
The shadow of a tower is found to be $ 60m $ shorter when the Sun’s altitude changes from $ {30^ \circ } $ to $ {60^ \circ } $ . The height of the tower from the ground is approximately:
(A) $ 62m $
(B) $ 301m $
(C) $ 101m $
(D) $ 75m $
(E) $ 52m $
Answer
504.6k+ views
Hint: The given question belongs to the height and distances concept of trigonometry domain. In the problem, we have to find the height of a tower given that the length of the shadow of the tower is $ 60m $ shorter when the Sun's altitude changes from $ {30^ \circ } $ to $ {60^ \circ } $ . We first draw a diagram for understanding the situation better and then use the concepts of trigonometry to find the height of the tower.
Complete step-by-step answer:
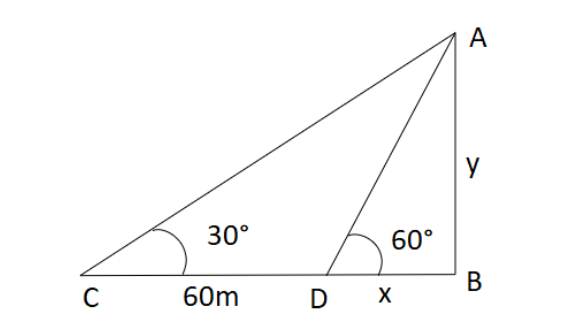
Let the tower be AB and length be y meters.
Now, we are given that the shadow of a tower is $ 60m $ shorter when the Sun’s altitude changes from $ {30^ \circ } $ to $ {60^ \circ } $ .
So, BC is the original shadow of the tower when the altitude of the sun is $ {30^ \circ } $ and BD is the shadow of the tower when the sun's altitude is $ {60^ \circ } $ .
So, we get the difference between the lengths of shadow as $ CD = 60m $ .
Let us assume that BD be of length x meters.
Now, using trigonometry in the triangle ADB,
$ \tan {60^ \circ } = \dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BD}} $
Substituting the values of AB and BD, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt 3 = \dfrac{y}{x} $
$ \Rightarrow y = \sqrt 3 x - - - - \left( 1 \right) $
Now, in triangle ABC, we have,
$ \tan {30^ \circ } = \dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}} $
Substituting the lengths of Ab and BC, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{y}{{x + 60}} $
Substituting the value of y from equation $ \left( 1 \right) $ in the above expression, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 x}}{{x + 60}} $
Cross multiplying the terms, we get,
$ \Rightarrow x + 60 = 3x $
Shifting the terms in the equation, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 2x = 60 $
Dividing both the sides of the equation by $ 2 $ , we get,
$ \Rightarrow x = 30 $
So, we get the value of x as $ 30 $ . Substituting the value of x in equation $ \left( 1 \right) $ , we get value of y as,
$ y = 30\sqrt 3 $
Hence, the height of the tower is $ 30\sqrt 3 $ meters.
Finding the approximate value, we get $ 30\sqrt 3 = 51.96 $ .
So, the approximate height of the tower is $ 52 $ meters.
Hence, option (E) is the correct answer.
So, the correct answer is “Option E”.
Note: We should have a strong grip over the concepts of trigonometry and height and distances in order to deal with such kinds of problems. We should have accuracy in calculations, derivatives and arithmetic in order to be sure of the final answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:

Let the tower be AB and length be y meters.
Now, we are given that the shadow of a tower is $ 60m $ shorter when the Sun’s altitude changes from $ {30^ \circ } $ to $ {60^ \circ } $ .
So, BC is the original shadow of the tower when the altitude of the sun is $ {30^ \circ } $ and BD is the shadow of the tower when the sun's altitude is $ {60^ \circ } $ .
So, we get the difference between the lengths of shadow as $ CD = 60m $ .
Let us assume that BD be of length x meters.
Now, using trigonometry in the triangle ADB,
$ \tan {60^ \circ } = \dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BD}} $
Substituting the values of AB and BD, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \sqrt 3 = \dfrac{y}{x} $
$ \Rightarrow y = \sqrt 3 x - - - - \left( 1 \right) $
Now, in triangle ABC, we have,
$ \tan {30^ \circ } = \dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}} = \dfrac{{AB}}{{BC}} $
Substituting the lengths of Ab and BC, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{y}{{x + 60}} $
Substituting the value of y from equation $ \left( 1 \right) $ in the above expression, we get,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 x}}{{x + 60}} $
Cross multiplying the terms, we get,
$ \Rightarrow x + 60 = 3x $
Shifting the terms in the equation, we get,
$ \Rightarrow 2x = 60 $
Dividing both the sides of the equation by $ 2 $ , we get,
$ \Rightarrow x = 30 $
So, we get the value of x as $ 30 $ . Substituting the value of x in equation $ \left( 1 \right) $ , we get value of y as,
$ y = 30\sqrt 3 $
Hence, the height of the tower is $ 30\sqrt 3 $ meters.
Finding the approximate value, we get $ 30\sqrt 3 = 51.96 $ .
So, the approximate height of the tower is $ 52 $ meters.
Hence, option (E) is the correct answer.
So, the correct answer is “Option E”.
Note: We should have a strong grip over the concepts of trigonometry and height and distances in order to deal with such kinds of problems. We should have accuracy in calculations, derivatives and arithmetic in order to be sure of the final answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




