
The shape of $C{{H}_{4}}$, $SO_{4}^{2-}$, $PO_{4}^{3-}$ is-
a) Trigonal
b) Angular
c) Tetrahedral
d) Trigonal bipyramidal
Answer
493.5k+ views
Hint: We can know the shape of these molecules with the help of hybridization. Hybridization is the intermixing of orbitals to form new orbitals of equivalent energy and by using the formula as $H=\dfrac{1}{2}(v+m-c+a)$, we can find the hybridization and know the shapes of these molecules. Now solve it.
Complete answer:
First of all, let’s discuss what hybridization is. By the term hybridization, we simply mean the intermixing of the orbitals of slightly different energies so as to redistribute their energies and to give a new set of orbitals of equivalent energies and shape. It is denoted by H.
It is not necessary in hybridization that only half-filled orbitals participate in it . In certain cases, even the filled orbitals of the valence shell participate in hybridization.
We can calculate the hybrids ion by using the formula as;-
$H=\dfrac{1}{2}(v+m-c+a)$
Here, V is the electrons in the valence shell, m stands for monovalent, c is the cation and a is the anion.
Now considering the statement as;-
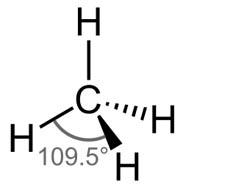
a) $C{{H}_{4}}$
$\begin{align}
& H=\dfrac{1}{2}(4+4) \\
& \text{ =}\dfrac{8}{2} \\
& \text{ =4} \\
\end{align}$
So, its geometry i.e. shape is tetrahedral.
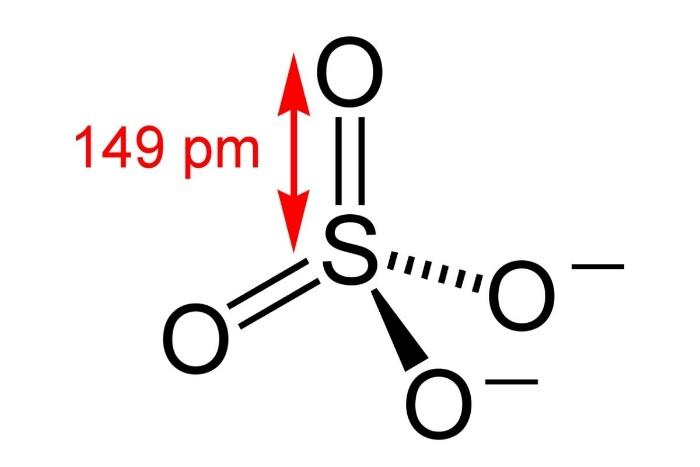
b) $SO_{4}^{2-}$
$\begin{align}
& H=\dfrac{1}{2}(6+2) \\
& \text{ =}\dfrac{8}{2} \\
& \text{ =4} \\
\end{align}$
So, its geometry i.e. shape is tetrahedral.
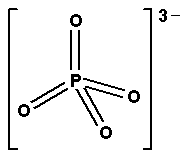
c) $PO_{4}^{3-}$
$\begin{align}
& H=\dfrac{1}{2}(5+3) \\
& \text{ =}\dfrac{8}{2} \\
& \text{ =4} \\
\end{align}$
So, its geometry i.e. shape is tetrahedral.
Thus, The shape of $C{{H}_{4}}$, $SO_{4}^{2-}$,$PO_{4}^{3-}$is tetrahedral.
So, the correct answer is “Option c”.
Note:
In hybridization, the number of hybrid orbitals formed is equal to the number of orbitals that get hybridized. The hybrid orbitals are always equivalent in energy and shape and are more effective in forming stable bonds than the pure atomic orbitals.
Complete answer:
First of all, let’s discuss what hybridization is. By the term hybridization, we simply mean the intermixing of the orbitals of slightly different energies so as to redistribute their energies and to give a new set of orbitals of equivalent energies and shape. It is denoted by H.
It is not necessary in hybridization that only half-filled orbitals participate in it . In certain cases, even the filled orbitals of the valence shell participate in hybridization.
We can calculate the hybrids ion by using the formula as;-
$H=\dfrac{1}{2}(v+m-c+a)$
Here, V is the electrons in the valence shell, m stands for monovalent, c is the cation and a is the anion.
Now considering the statement as;-
a) $C{{H}_{4}}$
$\begin{align}
& H=\dfrac{1}{2}(4+4) \\
& \text{ =}\dfrac{8}{2} \\
& \text{ =4} \\
\end{align}$
So, its geometry i.e. shape is tetrahedral.

b) $SO_{4}^{2-}$
$\begin{align}
& H=\dfrac{1}{2}(6+2) \\
& \text{ =}\dfrac{8}{2} \\
& \text{ =4} \\
\end{align}$
So, its geometry i.e. shape is tetrahedral.

c) $PO_{4}^{3-}$
$\begin{align}
& H=\dfrac{1}{2}(5+3) \\
& \text{ =}\dfrac{8}{2} \\
& \text{ =4} \\
\end{align}$
So, its geometry i.e. shape is tetrahedral.

Thus, The shape of $C{{H}_{4}}$, $SO_{4}^{2-}$,$PO_{4}^{3-}$is tetrahedral.
So, the correct answer is “Option c”.
Note:
In hybridization, the number of hybrid orbitals formed is equal to the number of orbitals that get hybridized. The hybrid orbitals are always equivalent in energy and shape and are more effective in forming stable bonds than the pure atomic orbitals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




