
The speed of earth about its axis is $\omega $. Its speed is increased to x times to make the effective acceleration due to gravity equal to zero at the equator, then x is around (g=10$m{{s}^{-1}}$, R=6400km)
A. 1
B. 8.5
C. 17
D. 34
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: Consider a man standing on the equator. Since earth is rotating, the man will also rotate in a circular path that coincides with the equator. The man will experience gravitational force ${{F}_{g}}$ = mg and a pseudo force ${{F}_{p}}=m{{\omega }^{2}}R$. Both will be in opposite directions. Equate ${{F}_{eff}}=mg-mR{{\omega }^{2}}$ to zero to find the new angular velocity. To find x, use $T=\dfrac{2\pi }{\omega }$.
Formula used:
${{F}_{g}}$ = mg
${{F}_{p}}=m{{\omega }^{2}}R$
$T=\dfrac{2\pi }{\omega }$
Complete step by step answer:
Suppose a man is standing on the equator of the earth. The earth will pull the man towards itself by the force of gravity. The magnitude of the gravitational force is equal to ${{F}_{g}}$ = mg.
m is the mass of the man and g is acceleration due to the gravitational force. The direction of the gravitational force is towards the centre of the earth.
We know that earth spins or rotates about an axis passing through its centre. Since it is in a rotational motion, it has an angular velocity $\omega $ as shown in the figure.
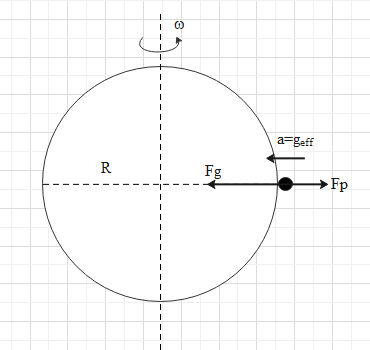
Let's analyse the motion of the mass on the equator.
Since the earth is rotating, the man will also rotate in a circular path which is coinciding with the equator with an angular velocity $\omega $. When a body is in a circular motion, it experiences a pseudo force equal to ${{F}_{p}}=m{{\omega }^{2}}R$, pointing radially outwards of the circular path. R is the radius of the circular path.
Therefore, the man will experience a pseudo force equal to ${{F}_{p}}=m{{\omega }^{2}}R$ and directing in the opposite direction of the gravitational force. Here, R is the radius of earth.
The effective gravitational force is less than mg. i.e. ${{F}_{eff}}={{F}_{g}}-{{F}_{p}}$
$\Rightarrow {{F}_{eff}}=mg-mR{{\omega }^{2}}$.
Due to this, the effective acceleration due to gravity is less than g. Let the effective acceleration be ${{g}_{eff}}$.
By Newton’s second law, F = ma. Hence,
$\Rightarrow {{F}_{eff}}=mg-mR{{\omega }^{2}}=m{{g}_{eff}}$
$\Rightarrow {{g}_{eff}}=g-{{\omega }^{2}}R$ ….. (i).
It is given that the angular velocity of the earth is increased by x times. Let the new angular velocity be $\omega '$.
When the angular velocity is $\omega '$, the effective acceleration due to gravity becomes zero.
Hence, according to equation (i),
${{g}_{eff}}=0=g-\omega {{'}^{2}}R$
$\Rightarrow g-\omega {{'}^{2}}R=0$
$\Rightarrow \omega {{'}^{2}}=\dfrac{g}{R}$
$\Rightarrow \omega '=\sqrt{\dfrac{g}{R}}$.
It is given that $\omega '=x\omega $ …. (ii).
To find the value of x, let use the relation between time period (T) and angular velocity.
i.e. $T=\dfrac{2\pi }{\omega }$.
When the angular velocity of earth is $\omega $, the time period of earth is 24 hours.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{2\pi }{\omega }=24h=24\times 3600s$
$\Rightarrow \omega =\dfrac{2\pi }{24\times 3600}=\dfrac{\pi }{24\times 1800}{{s}^{-1}}$
Substitute the value of $\omega $ and $\omega '$ in equation (ii).
