discussion we observed it is transparent, hence it is used in rear lights, lenses, glasses, instrument clusters for vehicles. Also it is used in the form of sheets to build the windows, skylights, bullet proof security barriers, LCD screens, etc.
Hence the correct option is (b).
Note:
The monomer is synthesised by using acetone and hydrogen cyanide. When the formation of cyanohydrin takes place at $ 150^\circ C $ , sulphuric acid is added and the molecule rearranges to methyl methacrylate.
Complete step by step solution:
Acrylic polymers are the set of polymers noted for their transparency, resistance to breakage and elasticity. They are very popularly known as acrylics or polyacrylates.
For e.g. Polyacrylic acid, of polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA), polyacrylonitrile etc.
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) can be prepared by emulsion polymerisation, solution polymerisation and bulk polymerisation.
Generally we use radical initiation methods but anionic polymerisation, another important method can also be performed.

Polymers are colourless, transparent plastic with an excellent outdoor life period and very good strength. It is an amorphous polymer in nature which is mainly due to the presence of bulky side groups in the parent chain.
It is used in remote control or heat sensors as they allow specific I.R wavelengths to pass through blocking visible light. When it is burnt, it gives $ CO,C{O_2},{H_2}O $ and low molecular weight compounds including formaldehyde.
As from the above discussion we observed it is transparent, hence it is used in rear lights, lenses, glasses, instrument clusters for vehicles. Also it is used in the form of sheets to build the windows, skylights, bullet proof security barriers, LCD screens, etc.
Hence the correct option is (b).
Note:
The monomer is synthesised by using acetone and hydrogen cyanide. When the formation of cyanohydrin takes place at $ 150^\circ C $ , sulphuric acid is added and the molecule rearranges to methyl methacrylate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




