
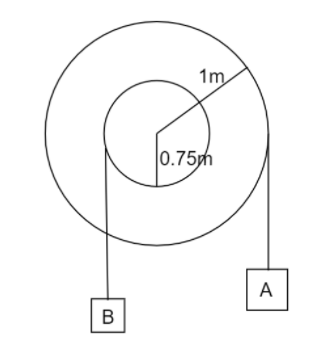
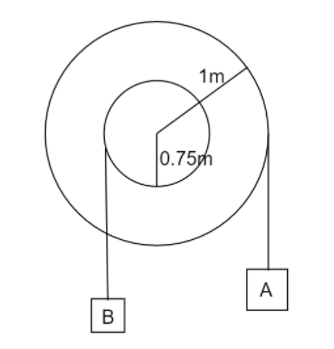
The step pulley shown starts from rest and accelerates at $2$$rad$ ${s^{ - 2}}$,
What time $t$ is required for block A to move $20m$ ?
A) $4.47s$
B) $3.47s$
C) $5.47s$
D) $6.47s$


Answer
478.5k+ views
Hint: A changing angular velocity indicates the presence of an angular acceleration in a rigid body, typically measured in $rad$ ${s^{ - 2}}$. Find the translational acceleration for both blocks A and B. Use the second equation of motion which is $S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$ and find the value of $t$.
Complete step by step answer:
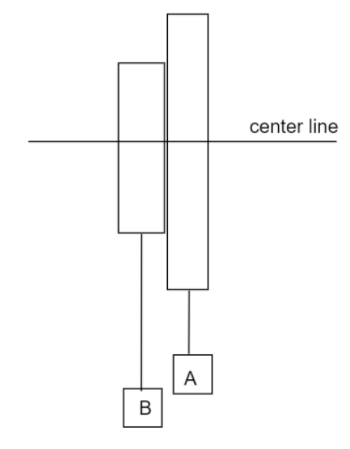
Here, the block A moves with an acceleration of ${a_A}$ downwards and the block B moves with an acceleration of ${a_B}$ upwards.
Given is $R = 1m$and $r = 0.75m$
We know, Translational acceleration is given by $a = r\alpha $ where $r$ is the radius from the axis of rotation and $\alpha $ is angular acceleration. The angular acceleration is the rate of change of the angular velocity, just as acceleration is the rate of change of velocity.
So for block A angular acceleration ${a_A} = 2 \times 1 = 2m/{s^2}$
And for block B angular acceleration ${a_B} = 2 \times 0.75 = 1.5m/{s^2}$
Initially, it is starting from rest so $u = 0$
${a_A} = 2m/{s^2}$
For block A to move to a Distance $S = 20m$
Using the second equation of motion
$S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
Putting the values from above
$ \Rightarrow 20 = 0 \times t + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 2 \times {t^2}$
$ \Rightarrow t = \sqrt {20} $
$ \Rightarrow t = 4.47s$
Hence time required by block A to move $20m$ is $4.47s$. So, option (A) is correct.
Note: The translational acceleration of a point on the object rotating is given by $a = r\alpha $ where $r$ is the radius or distance from the axis of rotation. This is also the tangential component of acceleration: it is tangential to the direction of motion of the point. If this component is $0$, the motion is a uniform circular motion, and the velocity changes in direction only.
Complete step by step answer:

Here, the block A moves with an acceleration of ${a_A}$ downwards and the block B moves with an acceleration of ${a_B}$ upwards.
Given is $R = 1m$and $r = 0.75m$
We know, Translational acceleration is given by $a = r\alpha $ where $r$ is the radius from the axis of rotation and $\alpha $ is angular acceleration. The angular acceleration is the rate of change of the angular velocity, just as acceleration is the rate of change of velocity.
So for block A angular acceleration ${a_A} = 2 \times 1 = 2m/{s^2}$
And for block B angular acceleration ${a_B} = 2 \times 0.75 = 1.5m/{s^2}$
Initially, it is starting from rest so $u = 0$
${a_A} = 2m/{s^2}$
For block A to move to a Distance $S = 20m$
Using the second equation of motion
$S = ut + \dfrac{1}{2}a{t^2}$
Putting the values from above
$ \Rightarrow 20 = 0 \times t + \dfrac{1}{2} \times 2 \times {t^2}$
$ \Rightarrow t = \sqrt {20} $
$ \Rightarrow t = 4.47s$
Hence time required by block A to move $20m$ is $4.47s$. So, option (A) is correct.
Note: The translational acceleration of a point on the object rotating is given by $a = r\alpha $ where $r$ is the radius or distance from the axis of rotation. This is also the tangential component of acceleration: it is tangential to the direction of motion of the point. If this component is $0$, the motion is a uniform circular motion, and the velocity changes in direction only.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




