
The set of values of m for which the cord of slope m of the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=16\] touches the parabola, \[{{y}^{2}}=8x\]
A.. \[\left( -\infty ,-1 \right)\cup \left( 1,\infty \right)\]
B.. \[\left( -\infty ,\infty \right)\]
C.. \[\left( -\infty ,-\sqrt{\dfrac{\sqrt{2}+1}{2}} \right)\cup \left( \sqrt{\dfrac{\sqrt{2}+1}{2}},\infty \right)\]
D.. \[\left( -1,1 \right)\]
Answer
582k+ views
Hint: In this question first of all we need to construct the graph of these two curves and then find out the points of intersection between them and after that we need to find the region of graph where the given conditions are satisfied in this case we need to find the region where there are chords drawn from circle just touches the parabola or we can say that chords of circle which are tangent to parabola. We need to find the region just by analyzing the graph and we will find that the region is from Y-axis to the points of intersection as chords are present only inside the circle. So now we will find the slope of tangents to parabola at extreme points and will come up with the range of values of m or slope of cords.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First of all we need to construct the graph of these two functions so that we are able to understand the whole process for solving the question and the ideology we want to work with.
Now one equation is of circle with its center lying at origin and the radius of circle is 4, the equation of circle is \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=16\] or in the general form is \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{4}^{2}}\].
The other equation is of a parabola which opens in the rightward direction in the Cartesian plane, the equation of the parabola is \[{{y}^{2}}=8x\].
The graph is as follows,
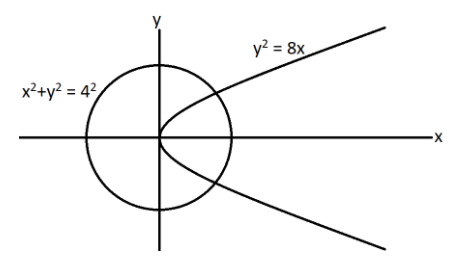
Now, it is given that the chord of slope m of the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=16\] touches the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=8x$ that means the chord will be a tangent to the given parabola.
Now we know that the equation of tangent to the parabola: ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ will be: $y=mx+\dfrac{a}{m}$ .
Now, we have with us the parabola: ${{y}^{2}}=8x$ now we will compare it with the standard equation of the parabola that is: ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ to find the value of $a$ , therefore:
${{y}^{2}}=8x\Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}=4.2.x\Rightarrow a=2$
Therefore the tangent equation will be: $y=mx+\dfrac{2}{m}$ .
Since, it is given that the tangent to the parabola is the chord of the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{4}^{2}}\]. , therefore the equation of the chord will also be: $y=mx+\dfrac{2}{m}$ , where m is the slope of the line.
Now, we know that for chords the perpendicular distance has to be less than the radius.
