
The solution of the equation ${{\cos }^{2}}\theta +\sin \theta +1=0$ , lies in the interval
(a) $\left( -\dfrac{\pi }{4},\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)$
(b) $\left( \dfrac{\pi }{4},\dfrac{3\pi }{4} \right)$
(c) $\left( \dfrac{3\pi }{4},\dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right)$
(d) $\left( \dfrac{5\pi }{4},\dfrac{7\pi }{4} \right)$
Answer
599.4k+ views
Hint: First we have to convert the given equation ${{\cos }^{2}}\theta +\sin \theta +1=0$ in terms of sine using the identity \[{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta \] . On putting this value and solving the equation, we will get a quadratic equation in terms of $\sin \theta $ and there will be factors at the end. Then we should know that the range of the sine function is \[\left[ -1,1 \right]\] , so comparing the 2 factors which lie in this range is the answer. And then by plotting the range in the graph we will see in which range that factor lies. That range is our answer.
Complete step by step solution:
Here, we are given with equation ${{\cos }^{2}}\theta +\sin \theta +1=0$ . So, now we have to convert this equation in the form of $\sin \theta $ . So, we will have the identity given as ${{\sin }^{2}}\theta +{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1$ .
So, we can make ${{\cos }^{2}}\theta $ as subject and will get \[{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta \] . On putting this value in the given equation, we get
${{\cos }^{2}}\theta +\sin \theta +1=0$
\[\Rightarrow 1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta +\sin \theta +1=0\]
On multiplying minus sign on both sides of above equation i.e. LHS and RHS we get
\[\Rightarrow {{\sin }^{2}}\theta -\sin \theta -1-1=0\]
\[\Rightarrow {{\sin }^{2}}\theta -\sin \theta -2=0\]
Now, we can see that there is \[-\sin \theta \] which in other ways can be written as \[-2\sin \theta +\sin \theta \] . So, on putting this value to the equation, we get
\[\Rightarrow {{\sin }^{2}}\theta -2\sin \theta +\sin \theta -2=0\]
Now, taking common terms from the equation we get as
\[\Rightarrow \sin \theta \left( \sin \theta -2 \right)+1\left( \sin \theta -2 \right)=0\]
\[\Rightarrow \left( \sin \theta -2 \right)\left( \sin \theta +1 \right)=0\]
Thus, we have two equation which means on solving we get values as
\[\left( \sin \theta -2 \right)=0\Rightarrow \sin \theta =2\] and \[\left( \sin \theta +1 \right)=0\Rightarrow \sin \theta =-1\]
Now, we know that the range of the sine function is \[\left[ -1,1 \right]\] .
So, here we will not consider \[\sin \theta =2\] . We know that \[\sin \dfrac{\pi }{2}=1\] . So, similarly \[\sin \left( -\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)=\sin \left( 2\pi -\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)=\sin \dfrac{3\pi }{2}=-1\] .
Thus, we have to find out the given option in which the range angle \[\dfrac{3\pi }{2}\] lies between the third and fourth quadrant.
We should know the four quadrants in the graph so it is easy to plot all the points in the graphs.
Here, All means in first quadrant all functions are positive, in second quadrant only sine functions are positive, in third quadrant tan functions are positive only and in fourth quadrant only cos functions are positive. Except positive all other angles are negative in respective quadrants.
Taking option (a): $\left( -\dfrac{\pi }{4},\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)$ the graph is as shown below.
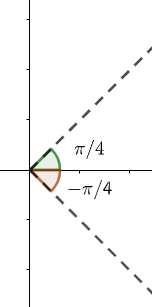
This option does not lie between the third and fourth quadrant, so this is not the answer.
Now option(b): $\left( \dfrac{\pi }{4},\dfrac{3\pi }{4} \right)$ .
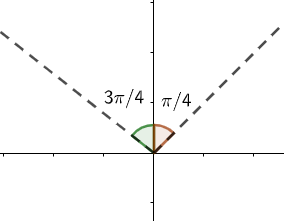
This range lies between the first and second quadrant. So, this is not the answer.
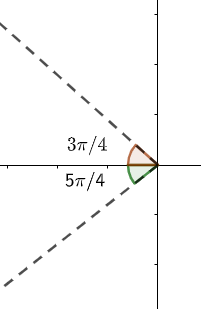
Similarly, option (c) i.e. $\left( \dfrac{3\pi }{4},\dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right)$ will lie between the second and third quadrant. So, this is also incorrect.
Taking option (d): $\left( \dfrac{5\pi }{4},\dfrac{7\pi }{4} \right)$ . This will be between the third and fourth quadrant.
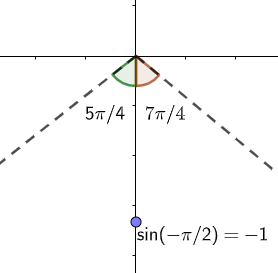
Thus, this is the correct answer.
Hence, option (d) is correct.
Note: Instead of finding range by plotting in graph it is easy to convert range in degree form for all given options. As, we know that \[\sin \dfrac{3\pi }{2}=-1\] is basically $\dfrac{3\times 180}{2}=270{}^\circ $ where taking $\pi =180{}^\circ $ to convert in degree form. So, now we have to find in which range $270{}^\circ $ lies. So, converting all the option in degree form which we get as $\left( -45{}^\circ ,45{}^\circ \right),\left( 45{}^\circ ,135{}^\circ \right),\left( 135{}^\circ ,225{}^\circ \right),\left( 225{}^\circ ,315{}^\circ \right)$ . We can easily see the option (d) is the correct range where $270{}^\circ $ comes in between.
Complete step by step solution:
Here, we are given with equation ${{\cos }^{2}}\theta +\sin \theta +1=0$ . So, now we have to convert this equation in the form of $\sin \theta $ . So, we will have the identity given as ${{\sin }^{2}}\theta +{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1$ .
So, we can make ${{\cos }^{2}}\theta $ as subject and will get \[{{\cos }^{2}}\theta =1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta \] . On putting this value in the given equation, we get
${{\cos }^{2}}\theta +\sin \theta +1=0$
\[\Rightarrow 1-{{\sin }^{2}}\theta +\sin \theta +1=0\]
On multiplying minus sign on both sides of above equation i.e. LHS and RHS we get
\[\Rightarrow {{\sin }^{2}}\theta -\sin \theta -1-1=0\]
\[\Rightarrow {{\sin }^{2}}\theta -\sin \theta -2=0\]
Now, we can see that there is \[-\sin \theta \] which in other ways can be written as \[-2\sin \theta +\sin \theta \] . So, on putting this value to the equation, we get
\[\Rightarrow {{\sin }^{2}}\theta -2\sin \theta +\sin \theta -2=0\]
Now, taking common terms from the equation we get as
\[\Rightarrow \sin \theta \left( \sin \theta -2 \right)+1\left( \sin \theta -2 \right)=0\]
\[\Rightarrow \left( \sin \theta -2 \right)\left( \sin \theta +1 \right)=0\]
Thus, we have two equation which means on solving we get values as
\[\left( \sin \theta -2 \right)=0\Rightarrow \sin \theta =2\] and \[\left( \sin \theta +1 \right)=0\Rightarrow \sin \theta =-1\]
Now, we know that the range of the sine function is \[\left[ -1,1 \right]\] .
So, here we will not consider \[\sin \theta =2\] . We know that \[\sin \dfrac{\pi }{2}=1\] . So, similarly \[\sin \left( -\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)=\sin \left( 2\pi -\dfrac{\pi }{2} \right)=\sin \dfrac{3\pi }{2}=-1\] .
Thus, we have to find out the given option in which the range angle \[\dfrac{3\pi }{2}\] lies between the third and fourth quadrant.
We should know the four quadrants in the graph so it is easy to plot all the points in the graphs.
Here, All means in first quadrant all functions are positive, in second quadrant only sine functions are positive, in third quadrant tan functions are positive only and in fourth quadrant only cos functions are positive. Except positive all other angles are negative in respective quadrants.
Taking option (a): $\left( -\dfrac{\pi }{4},\dfrac{\pi }{4} \right)$ the graph is as shown below.

