
The shape of the nucleus of WBC is usually
A) Spherical
B) Irregular
C) Oval
D) Spindle-shaped
Answer
481.8k+ views
Hint: The full form of WBC is White Blood Cells, which are also known as Leukocytes. They are mainly responsible for the defence of our body from pathogens, and there are many types of white blood cells working for different types of pathogens.
Complete answer:
The correct answer to this question is the shape of the nucleus of WBC is usually irregular. Let us see how. WBC or white blood cells are also more commonly known as leukocytes, they have the function of the defence mechanism in our body. They are defensive against pathogens, which are disease-causing organisms. There are many types of WBC or leukocytes, and their nuclei are shaped differently as shown in the figure below.
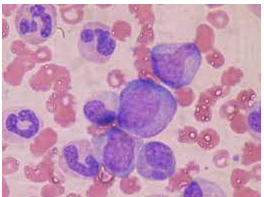
If we talk about acidophils, their nucleus is bi-lobes, meaning they are made up of two lobes. Their shape is somewhat oval. In the case of basophil, the nucleus has an ‘S’ shape and can contain two to three lobes. And in the case of neutrophils, the nucleus is made up of three to five lobes.
These WBC’s or leukocytes come under the category of granulocytes as their cytoplasm contains granules. On the contrary, there are agranulocytes that do not have distinct granules in their cytoplasm.
Agranulocytes include monocytes and lymphocytes. If we talk about monocytes, their nucleus are kidney bean shaped and if we look at the lymphocytes, their nucleus is large and spherical in shape.
Now, as we have seen that different types of WBC or leukocytes have differently shaped nuclei, we can say that usually, the shape of the nucleus of WBC or leukocytes is irregular.
Thus, the correct answer is option ‘B’.
Note: WBC are the very important immunological cells in our body that help us to fight against diseases and disease-causing foreign pathogens. They are produced in the bone marrow and are found in the blood and lymph. These cells are released in response to the decrease in immune power.
Complete answer:
The correct answer to this question is the shape of the nucleus of WBC is usually irregular. Let us see how. WBC or white blood cells are also more commonly known as leukocytes, they have the function of the defence mechanism in our body. They are defensive against pathogens, which are disease-causing organisms. There are many types of WBC or leukocytes, and their nuclei are shaped differently as shown in the figure below.

If we talk about acidophils, their nucleus is bi-lobes, meaning they are made up of two lobes. Their shape is somewhat oval. In the case of basophil, the nucleus has an ‘S’ shape and can contain two to three lobes. And in the case of neutrophils, the nucleus is made up of three to five lobes.
These WBC’s or leukocytes come under the category of granulocytes as their cytoplasm contains granules. On the contrary, there are agranulocytes that do not have distinct granules in their cytoplasm.
Agranulocytes include monocytes and lymphocytes. If we talk about monocytes, their nucleus are kidney bean shaped and if we look at the lymphocytes, their nucleus is large and spherical in shape.
Now, as we have seen that different types of WBC or leukocytes have differently shaped nuclei, we can say that usually, the shape of the nucleus of WBC or leukocytes is irregular.
Thus, the correct answer is option ‘B’.
Note: WBC are the very important immunological cells in our body that help us to fight against diseases and disease-causing foreign pathogens. They are produced in the bone marrow and are found in the blood and lymph. These cells are released in response to the decrease in immune power.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