Now, we know that the formula for perpendicular distance from a point say $\left( a,b \right)$ to the line: $Ax+By+C=0$ is: $d=\dfrac{\left| Aa+Bb+C \right|}{\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}}}$
Now, as we saw above the perpendicular distance from the centre of the circle that is $\left( 0,0 \right)$ to the chord $y=mx+\dfrac{2}{m}$ will be: $d=\dfrac{\left| \dfrac{2}{m} \right|}{\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}$
Now, this distance should be less than the radius of the circle that is $4$
Therefore:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\left| \dfrac{2}{m} \right|}{\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}<4\Rightarrow \left| \dfrac{2}{m} \right|<4\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}$
We will now square both the sides:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \left| \dfrac{2}{m} \right|<4\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}\Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{{{m}^{2}}}<16\left( 1+{{m}^{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{m}^{2}}}<4\left( 1+{{m}^{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 4{{m}^{4}}+4{{m}^{2}}-1>0\text{ }........\text{equation 1} \\
\end{align}$
Now, we will substitute ${{m}^{2}}=t$ , in order to solve the given equation, therefore the equation will become:
$4{{t}^{2}}+4t-1>0$
Now, we will find the value of $t$ :
We know that for a quadratic equation $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$ , the value of \[x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}\]
Therefore,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow t=\dfrac{-4\pm \sqrt{{{4}^{2}}-4\left( 4 \right)\left( -1 \right)}}{2\left( 4 \right)}\Rightarrow t=\dfrac{-4\pm \sqrt{16+16}}{8} \\
& \Rightarrow t=\dfrac{-4\pm \sqrt{32}}{8} \\
& \Rightarrow t=\dfrac{-1\pm \sqrt{2}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow t=\dfrac{-1-\sqrt{2}}{2},\dfrac{-1+\sqrt{2}}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we will re-substitute: ${{m}^{2}}=t$
Therefore, \[{{m}^{2}}=\dfrac{-1-\sqrt{2}}{2},\dfrac{-1+\sqrt{2}}{2}\]
We will now take the roots for both the sides:
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow m=\pm \sqrt{\dfrac{-1-\sqrt{2}}{2}},\pm \sqrt{\dfrac{-1+\sqrt{2}}{2}}\Rightarrow m=\pm \sqrt{\left( -1 \right)\dfrac{1+\sqrt{2}}{2}},\pm \sqrt{\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow m=\pm i\sqrt{\dfrac{1+\sqrt{2}}{2}},\pm \sqrt{\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, equation 1 will be: $4{{m}^{4}}+4{{m}^{2}}-1>0$ will have two imaginary roots and two real roots.
Now, are slope has to be real therefore: we will consider the values of m as \[\pm \sqrt{\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2}}\]
Now, we need equation 1: $4{{m}^{4}}+4{{m}^{2}}-1>0\Rightarrow \left( m-\sqrt{\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2}} \right)\left( m+\sqrt{\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2}} \right)>0$
Hence, \[m\in \left( -\infty ,-\sqrt{\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2}} \right)\cup \left( \sqrt{\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2}},\infty \right)\]
Therefore, option C is correct.
Note: Do not forget to add the symbol of \[\pm \] before the square root because only then you will get the two slopes which are opposite in sign but are numerically same. There are infinite lines or tangents in between these two slopes so that is why we have to represent in the form of intervals. Always cross check the roots obtained by the equation such that it should satisfy all the equations and conditions in the question by just putting them in the equation and comparing the values of other variables, if they are the same the root is okay.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First of all we need to construct the graph of these two functions so that we are able to understand the whole process for solving the question and the ideology we want to work with.
Now one equation is of circle with its center lying at origin and the radius of circle is 4, the equation of circle is \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=16\] or in the general form is \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{4}^{2}}\].
The other equation is of a parabola which opens in the rightward direction in the Cartesian plane, the equation of the parabola is \[{{y}^{2}}=8x\].
The graph is as follows,

Now, it is given that the chord of slope m of the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}=16\] touches the parabola ${{y}^{2}}=8x$ that means the chord will be a tangent to the given parabola.
Now we know that the equation of tangent to the parabola: ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ will be: $y=mx+\dfrac{a}{m}$ .
Now, we have with us the parabola: ${{y}^{2}}=8x$ now we will compare it with the standard equation of the parabola that is: ${{y}^{2}}=4ax$ to find the value of $a$ , therefore:
${{y}^{2}}=8x\Rightarrow {{y}^{2}}=4.2.x\Rightarrow a=2$
Therefore the tangent equation will be: $y=mx+\dfrac{2}{m}$ .
Since, it is given that the tangent to the parabola is the chord of the circle \[{{x}^{2}}+{{y}^{2}}={{4}^{2}}\]. , therefore the equation of the chord will also be: $y=mx+\dfrac{2}{m}$ , where m is the slope of the line.
Now, we know that for chords the perpendicular distance has to be less than the radius.