This option does not lie between the third and fourth quadrant, so this is not the answer.
Now option(b): $\left( \dfrac{\pi }{4},\dfrac{3\pi }{4} \right)$ .

This range lies between the first and second quadrant. So, this is not the answer.
Similarly, option (c) i.e. $\left( \dfrac{3\pi }{4},\dfrac{5\pi }{4} \right)$ will lie between the second and third quadrant. So, this is also incorrect.

Taking option (d): $\left( \dfrac{5\pi }{4},\dfrac{7\pi }{4} \right)$ . This will be between the third and fourth quadrant.

Thus, this is the correct answer.
Hence, option (d) is correct.
Note: Instead of finding range by plotting in graph it is easy to convert range in degree form for all given options. As, we know that \[\sin \dfrac{3\pi }{2}=-1\] is basically $\dfrac{3\times 180}{2}=270{}^\circ $ where taking $\pi =180{}^\circ $ to convert in degree form. So, now we have to find in which range $270{}^\circ $ lies. So, converting all the option in degree form which we get as $\left( -45{}^\circ ,45{}^\circ \right),\left( 45{}^\circ ,135{}^\circ \right),\left( 135{}^\circ ,225{}^\circ \right),\left( 225{}^\circ ,315{}^\circ \right)$ . We can easily see the option (d) is the correct range where $270{}^\circ $ comes in between.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




