
The state of hybridisation for the transition state of hydrolysis mechanism of \[{\text{BC}}{{\text{l}}_3}\] and \[{\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_4}\] are respectively
A) \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}{\text{, s}}{{\text{p}}^3}{\text{d}}\]
B) \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}{\text{, s}}{{\text{p}}^3}\]
C) \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}{\text{, s}}{{\text{p}}^3}{{\text{d}}^2}\]
D) \[{\text{s}}{{\text {p}}^3}{\text{, s}}{{\text{p}}^3}{\text{d}}\]
Answer
548.1k+ views
Hint:
During hydrolysis the water molecule adds up with positive charge on oxygen to the central atom which will get negative. The number of bond pairs and lone pairs in the intermediate structure will give us the hybridisation.
Complete step by step solution:
Hydrolysis refers to the breaking of molecules in the presence of water. The addition of water molecules occurs in the intermediate step.
When hydrolysis of \[{\text{BC}}{{\text{l}}_3}\] occurs then the intermediate that forms have the formula: \[{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_3}\mathop {\text{B}}\limits^ - \mathop {{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{H}}}\limits^ + \]
The structure of the intermediate formed is:
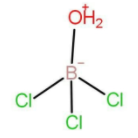
As we can see that it forms 4 bonds. There is no lone pair of electrons present on the central atom. The negative charge signifies the extra electron that has been taken by boron to form forth bond and not the lone pair of electrons. The hybridisation with 4 bond pairs and zero lone pair will be \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}\] . The geometry formed will be tetrahedral.
When hydrolysis of \[{\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_4}\] occurs then the intermediate that forms have the formula: \[{{\text{F}}_4}\mathop {\text{S}}\limits^ - \mathop {{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{H}}}\limits^ + \]
The structure of the intermediate formed is:
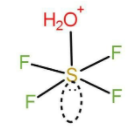
As we can see that it forms 5 bonds. There is one lone pair of electrons present on the central atom that is sulphur. The hybridisation here will be octahedral. Since we have 5 bond pairs and one lone pair of electrons the geometry of this intermediate will be square pyramidal.
Thus, the correct option is C.
Note:
The intermediate that forms in between reactions is not very stable and hence it converts to the product. There are two types of reaction, one in which transition state is involved while converting the reactants to products. The other one includes the formation of intermediate. Carbocation, carbanion, carbine etc. are some reaction intermediates.
During hydrolysis the water molecule adds up with positive charge on oxygen to the central atom which will get negative. The number of bond pairs and lone pairs in the intermediate structure will give us the hybridisation.
Complete step by step solution:
Hydrolysis refers to the breaking of molecules in the presence of water. The addition of water molecules occurs in the intermediate step.
When hydrolysis of \[{\text{BC}}{{\text{l}}_3}\] occurs then the intermediate that forms have the formula: \[{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_3}\mathop {\text{B}}\limits^ - \mathop {{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{H}}}\limits^ + \]
The structure of the intermediate formed is:

As we can see that it forms 4 bonds. There is no lone pair of electrons present on the central atom. The negative charge signifies the extra electron that has been taken by boron to form forth bond and not the lone pair of electrons. The hybridisation with 4 bond pairs and zero lone pair will be \[{\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^3}\] . The geometry formed will be tetrahedral.
When hydrolysis of \[{\text{S}}{{\text{F}}_4}\] occurs then the intermediate that forms have the formula: \[{{\text{F}}_4}\mathop {\text{S}}\limits^ - \mathop {{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{H}}}\limits^ + \]
The structure of the intermediate formed is:

As we can see that it forms 5 bonds. There is one lone pair of electrons present on the central atom that is sulphur. The hybridisation here will be octahedral. Since we have 5 bond pairs and one lone pair of electrons the geometry of this intermediate will be square pyramidal.
Thus, the correct option is C.
Note:
The intermediate that forms in between reactions is not very stable and hence it converts to the product. There are two types of reaction, one in which transition state is involved while converting the reactants to products. The other one includes the formation of intermediate. Carbocation, carbanion, carbine etc. are some reaction intermediates.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