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{\dfrac{g}{R}}=x\dfrac{\pi }{24\times 1800}$
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{24\times 1800}{\pi }\sqrt{\dfrac{g}{R}}$
It is given g=10$m{{s}^{-1}}$, R=6400km =6400000m
Substitute the values of g and R.
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{24\times 1800}{\pi }\sqrt{\dfrac{10}{6400000}}=17.18$
Out of the given options 17.18 is closest to 17.
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note:
From this question we can understand that the acceleration due to gravity on earth also depends on the rotation of earth about its axis. And due to this the acceleration due to gravity is not exactly equal to g.
Formula used:
${{F}_{g}}$ = mg
${{F}_{p}}=m{{\omega }^{2}}R$
$T=\dfrac{2\pi }{\omega }$
Complete step by step answer:
Suppose a man is standing on the equator of the earth. The earth will pull the man towards itself by the force of gravity. The magnitude of the gravitational force is equal to ${{F}_{g}}$ = mg.
m is the mass of the man and g is acceleration due to the gravitational force. The direction of the gravitational force is towards the centre of the earth.
We know that earth spins or rotates about an axis passing through its centre. Since it is in a rotational motion, it has an angular velocity $\omega $ as shown in the figure.

Let's analyse the motion of the mass on the equator.
Since the earth is rotating, the man will also rotate in a circular path which is coinciding with the equator with an angular velocity $\omega $. When a body is in a circular motion, it experiences a pseudo force equal to ${{F}_{p}}=m{{\omega }^{2}}R$, pointing radially outwards of the circular path. R is the radius of the circular path.
Therefore, the man will experience a pseudo force equal to ${{F}_{p}}=m{{\omega }^{2}}R$ and directing in the opposite direction of the gravitational force. Here, R is the radius of earth.
The effective gravitational force is less than mg. i.e. ${{F}_{eff}}={{F}_{g}}-{{F}_{p}}$
$\Rightarrow {{F}_{eff}}=mg-mR{{\omega }^{2}}$.
Due to this, the effective acceleration due to gravity is less than g. Let the effective acceleration be ${{g}_{eff}}$.
By Newton’s second law, F = ma. Hence,
$\Rightarrow {{F}_{eff}}=mg-mR{{\omega }^{2}}=m{{g}_{eff}}$
$\Rightarrow {{g}_{eff}}=g-{{\omega }^{2}}R$ ….. (i).
It is given that the angular velocity of the earth is increased by x times. Let the new angular velocity be $\omega '$.
When the angular velocity is $\omega '$, the effective acceleration due to gravity becomes zero.
Hence, according to equation (i),
${{g}_{eff}}=0=g-\omega {{'}^{2}}R$
$\Rightarrow g-\omega {{'}^{2}}R=0$
$\Rightarrow \omega {{'}^{2}}=\dfrac{g}{R}$
$\Rightarrow \omega '=\sqrt{\dfrac{g}{R}}$.
It is given that $\omega '=x\omega $ …. (ii).
To find the value of x, let use the relation between time period (T) and angular velocity.
i.e. $T=\dfrac{2\pi }{\omega }$.
When the angular velocity of earth is $\omega $, the time period of earth is 24 hours.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{2\pi }{\omega }=24h=24\times 3600s$
$\Rightarrow \omega =\dfrac{2\pi }{24\times 3600}=\dfrac{\pi }{24\times 1800}{{s}^{-1}}$
Substitute the value of $\omega $ and $\omega '$ in equation (ii).
$\Rightarrow \sqrt{\dfrac{g}{R}}=x\dfrac{\pi }{24\times 1800}$
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{24\times 1800}{\pi }\sqrt{\dfrac{g}{R}}$
It is given g=10$m{{s}^{-1}}$, R=6400km =6400000m
Substitute the values of g and R.
$\Rightarrow x=\dfrac{24\times 1800}{\pi }\sqrt{\dfrac{10}{6400000}}=17.18$
Out of the given options 17.18 is closest to 17.
Hence, the correct answer is option C.
Note:
From this question we can understand that the acceleration due to gravity on earth also depends on the rotation of earth about its axis. And due to this the acceleration due to gravity is not exactly equal to g.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




