
The set of quantum numbers \[n\text{ }=\text{ }4,\text{ }l\text{ }=\text{ }0,\text{ }m\text{ }=\text{ }0,\text{ }s\text{ }=\text{ }+\dfrac{1}{2}\text{ }\]corresponds to the most loosely bound ground state electron of which one of the following atoms?
A. \[Na\]
B. \[Cl\]
C. \[Cr\]
D. \[Rb\]
Answer
603.6k+ views
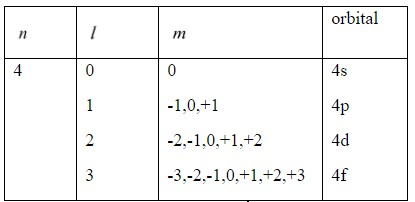
Hint: \[n\](principal quantum number)
\[l\](azimuthal quantum number) [\[l\]= (\[n-1\])]
\[m\](magnetic quantum number) (-\[l\],.., 0,..,+\[l\])
\[s\](spin quantum number)
By taking the given values and using these formulas, derive the electronic configuration and find out the atom.
The element is a transition metal.
Complete step by step answer:
As per given information, the atom has 4s orbital as the outer shell, so there are two electrons in the valence shell.
= 4, so the atom belongs to any element of the fourth period of the periodic table.
The element may be anyone from potassium to zinc. In short, any element from atomic number 19 to 30 will be the correct answer.
Chromium (\[Cr\]) is the element with the given set of quantum numbers in the question.
Electronic configuration is \[[Ar]3{{d}^{5}}4{{s}^{1}}\]. The valence shell has one electron, the element belongs to the fourth period with\[\text{ }l\text{ }=\text{ }0,\text{ }m\text{ }=\text{ }0\].
So, the correct option is C.
Note: \[n\](principal quantum number) determines the energy and size of an atom. The number indicates the period in which the element belongs to in the periodic table.
\[l\](azimuthal quantum number) determines the shape and angular dependence of an atom.
\[m\](magnetic quantum number) determines the orientation of the atom in space. It also determines the number of electrons possible to be present in the valence shell.
\[s\](spin quantum number) determines the electron spin (magnetic moment) of the atom.
\[l\](azimuthal quantum number) [\[l\]= (\[n-1\])]
\[m\](magnetic quantum number) (-\[l\],.., 0,..,+\[l\])
\[s\](spin quantum number)
By taking the given values and using these formulas, derive the electronic configuration and find out the atom.
The element is a transition metal.

Complete step by step answer:
As per given information, the atom has 4s orbital as the outer shell, so there are two electrons in the valence shell.
= 4, so the atom belongs to any element of the fourth period of the periodic table.
The element may be anyone from potassium to zinc. In short, any element from atomic number 19 to 30 will be the correct answer.
Chromium (\[Cr\]) is the element with the given set of quantum numbers in the question.
Electronic configuration is \[[Ar]3{{d}^{5}}4{{s}^{1}}\]. The valence shell has one electron, the element belongs to the fourth period with\[\text{ }l\text{ }=\text{ }0,\text{ }m\text{ }=\text{ }0\].
So, the correct option is C.
Note: \[n\](principal quantum number) determines the energy and size of an atom. The number indicates the period in which the element belongs to in the periodic table.
\[l\](azimuthal quantum number) determines the shape and angular dependence of an atom.
\[m\](magnetic quantum number) determines the orientation of the atom in space. It also determines the number of electrons possible to be present in the valence shell.
\[s\](spin quantum number) determines the electron spin (magnetic moment) of the atom.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




