
The shape of $SC{l_4}$ is best described as a:
a) Square
b) Tetrahedron
c) Square pyramidal
d) See saw
Answer
559.8k+ views
Hint:The knowledge of $VSEPR$ theory is very important to answer these questions. Also the formula to calculate the steric number is also necessary here. We have to mention the lone pair and bond pair of$SC{l_4}$.
Complete step by step answer
$VSEPR$ Theory was developed by Gillespie in 1957. It helps to predict and explain the molecular shapes of bond angles of molecules more appropriately.
The formula to calculate the steric number of a compound is-
$SN = \dfrac{1}{2}[V + M - C + A]$ Where $V$the number of valence electrons on central atom is,$M$ is the number of monovalent side atom, $C$is the cationic charge and $A$ is the anionic charge on the given compound. It is used to calculate the hybridisation of a compound by knowing the bond pairs and lone pairs.
Hybridisation is the process of mixing of atomic orbitals to form new orbitals, with different shapes and bond angles.
We have been given with the compound $SC{l_4}$ .
In this compound the central atom is sulphur with six valence electrons as it belongs to the oxygen family and the compound has four monoatomic side atoms.
$\therefore V = 6;M = 4;C = 0;A = 0$
On substituting the values in the formula of steric number we get,
$
SN = \dfrac{1}{2}[6 + 4 - 0 + 0] \\
\Rightarrow SN = \dfrac{1}{2}[10] \\
\Rightarrow SN = 5(4b.p + 1l.p) \\
$
Therefore $SC{l_4}$ has $4$ bond pairs and $1$ lone pair.
The hybridisation of $SC{l_4}$ will be $s{p^3}d$ and the shape of the compound becomes like see saw.
The following diagram will be the correct representation:
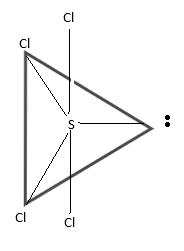
Hence,The correct option is (D).
Note: Steric numbers equal to $5$ with one lone pair have see-saw structure, with two lone pairs have T-shaped geometry and with three lone pairs have linear geometry. Hence the effect of lone pairs on the shape of molecules can be easily noted.
Complete step by step answer
$VSEPR$ Theory was developed by Gillespie in 1957. It helps to predict and explain the molecular shapes of bond angles of molecules more appropriately.
The formula to calculate the steric number of a compound is-
$SN = \dfrac{1}{2}[V + M - C + A]$ Where $V$the number of valence electrons on central atom is,$M$ is the number of monovalent side atom, $C$is the cationic charge and $A$ is the anionic charge on the given compound. It is used to calculate the hybridisation of a compound by knowing the bond pairs and lone pairs.
Hybridisation is the process of mixing of atomic orbitals to form new orbitals, with different shapes and bond angles.
We have been given with the compound $SC{l_4}$ .
In this compound the central atom is sulphur with six valence electrons as it belongs to the oxygen family and the compound has four monoatomic side atoms.
$\therefore V = 6;M = 4;C = 0;A = 0$
On substituting the values in the formula of steric number we get,
$
SN = \dfrac{1}{2}[6 + 4 - 0 + 0] \\
\Rightarrow SN = \dfrac{1}{2}[10] \\
\Rightarrow SN = 5(4b.p + 1l.p) \\
$
Therefore $SC{l_4}$ has $4$ bond pairs and $1$ lone pair.
The hybridisation of $SC{l_4}$ will be $s{p^3}d$ and the shape of the compound becomes like see saw.
The following diagram will be the correct representation:

Hence,The correct option is (D).
Note: Steric numbers equal to $5$ with one lone pair have see-saw structure, with two lone pairs have T-shaped geometry and with three lone pairs have linear geometry. Hence the effect of lone pairs on the shape of molecules can be easily noted.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




