
The semi-vertical angle of a cone is \[{45^\circ}\]. If the height of the cone is 20.025, then its approximate lateral surface area is
A. \[401\sqrt 2 \pi \]
B. \[400\sqrt 2 \pi \]
C. \[399\sqrt 2 \pi \]
D. None of these
Answer
620.1k+ views
Hint: First of all, find the slant height of the cone and relation between radius and height of the cone by the given semi-vertical angle. Now, the approximate lateral surface area of the cone is given by \[S + \Delta S\] where \[S\] is the LSA of the cone. So, use this concept to reach the solution of the given problem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let \[r\] be the radius, \[h\] be the height and \[l\] be the slant height of a cone of semi-vertical angle \[{45^\circ}\].
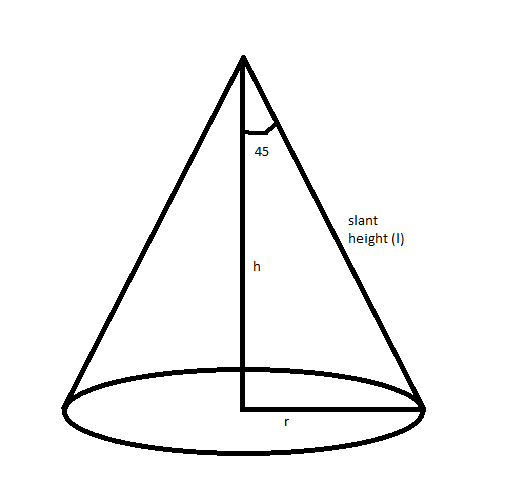
From the figure,
\[
\Rightarrow \tan {45^\circ} = \dfrac{r}{h} \\
\Rightarrow 1 = \dfrac{r}{h} \\
\therefore r = h \\
\]
We know that \[l = \sqrt {{r^2} + {h^2}} \].
So, slant height of the given cone is
\[
\Rightarrow l = \sqrt {{r^2} + {h^2}} \\
\Rightarrow l = \sqrt {{h^2} + {h^2}} = \sqrt {2{h^2}} {\text{ }}\left[ {\because r = h} \right] \\
\therefore l = \sqrt 2 h \\
\]
Let \[h = 20\] and \[h + \Delta h = 20.0025\]
So, \[\Delta h = 20.025 - 20 = 0.025\]
We know that the lateral surface area of the cone with radius \[r\] and slant height \[l\] is given by \[S = \pi rl\].
So, the lateral surface area of the given cone is
$\Rightarrow$ \[S = \pi h\sqrt 2 h = \sqrt 2 \pi {h^2}{\text{ }}\left[ {\because r = h{\text{ and }}l = \sqrt 2 h} \right]\]
The approximate lateral surface area of the cone is given by \[S + \Delta S\].
Now, consider \[\Delta S\]
\[
\Rightarrow \Delta S = {\left( {\dfrac{{ds}}{{dh}}} \right)_{h = 20}}\Delta h \\
\Rightarrow \Delta S = {\left[ {\dfrac{d}{{dh}}\left( {\sqrt 2 \pi {h^2}} \right)} \right]_{h = 20}}\Delta h \\
\Rightarrow \Delta S = {\left[ {2\sqrt 2 \pi h} \right]_{h = 20}}\Delta h \\
\Rightarrow \Delta S = \left[ {40\sqrt 2 \pi } \right] \times 0.025{\text{ }}\left[ {\because \Delta h = 0.025} \right] \\
\therefore \Delta S = \sqrt 2 \pi \\
\]
And
\[
\Rightarrow S = \sqrt 2 \pi {h^2} \\
\Rightarrow S = \sqrt 2 \pi {\left( {20} \right)^2}{\text{ }}\left[ {\because h = 20} \right] \\
\therefore S = 400\sqrt 2 \pi \\
\]
Hence the approximate value of lateral surface area of the cone is
\[S + \Delta S = 400\sqrt 2 \pi + \sqrt 2 \pi = 401\sqrt 2 \pi \]
Thus, the correct option is A. \[401\sqrt 2 \pi \]
Note: The semi-vertical angle of the cone is the angle between the height and slant height of the cone. The slant height of the cone of radius \[r\] and height \[h\] is given by \[l = \sqrt {{r^2} + {h^2}} \]. The lateral surface area of the cone with radius \[r\] and slant height \[l\] is given by \[S = \pi rl\].
Complete step-by-step answer:
Let \[r\] be the radius, \[h\] be the height and \[l\] be the slant height of a cone of semi-vertical angle \[{45^\circ}\].

