
The sides of a right triangle are a,a+d and a+2d , with a and $$d$$ both positive. The ratio of a to $$d$$ is:
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: We need to apply Pythagoras theorem for solving this problem. Sides are given. We need to equate to solve this question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given are Sides of right angled triangle is and $$\left[ {a,d > 0} \right]$$
Let $$AB = a;BC = a + d;CA = a + 2d$$
△ is right angled at $$B$$
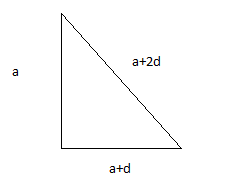
In△
$$A{B^2} + B{C^2} = A{C^2}$$ (Pythagoras theorem)
$$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow {a^2} + {(a + d)^2} = {(a + 2d)^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {a^2} = {(a + 2d)^2} - {(a + b)^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {a^2} = (a + 2d + a + d)(a + 2d - a - d)[{a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)] \cr
& \Rightarrow {a^2} = 2ad + 3{d^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {a^2} - 2ad = 3{d^2} \cr} $$
Adding $${d^2}$$ to both the sides
$$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow {a^2} - 2ad + {d^2} = 4{d^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {(a - d)^2} = 4{d^2}[{(a - b)^2} = {a^2} - 2ab + {b^2}] \cr} $$
Taking both sides
$$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow a - d = 2d;a - d = - 2d \cr
& \Rightarrow a =3 d;a = - d \cr} $$
$$a = - d$$ is not possible as $$a\& d$$are positive.
$$\eqalign{
& \therefore a = 3d \cr
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{a}{d} = 3 \cr} $$
Note: In a right angled triangle the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides is known as the Pythagoras theorem. As a and d is positive we have neglected negative value.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Given are Sides of right angled triangle is and $$\left[ {a,d > 0} \right]$$
Let $$AB = a;BC = a + d;CA = a + 2d$$
△ is right angled at $$B$$

In△
$$A{B^2} + B{C^2} = A{C^2}$$ (Pythagoras theorem)
$$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow {a^2} + {(a + d)^2} = {(a + 2d)^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {a^2} = {(a + 2d)^2} - {(a + b)^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {a^2} = (a + 2d + a + d)(a + 2d - a - d)[{a^2} - {b^2} = (a + b)(a - b)] \cr
& \Rightarrow {a^2} = 2ad + 3{d^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {a^2} - 2ad = 3{d^2} \cr} $$
Adding $${d^2}$$ to both the sides
$$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow {a^2} - 2ad + {d^2} = 4{d^2} \cr
& \Rightarrow {(a - d)^2} = 4{d^2}[{(a - b)^2} = {a^2} - 2ab + {b^2}] \cr} $$
Taking both sides
$$\eqalign{
& \Rightarrow a - d = 2d;a - d = - 2d \cr
& \Rightarrow a =3 d;a = - d \cr} $$
$$a = - d$$ is not possible as $$a\& d$$are positive.
$$\eqalign{
& \therefore a = 3d \cr
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{a}{d} = 3 \cr} $$
Note: In a right angled triangle the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides is known as the Pythagoras theorem. As a and d is positive we have neglected negative value.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

Citizens of India can vote at the age of A 18 years class 8 social science CBSE

Full form of STD, ISD and PCO

Advantages and disadvantages of science

Right to vote is a AFundamental Right BFundamental class 8 social science CBSE

What are the 12 elements of nature class 8 chemistry CBSE





