
The sides of a right triangle are in A.P. and the area of the triangle is 24cm. Find the sides of the triangle?
Answer
576k+ views
Hint: In the above question right triangle is mentioned which has the property of Pythagoras theorem:
$A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$ (Square of hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.)
Arithmetic progression mentioned in the question has the form:
$2b = a + c$ (a, b, c are the terms of the A.P.)
Above mentioned theorem and AP formula will be used to solve the problem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Arithmetic progression: Arithmetic Progression is a sequence of numbers such that the difference of any two successive numbers is a constant.
Let 1, 2, 3, 4,5 ......is a sequence with a common difference of one.
Pythagoras Theorem states that: In a right triangle square of the longest side is equal to the sum of the square of the other two sides.
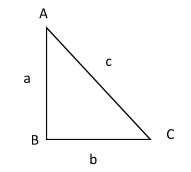
$A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$(mathematical expression for Pythagoras theorem)
Now comes to the calculation part:
Let sides of the triangle be a, b and c.
As the sides are in AP then;
$2b = a + c$
We can also write as:
$ \Rightarrow c = 2b - a$.............1
Substitute the value of c in the expression of Pythagoras theorem.
$
\Rightarrow {c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} \\
\Rightarrow {(2b - a)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2}
$ (Value of c is substituted)
$
\Rightarrow 4{b^2} + {a^2} - 4ab = {a^2} + {b^2} \\
\Rightarrow 3{b^2} = 4ab
$
Area of the triangle is 24cm2:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}a \times b = 24$ (From this we will find ab)
$ \Rightarrow ab = 48$ ................2
Substituting the value of ab in expression $3{b^2} = 4ab$:
$
\Rightarrow 3{b^2} = 4 \times 48 \\
\Rightarrow {b^2} = 4 \times 16 \\
\Rightarrow b = 8
$ (Value of side b is calculated as 8)
Side a and c is:
From expression 2 we have:
$
\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{48}}{b} \\
\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{48}}{8} = 6
$ (a=6)
From expression 1:
$
\Rightarrow c = 2b - a \\
\Rightarrow c = 2 \times 8 - 6 \\
\Rightarrow c = 10
$ (c=10)
Sides of the triangle are:6, 8 and 10.
Note: To find the $n^{th}$ term of the arithmetic progression we have the expression:
${a_n} = a + (n - 1)d$
Where a is the first term of the AP, n is the nth term of the sequence and d is the common difference.
$A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$ (Square of hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.)
Arithmetic progression mentioned in the question has the form:
$2b = a + c$ (a, b, c are the terms of the A.P.)
Above mentioned theorem and AP formula will be used to solve the problem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Arithmetic progression: Arithmetic Progression is a sequence of numbers such that the difference of any two successive numbers is a constant.
Let 1, 2, 3, 4,5 ......is a sequence with a common difference of one.
Pythagoras Theorem states that: In a right triangle square of the longest side is equal to the sum of the square of the other two sides.

$A{C^2} = A{B^2} + B{C^2}$(mathematical expression for Pythagoras theorem)
Now comes to the calculation part:
Let sides of the triangle be a, b and c.
As the sides are in AP then;
$2b = a + c$
We can also write as:
$ \Rightarrow c = 2b - a$.............1
Substitute the value of c in the expression of Pythagoras theorem.
$
\Rightarrow {c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} \\
\Rightarrow {(2b - a)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2}
$ (Value of c is substituted)
$
\Rightarrow 4{b^2} + {a^2} - 4ab = {a^2} + {b^2} \\
\Rightarrow 3{b^2} = 4ab
$
Area of the triangle is 24cm2:
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2}a \times b = 24$ (From this we will find ab)
$ \Rightarrow ab = 48$ ................2
Substituting the value of ab in expression $3{b^2} = 4ab$:
$
\Rightarrow 3{b^2} = 4 \times 48 \\
\Rightarrow {b^2} = 4 \times 16 \\
\Rightarrow b = 8
$ (Value of side b is calculated as 8)
Side a and c is:
From expression 2 we have:
$
\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{48}}{b} \\
\Rightarrow a = \dfrac{{48}}{8} = 6
$ (a=6)
From expression 1:
$
\Rightarrow c = 2b - a \\
\Rightarrow c = 2 \times 8 - 6 \\
\Rightarrow c = 10
$ (c=10)
Sides of the triangle are:6, 8 and 10.
Note: To find the $n^{th}$ term of the arithmetic progression we have the expression:
${a_n} = a + (n - 1)d$
Where a is the first term of the AP, n is the nth term of the sequence and d is the common difference.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




