
The shape of molecule which has 3 bond pairs and 1 lone pair of electrons is:
a.) Tetrahedral
b.) Octahedral
c.) Pyramidal
d.) Triangular planar
Answer
584.1k+ views
Hint: In order to solve the given problem and find the shape of the molecule; we will use the renowned VSEPR’s theory. We will first study in brief about the VSEPR’s theory along with its rules for different types of structures. Further we will study the particular case of 3 bond pairs and 1 lone pair with the help of an example relevant to this type. We will also see the figure of the molecule and will finally decide the correct shape out of the given options.
Complete step by step answer:
The model used in chemistry to determine the geometry of individual molecules from the number of electron pairs circling their core atoms is the Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory, or VSEPR theory. The Gillespie-Nyholm theory is also named after its two principal creators, Ronald Gillespie and Ronald Nyholm. It is based on the fact that there is a repulsion of both atoms between the pairs of valence electrons, and the atoms will therefore appear to organise themselves in a manner that minimises the repulsion of this electron pair. The geometry of the resulting molecule is determined by this arrangement of the atom.
There are a set of rules and postulates for different structures according to this theory. This theory also predicts the shape for different sample structures.
According to this VSEPR’s theory the molecule having 3 bond pairs and 1 lone pair will have a triangular pyramidal structure where the three bonds are present as the base of the pyramid and lone pair at the top. According to the VSEPR’s theory these types of molecules have $s{p_3}$ hybridization. And so the structure is such.
The simple example of such a molecule is \[P{H_3},N{H_3}\] .
The diagram of such figure is as follows:
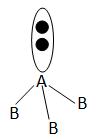
In these types of cases the repulsion between the lone pair and the bond pair is larger than the bond pair bond pair repulsion. So the structure is a bit distorted.
Hence, the shape of a molecule which has 3 bond pairs and 1 lone pair of electrons is pyramidal.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: In order to solve such types of problems students must remember some common and important postulates of the VSEPR’s theory. Students must know how to calculate the hybridization state of the molecule on the basis of the number of lone pairs and bond pairs. Students must remember the shapes for some common hybridization state.
Complete step by step answer:
The model used in chemistry to determine the geometry of individual molecules from the number of electron pairs circling their core atoms is the Valence shell electron pair repulsion theory, or VSEPR theory. The Gillespie-Nyholm theory is also named after its two principal creators, Ronald Gillespie and Ronald Nyholm. It is based on the fact that there is a repulsion of both atoms between the pairs of valence electrons, and the atoms will therefore appear to organise themselves in a manner that minimises the repulsion of this electron pair. The geometry of the resulting molecule is determined by this arrangement of the atom.
There are a set of rules and postulates for different structures according to this theory. This theory also predicts the shape for different sample structures.
According to this VSEPR’s theory the molecule having 3 bond pairs and 1 lone pair will have a triangular pyramidal structure where the three bonds are present as the base of the pyramid and lone pair at the top. According to the VSEPR’s theory these types of molecules have $s{p_3}$ hybridization. And so the structure is such.
The simple example of such a molecule is \[P{H_3},N{H_3}\] .
The diagram of such figure is as follows:

In these types of cases the repulsion between the lone pair and the bond pair is larger than the bond pair bond pair repulsion. So the structure is a bit distorted.
Hence, the shape of a molecule which has 3 bond pairs and 1 lone pair of electrons is pyramidal.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: In order to solve such types of problems students must remember some common and important postulates of the VSEPR’s theory. Students must know how to calculate the hybridization state of the molecule on the basis of the number of lone pairs and bond pairs. Students must remember the shapes for some common hybridization state.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




