
The sides of an acute triangle measure $14\;cm$ , $18\;cm$ , and $20\;cm$ , respectively. Which of the following equations, when solved for $\theta $ , gives the measure of the smallest angle of the triangle? (Note: For any triangle with sides of length $a,b{\text{ and c}}$ that are opposite angles $A,B{\text{ and C}}$ , respectively , $\dfrac{{\sin A}}{A} = \dfrac{{\sin B}}{B} = \dfrac{{\sin C}}{C}$ and ${c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab{\text{ }}\operatorname{Cos} {\text{ C}}$ ) .
A. $\dfrac{{sin\theta }}{{14}} = \dfrac{1}{{18}}$
B. $\dfrac{{sin\theta }}{{14}} = \dfrac{1}{{20}}$
C. $\dfrac{{sin\theta }}{{20}} = \dfrac{1}{{14}}$
D. ${14^2} = {18^2} + {20^2} - 2(18)(20)\cos \theta $
E. ${20^2} = {18^2} + {14^2} - 2(18)(14)\cos \theta $
Answer
511.2k+ views
Hint:As given in question for any triangle with sides $A,B{\text{ and C}}$ , we have the $\dfrac{{\sin A}}{A} = \dfrac{{\sin B}}{B} = \dfrac{{\sin C}}{C}$ from the law of sines . From the laws of cosines we have ${c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\operatorname{Cos} {\text{ C}}$.
Complete step by step answer:
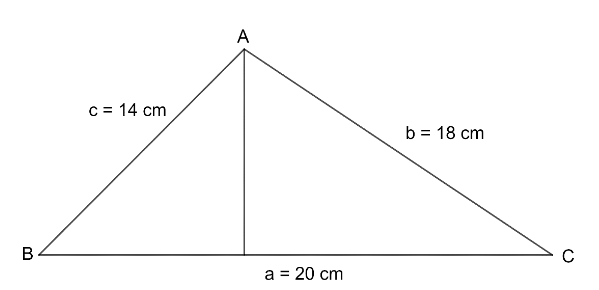
Given : - Side ${\text{A = 20 cm}}$ , Side ${\text{B = 18 cm}}$ , Side ${\text{C = 14 cm}}$
For a triangle can write the cosines as
$\operatorname{Cos} {\text{ A}} = \dfrac{{{b^2} + {c^2} - {a^2}}}{{2bc}}$
$\Rightarrow \operatorname{Cos} {\text{ B}} = \dfrac{{{c^2} + {a^2} - {b^2}}}{{2ac}}$
And $\operatorname{Cos} {\text{ C}} = \dfrac{{{a^2} + {b^2} - {c^2}}}{{2ab}}$
Since , the triangle given in the question has the smallest side of $14\;cm$ which means the angle opposite to this side will be smallest (which we have learnt in earlier classes ) .
So , here in the figure we have $c$ as the smallest side opposite to angle ${\text{C}}$.
Here the angle ${\text{C}}$ is assumed to be $\theta $ as it is asked in the question .
By using LAWS OF COSINES , we have ,
$\operatorname{Cos} {\text{ C}} = \dfrac{{{a^2} + {b^2} - {c^2}}}{{2ab}}$
Substituting the values of $a,b{\text{ and c}}$ , we get
$\operatorname{Cos} {\text{ }}\theta = \dfrac{{{{20}^2} + {{18}^2} - {{14}^2}}}{{2 \times 20 \times 18}}$
On solving further , we get
${14^2} = {18^2} + {20^2} - 2(18)(20)\cos \theta $
This is the required answer.
Therefore, option D is the correct answer.
Note:The acute angled triangle is a triangle in which all three measures less than ${90^ \circ }$, If any angle measures ${90^ \circ }$ or more degrees, we no longer have an acute triangle. The Law of Cosines is used to find the remaining parts of an oblique (non-right) triangle when either the lengths of two sides and the measure of the included angle is known (SAS) or the lengths of the three sides (SSS) are known .
Complete step by step answer:

Given : - Side ${\text{A = 20 cm}}$ , Side ${\text{B = 18 cm}}$ , Side ${\text{C = 14 cm}}$
For a triangle can write the cosines as
$\operatorname{Cos} {\text{ A}} = \dfrac{{{b^2} + {c^2} - {a^2}}}{{2bc}}$
$\Rightarrow \operatorname{Cos} {\text{ B}} = \dfrac{{{c^2} + {a^2} - {b^2}}}{{2ac}}$
And $\operatorname{Cos} {\text{ C}} = \dfrac{{{a^2} + {b^2} - {c^2}}}{{2ab}}$
Since , the triangle given in the question has the smallest side of $14\;cm$ which means the angle opposite to this side will be smallest (which we have learnt in earlier classes ) .
So , here in the figure we have $c$ as the smallest side opposite to angle ${\text{C}}$.
Here the angle ${\text{C}}$ is assumed to be $\theta $ as it is asked in the question .
By using LAWS OF COSINES , we have ,
$\operatorname{Cos} {\text{ C}} = \dfrac{{{a^2} + {b^2} - {c^2}}}{{2ab}}$
Substituting the values of $a,b{\text{ and c}}$ , we get
$\operatorname{Cos} {\text{ }}\theta = \dfrac{{{{20}^2} + {{18}^2} - {{14}^2}}}{{2 \times 20 \times 18}}$
On solving further , we get
${14^2} = {18^2} + {20^2} - 2(18)(20)\cos \theta $
This is the required answer.
Therefore, option D is the correct answer.
Note:The acute angled triangle is a triangle in which all three measures less than ${90^ \circ }$, If any angle measures ${90^ \circ }$ or more degrees, we no longer have an acute triangle. The Law of Cosines is used to find the remaining parts of an oblique (non-right) triangle when either the lengths of two sides and the measure of the included angle is known (SAS) or the lengths of the three sides (SSS) are known .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




