
The spring balance A reads 2 kg with a block m suspended from it. A balance B reads 5 kg when a beaker with liquid is put on the pan of the balance. The two balances are now arranged so that the hanging mass is inside liquid in the beaker as shown in the figure. In this situation,
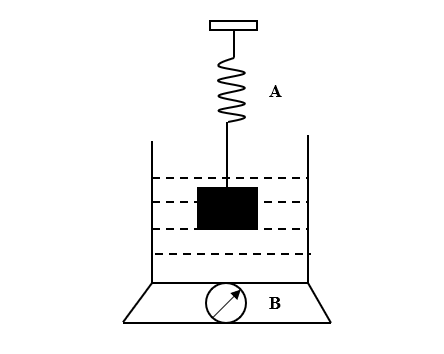
A. the balance A will read more than 2 kg
B. the balance B will read more than 5 kg
C. the balance A will read less than 2 kg and B will read more than 5 kg
D. the balance A and B will read 2 kg and 5 kg, respectively

Answer
554.4k+ views
Hint: When a mass is suspended from the spring balance and completely submerged in the water, it experiences an upward force exerted by the liquid which causes the weight of the mass to decrease. When a balance is placed below the mass, then the mass experiences a downward buoyant force which is exerted by the water. This causes an increase in the weight of the mass. Use this information to answer this question.
Complete answer:
It is given that the spring balance A reads 2 kg. When the mass is immersed in the liquid, it experiences a downward force and an upward force. The downward force is due to the gravitational pull while the upward is the Buoyant force which is due to the displacement of water.
Downward force is given by,
${F}_{down}= mg$
Upward force is given by,
${F}_{up}= {F}_{b}$
Thus, the net tension on the spring will be,
$T= {F}_{down}-{F}_{up}$
Substituting the values in above equation we get,
$T= mg- {F}_{b}$
This new tension on A will be less as compared to earlier.
$T= mg- {F}_{b} < 2 kg$
Now, it is given that the balance B reads 5 kg when a beaker with liquid is put on the pan of the balance. The mass experiences buoyant force. According to Newton’s third law, every action has an equal and opposite reaction. So, for this upward buoyant force, there will be a downward buoyant force. This force adds to the weight of the water. So, now the balance will read 5 kg plus an additional weight. Thus, the reading of the balance will be greater than 5 kg.
So, the correct answer is option B and C.
Note:
The upward buoyant force makes a body appear lighter when immersed in liquid partially or completely. The buoyant force will be the same no matter how deep an object is immersed. It does not depend on the depth of the water. It depends on the volume of liquid displaced or the volume of the body submerged in the liquid. The force of buoyancy or buoyant force increases with increase in acceleration due to gravity.
Complete answer:
It is given that the spring balance A reads 2 kg. When the mass is immersed in the liquid, it experiences a downward force and an upward force. The downward force is due to the gravitational pull while the upward is the Buoyant force which is due to the displacement of water.
Downward force is given by,
${F}_{down}= mg$
Upward force is given by,
${F}_{up}= {F}_{b}$
Thus, the net tension on the spring will be,
$T= {F}_{down}-{F}_{up}$
Substituting the values in above equation we get,
$T= mg- {F}_{b}$
This new tension on A will be less as compared to earlier.
$T= mg- {F}_{b} < 2 kg$
Now, it is given that the balance B reads 5 kg when a beaker with liquid is put on the pan of the balance. The mass experiences buoyant force. According to Newton’s third law, every action has an equal and opposite reaction. So, for this upward buoyant force, there will be a downward buoyant force. This force adds to the weight of the water. So, now the balance will read 5 kg plus an additional weight. Thus, the reading of the balance will be greater than 5 kg.
So, the correct answer is option B and C.
Note:
The upward buoyant force makes a body appear lighter when immersed in liquid partially or completely. The buoyant force will be the same no matter how deep an object is immersed. It does not depend on the depth of the water. It depends on the volume of liquid displaced or the volume of the body submerged in the liquid. The force of buoyancy or buoyant force increases with increase in acceleration due to gravity.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




