
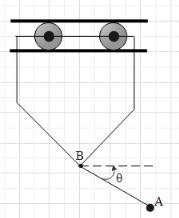
The simple pendulum A of mass ${{m}_{A}}$ and length l is suspended from the trolley B of mass ${{m}_{B}}$. If the system is released from rest at $\theta =0$, determine the velocity ${{v}_{B}}$ of the trolley and tension in the string when $\theta ={{90}^{\circ }}$. Friction is negligible.

Answer
559.2k+ views
Hint:The net force on the system in horizontal direction is zero. Therefore, use the law of conservation of momentum. Then use the work energy theorem, where the work done by the gravity is equal to the change in the kinetic energy of the system.
Formula used:
$W=mgh$
where W is the work done by gravity on a mass m when it comes down from height h. g is acceleration due to gravity.
$K=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}$
where K is the kinetic energy of mass m travelling with speed v.
$P=mv$
where P is momentum.
Complete step by step answer:
The net force acting on the given system is the gravitational force ${{F}_{g}}={{m}_{A}}g$ (acting on the bob of the pendulum). Due to the gravitational force, the bob will come down and the trolley will move in front.From the work-energy theorem we know that the total work done on a system is equal to the change in its kinetic energy. i.e. $W=\Delta K$.
Here, the work done on the system is,
$W={{m}_{A}}gl$ …. (i), when $\theta ={{90}^{\circ }}$.
Let the kinetic energy of the bob and the trolley be, ${{K}_{A}}=\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{A}}v_{A}^{2}$ and ${{K}_{B}}=\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{B}}v_{B}^{2}$.
Since the system was at rest initially, $\Delta K={{K}_{A}}+{{K}_{B}}$.
$\Delta K=\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{A}}v_{A}^{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{B}}v_{B}^{2}$ ….. (ii).
Now, equate (i) and (ii).
$ {{m}_{A}}gl=\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{A}}v_{A}^{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{B}}v_{B}^{2}$ …. (iii).
The net force on the system in the horizontal direction is zero. This means that the momentum of the system in the horizontal direction is constant. Initially momentum of the system is zero. And when $\theta ={{90}^{\circ }}$, the trolley and the bob are moving in opposite directions.Therefore, we can say that ${{m}_{A}}{{v}_{A}}={{m}_{B}}{{v}_{B}}$.
${{v}_{A}}=\dfrac{{{m}_{B}}{{v}_{B}}}{{{m}_{A}}}$
Substitute this value in (iii).
$\Rightarrow {{m}_{A}}gl=\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{A}}{{\left( \dfrac{{{m}_{B}}{{v}_{B}}}{{{m}_{A}}} \right)}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{B}}v_{B}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow {{m}_{A}}gl=\dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{m_{B}^{2}v_{B}^{2}}{{{m}_{A}}}+\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{B}}v_{B}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow 2m_{A}^{2}gl=m_{B}^{2}v_{B}^{2}+{{m}_{A}}{{m}_{B}}v_{B}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow v_{B}^{2}=\dfrac{2m_{A}^{2}gl}{m_{B}^{2}+{{m}_{A}}{{m}_{B}}}$
$\therefore {{v}_{B}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{2m_{A}^{2}gl}{m_{B}^{2}+{{m}_{A}}{{m}_{B}}}}$
Note:You may be wondering if the gravitational force is acting on the bob and as a result it is accelerating. However, the gravitational force on the trolley is balanced by the normal reaction. Then how it is being accelerated. It is due to the third law of motion, which says that every action has an equal and opposite reaction.As the bob comes down, it exerts a force on the trolley and in return the trolley exerts a force on the bob of equal magnitude but opposite in direction.The work done by the reaction forces add up to zero.
Formula used:
$W=mgh$
where W is the work done by gravity on a mass m when it comes down from height h. g is acceleration due to gravity.
$K=\dfrac{1}{2}m{{v}^{2}}$
where K is the kinetic energy of mass m travelling with speed v.
$P=mv$
where P is momentum.
Complete step by step answer:
The net force acting on the given system is the gravitational force ${{F}_{g}}={{m}_{A}}g$ (acting on the bob of the pendulum). Due to the gravitational force, the bob will come down and the trolley will move in front.From the work-energy theorem we know that the total work done on a system is equal to the change in its kinetic energy. i.e. $W=\Delta K$.
Here, the work done on the system is,
$W={{m}_{A}}gl$ …. (i), when $\theta ={{90}^{\circ }}$.
Let the kinetic energy of the bob and the trolley be, ${{K}_{A}}=\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{A}}v_{A}^{2}$ and ${{K}_{B}}=\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{B}}v_{B}^{2}$.
Since the system was at rest initially, $\Delta K={{K}_{A}}+{{K}_{B}}$.
$\Delta K=\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{A}}v_{A}^{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{B}}v_{B}^{2}$ ….. (ii).
Now, equate (i) and (ii).
$ {{m}_{A}}gl=\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{A}}v_{A}^{2}+\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{B}}v_{B}^{2}$ …. (iii).
The net force on the system in the horizontal direction is zero. This means that the momentum of the system in the horizontal direction is constant. Initially momentum of the system is zero. And when $\theta ={{90}^{\circ }}$, the trolley and the bob are moving in opposite directions.Therefore, we can say that ${{m}_{A}}{{v}_{A}}={{m}_{B}}{{v}_{B}}$.
${{v}_{A}}=\dfrac{{{m}_{B}}{{v}_{B}}}{{{m}_{A}}}$
Substitute this value in (iii).
$\Rightarrow {{m}_{A}}gl=\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{A}}{{\left( \dfrac{{{m}_{B}}{{v}_{B}}}{{{m}_{A}}} \right)}^{2}}+\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{B}}v_{B}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow {{m}_{A}}gl=\dfrac{1}{2}\dfrac{m_{B}^{2}v_{B}^{2}}{{{m}_{A}}}+\dfrac{1}{2}{{m}_{B}}v_{B}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow 2m_{A}^{2}gl=m_{B}^{2}v_{B}^{2}+{{m}_{A}}{{m}_{B}}v_{B}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow v_{B}^{2}=\dfrac{2m_{A}^{2}gl}{m_{B}^{2}+{{m}_{A}}{{m}_{B}}}$
$\therefore {{v}_{B}}=\sqrt{\dfrac{2m_{A}^{2}gl}{m_{B}^{2}+{{m}_{A}}{{m}_{B}}}}$
Note:You may be wondering if the gravitational force is acting on the bob and as a result it is accelerating. However, the gravitational force on the trolley is balanced by the normal reaction. Then how it is being accelerated. It is due to the third law of motion, which says that every action has an equal and opposite reaction.As the bob comes down, it exerts a force on the trolley and in return the trolley exerts a force on the bob of equal magnitude but opposite in direction.The work done by the reaction forces add up to zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