Now, we know that the formula for perpendicular distance from a point say $\left( a,b \right)$ to the line: $Ax+By+C=0$ is: $d=\dfrac{\left| Aa+Bb+C \right|}{\sqrt{{{A}^{2}}+{{B}^{2}}}}$
Now, as we saw above the perpendicular distance from the centre of the circle that is $\left( 0,0 \right)$ to the chord $y=mx+\dfrac{2}{m}$ will be: $d=\dfrac{\left| \dfrac{2}{m} \right|}{\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}$
Now, this distance should be less than the radius of the circle that is $4$
Therefore:
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{\left| \dfrac{2}{m} \right|}{\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}}<4\Rightarrow \left| \dfrac{2}{m} \right|<4\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}$
We will now square both the sides:
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \left| \dfrac{2}{m} \right|<4\sqrt{1+{{m}^{2}}}\Rightarrow \dfrac{4}{{{m}^{2}}}<16\left( 1+{{m}^{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{{{m}^{2}}}<4\left( 1+{{m}^{2}} \right) \\
& \Rightarrow 4{{m}^{4}}+4{{m}^{2}}-1>0\text{ }........\text{equation 1} \\
\end{align}$
Now, we will substitute ${{m}^{2}}=t$ , in order to solve the given equation, therefore the equation will become:
$4{{t}^{2}}+4t-1>0$
Now, we will find the value of $t$ :
We know that for a quadratic equation $a{{x}^{2}}+bx+c=0$ , the value of \[x=\dfrac{-b\pm \sqrt{{{b}^{2}}-4ac}}{2a}\]
Therefore,
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow t=\dfrac{-4\pm \sqrt{{{4}^{2}}-4\left( 4 \right)\left( -1 \right)}}{2\left( 4 \right)}\Rightarrow t=\dfrac{-4\pm \sqrt{16+16}}{8} \\
& \Rightarrow t=\dfrac{-4\pm \sqrt{32}}{8} \\
& \Rightarrow t=\dfrac{-1\pm \sqrt{2}}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow t=\dfrac{-1-\sqrt{2}}{2},\dfrac{-1+\sqrt{2}}{2} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, we will re-substitute: ${{m}^{2}}=t$
Therefore, \[{{m}^{2}}=\dfrac{-1-\sqrt{2}}{2},\dfrac{-1+\sqrt{2}}{2}\]
We will now take the roots for both the sides:
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow m=\pm \sqrt{\dfrac{-1-\sqrt{2}}{2}},\pm \sqrt{\dfrac{-1+\sqrt{2}}{2}}\Rightarrow m=\pm \sqrt{\left( -1 \right)\dfrac{1+\sqrt{2}}{2}},\pm \sqrt{\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow m=\pm i\sqrt{\dfrac{1+\sqrt{2}}{2}},\pm \sqrt{\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2}} \\
\end{align}\]
Now, equation 1 will be: $4{{m}^{4}}+4{{m}^{2}}-1>0$ will have two imaginary roots and two real roots.
Now, are slope has to be real therefore: we will consider the values of m as \[\pm \sqrt{\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2}}\]
Now, we need equation 1: $4{{m}^{4}}+4{{m}^{2}}-1>0\Rightarrow \left( m-\sqrt{\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2}} \right)\left( m+\sqrt{\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2}} \right)>0$
Hence, \[m\in \left( -\infty ,-\sqrt{\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2}} \right)\cup \left( \sqrt{\dfrac{\sqrt{2}-1}{2}},\infty \right)\]
Therefore, option C is correct.
Note: Do not forget to add the symbol of \[\pm \] before the square root because only then you will get the two slopes which are opposite in sign but are numerically same. There are infinite lines or tangents in between these two slopes so that is why we have to represent in the form of intervals. Always cross check the roots obtained by the equation such that it should satisfy all the equations and conditions in the question by just putting them in the equation and comparing the values of other variables, if they are the same the root is okay.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