From the figure,
\[
\Rightarrow \tan {45^\circ} = \dfrac{r}{h} \\
\Rightarrow 1 = \dfrac{r}{h} \\
\therefore r = h \\
\]
We know that \[l = \sqrt {{r^2} + {h^2}} \].
So, slant height of the given cone is
\[
\Rightarrow l = \sqrt {{r^2} + {h^2}} \\
\Rightarrow l = \sqrt {{h^2} + {h^2}} = \sqrt {2{h^2}} {\text{ }}\left[ {\because r = h} \right] \\
\therefore l = \sqrt 2 h \\
\]
Let \[h = 20\] and \[h + \Delta h = 20.0025\]
So, \[\Delta h = 20.025 - 20 = 0.025\]
We know that the lateral surface area of the cone with radius \[r\] and slant height \[l\] is given by \[S = \pi rl\].
So, the lateral surface area of the given cone is
$\Rightarrow$ \[S = \pi h\sqrt 2 h = \sqrt 2 \pi {h^2}{\text{ }}\left[ {\because r = h{\text{ and }}l = \sqrt 2 h} \right]\]
The approximate lateral surface area of the cone is given by \[S + \Delta S\].
Now, consider \[\Delta S\]
\[
\Rightarrow \Delta S = {\left( {\dfrac{{ds}}{{dh}}} \right)_{h = 20}}\Delta h \\
\Rightarrow \Delta S = {\left[ {\dfrac{d}{{dh}}\left( {\sqrt 2 \pi {h^2}} \right)} \right]_{h = 20}}\Delta h \\
\Rightarrow \Delta S = {\left[ {2\sqrt 2 \pi h} \right]_{h = 20}}\Delta h \\
\Rightarrow \Delta S = \left[ {40\sqrt 2 \pi } \right] \times 0.025{\text{ }}\left[ {\because \Delta h = 0.025} \right] \\
\therefore \Delta S = \sqrt 2 \pi \\
\]
And
\[
\Rightarrow S = \sqrt 2 \pi {h^2} \\
\Rightarrow S = \sqrt 2 \pi {\left( {20} \right)^2}{\text{ }}\left[ {\because h = 20} \right] \\
\therefore S = 400\sqrt 2 \pi \\
\]
Hence the approximate value of lateral surface area of the cone is
\[S + \Delta S = 400\sqrt 2 \pi + \sqrt 2 \pi = 401\sqrt 2 \pi \]
Thus, the correct option is A. \[401\sqrt 2 \pi \]
Note: The semi-vertical angle of the cone is the angle between the height and slant height of the cone. The slant height of the cone of radius \[r\] and height \[h\] is given by \[l = \sqrt {{r^2} + {h^2}} \]. The lateral surface area of the cone with radius \[r\] and slant height \[l\] is given by \[S = \pi rl\].
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 10 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
A boat goes 24 km upstream and 28 km downstream in class 10 maths CBSE

State and explain Ohms law class 10 physics CBSE

Write a letter to the editor of a newspaper explaining class 10 english CBSE

Distinguish between soap and detergent class 10 chemistry CBSE

a Why did Mendel choose pea plants for his experiments class 10 biology CBSE

What is a "free hit" awarded for in limited-overs cricket?




