
The stomata in angiosperms open and close due to _______
A. The presence of gases inside the leaves
B. Their genetic constitution
C. Turgor pressure of guard cells
D. Turgor pressure of subsidiary cells
Answer
572.7k+ views
Hint: The stomata are small openings or pores that permit for gas exchange in plant tissue. Stomata are surrounded by specialised cells known as guard cells and act to open and close stomatal pores. Stomata are usually found in plant leaves, but in some stems, they can also be found.
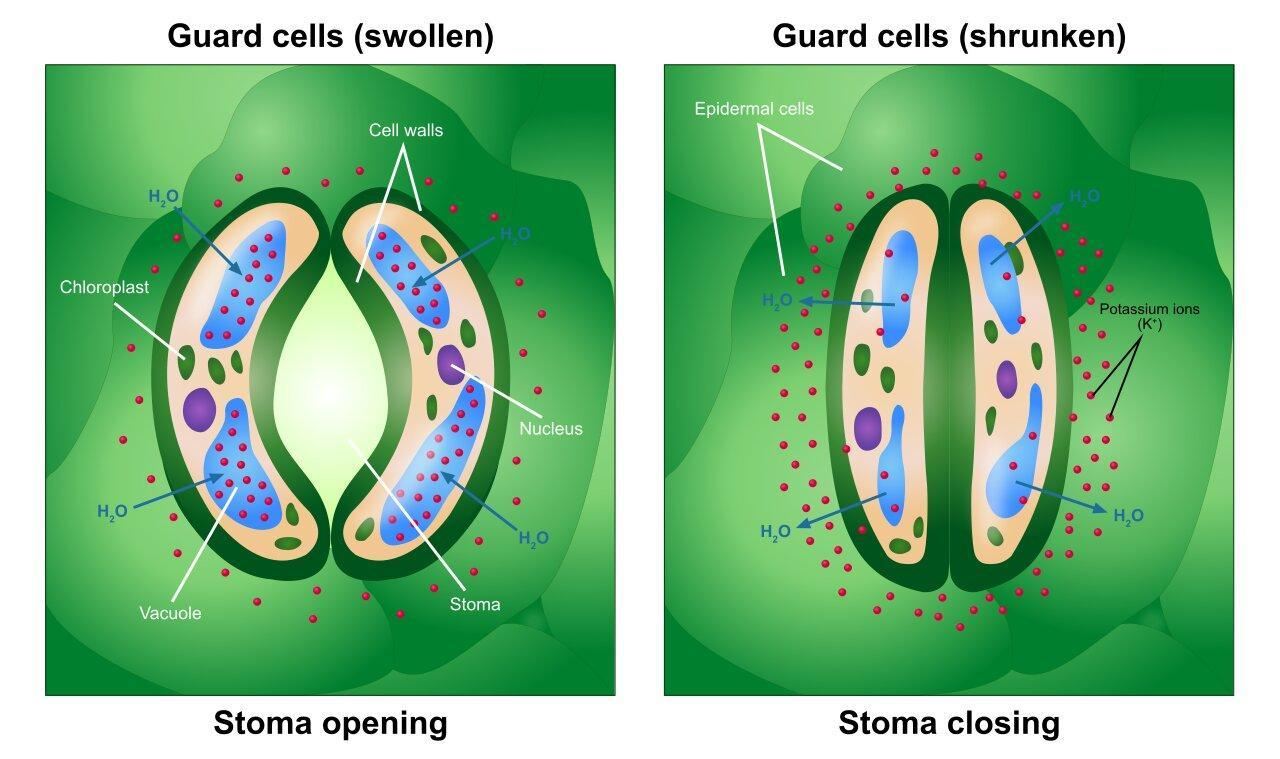
Complete answer: The guard cells are formed in pairs with a space that includes a stomatal pore within them. The stomatal pores are most significant when water is readily available, and when the water supply is significantly low, and the guard cells turn out to be flaccid; the guard cells are turgid and closed.
The diffusion of carbon dioxide from the air through the stomata into the mesophyll tissues is based on photosynthesis. Oxygen generated by photosynthesis exits the plant through the stomata as a by-product. When the stomata are open, evaporation loses water and must be replaced with water taken up by the roots through the transpiration stream. Plants must compensate with the water loss through the stomatal pores the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed from the air, and this is accomplished by both active and passive regulation of guard cell turgor and stomatal pore size.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note:
Turgor pressure can be constructed by cells of several species. Turgor pressure plays a vital role in key processes in plants, such as development, growth, structural support, signalling, and movement of organs, flowering and stress response. Turgor pressure is the force pushing the plasma membrane against the cell wall within the cell. It may be as small as 0.1-0.4 MPa but can reach 2-3 MPa as well.
Complete answer: The guard cells are formed in pairs with a space that includes a stomatal pore within them. The stomatal pores are most significant when water is readily available, and when the water supply is significantly low, and the guard cells turn out to be flaccid; the guard cells are turgid and closed.
The diffusion of carbon dioxide from the air through the stomata into the mesophyll tissues is based on photosynthesis. Oxygen generated by photosynthesis exits the plant through the stomata as a by-product. When the stomata are open, evaporation loses water and must be replaced with water taken up by the roots through the transpiration stream. Plants must compensate with the water loss through the stomatal pores the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed from the air, and this is accomplished by both active and passive regulation of guard cell turgor and stomatal pore size.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.

Note:
Turgor pressure can be constructed by cells of several species. Turgor pressure plays a vital role in key processes in plants, such as development, growth, structural support, signalling, and movement of organs, flowering and stress response. Turgor pressure is the force pushing the plasma membrane against the cell wall within the cell. It may be as small as 0.1-0.4 MPa but can reach 2-3 MPa as well.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




