
The section of a window consists of a rectangle surmounted by an equilateral triangle. If the perimeters be given as 16m, find the dimensions of the window in order that the maximum amount of light may be admitted.
A.2,5
B.3,3.5
C.3.75,2.375
D.4,2
Answer
594k+ views
Hint: First Assume the length of a triangle to be x and the length and width of the rectangle to be x and y respectively. We use the given data and for equations, by using the formulae of Area of an equilateral triangle$ = \dfrac{{\surd 3}}{4}{x^2}$ and Area of a rectangle\[\; = xy\], we combine both the equation to find the area of a given figure. After that, we use the second derivative test to find the maximum area of the given window.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given: Perimeter of the window is 16m
To find Dimensions of the window i.e. length and width.
Let ABCD be a rectangle and let CDE be an equilateral triangle described on the side CD of the rectangle.
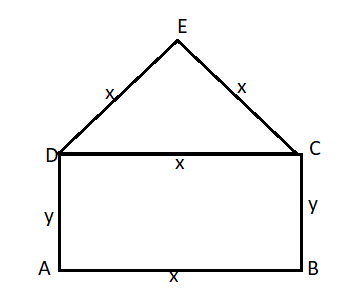
Let AB $ = $ x and BC $ = $ y
Perimeter of given window is 16m
\[ \Rightarrow \]$3{\text{x}} + 2{\text{y}} = 16$
\[ \Rightarrow \] ${\text{y}} = \dfrac{{16 - 3{\text{x}}}}{2}$ (A)
Let the area of a given figure is A.
∴ A Area of an equilateral triangle Area of a rectangle
\[ \Rightarrow \] A$ = \dfrac{{\surd 3}}{4}{{\text{x}}^2} + {\text{xy}}$ $\left( {{\text{area of equiletaral triangle}} = \dfrac{{\surd 3}}{4}{x^2}\& {\text{ }}area{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}rectangle = xy} \right)$
\[ \Rightarrow \] A$ = \dfrac{{\surd 3}}{4}{{\text{x}}^2} + {\text{x}}\left( {\dfrac{{16 - 3{\text{x}}}}{2}} \right)$ \[ \ldots \] $\left( 1 \right)$
Now, differentiating the above equation $\left( 1 \right)$ with respect to x
We get,
\[ \Rightarrow \]$\dfrac{{{\text{dA}}}}{{{\text{dx}}}} = \dfrac{{\text{d}}}{{{\text{dx}}}}\left( {\dfrac{{\surd 3}}{4}{{\text{x}}^2} + \left( {\dfrac{{16{\text{x}} - 3{{\text{x}}^2}}}{2}} \right)} \right)$
\[ \Rightarrow \]$\dfrac{{{\text{dA}}}}{{{\text{dx}}}} = \dfrac{{\surd 3}}{4}\left( {2{\text{x}}} \right) + \left( {\dfrac{{16 - 6{\text{x}}}}{2}} \right)$
\[ \Rightarrow \]$\dfrac{{{\text{dA}}}}{{{\text{dx}}}} = \dfrac{{\surd 3}}{2}\left( {\text{x}} \right) + 8 - 3{\text{x}}$ \[ \ldots \] (2) \[\]
For maximum or minimum we have,
$\dfrac{{dA}}{{dx}} = $0
On substituting the value of $\dfrac{{dA}}{{dx}}$from (2) we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \]$\dfrac{{\surd 3}}{2}\left( {\text{x}} \right) + 8 - 3{\text{x}} = $0
Taking the terms of x together and simplifying further we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \] $x\left( {3 - \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right) = 8$
\[ \Rightarrow \] $x\left( {\dfrac{{6 - \surd 3}}{2}} \right) = 8$
\[ \Rightarrow \] $x\left( {6 - \surd 3} \right) = 16$
\[ \Rightarrow \] $x = \dfrac{{16}}{{\left( {6 - \surd 3} \right)}}$
Again differentiating equation (2) with respect to x
We get,
$\dfrac{{{{\text{d}}^2}{\text{A}}}}{{{\text{d}}{x^2}}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} - 3$
Now as $\dfrac{{{{\text{d}}^2}{\text{A}}}}{{{\text{d}}{x^2}}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} - 3$<0 , Hence the area is maximum when ${\text{x}} = \dfrac{{16}}{{6 - \surd 3}}$
Now we substitute the value of x in equation (A), we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \]${\text{y}} = \dfrac{{16 - 3\left( {\dfrac{{16}}{{6 - \surd 3}}} \right)}}{2}$
On further simplification we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \]$y = \dfrac{{16 - \dfrac{{48}}{{6 - \surd 3}}}}{2}$
\[ \Rightarrow \]${\text{y}} = \dfrac{{16\left( {6 - \surd 3} \right) - 48}}{{2\left( {6 - \surd 3} \right)}}$
\[ \Rightarrow \]${\text{y}} = \dfrac{{96 - 16\surd 3 - 48}}{{2\left( {6 - \surd 3} \right)}}$
\[ \Rightarrow \]${\text{y}} = \dfrac{{48 - 16\surd 3}}{{2\left( {6 - \surd 3} \right)}}$
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[{\text{y}} = \dfrac{{24 - 8\surd 3}}{{\left( {6 - \surd 3} \right)}}\]
Hence, the breadth of a window $x = \dfrac{{16}}{{\left( {6 - \surd 3} \right)}} \approx 3.75$ and length of a window is ${\text{y}} = \dfrac{{24 - 8\surd 3}}{{\left( {6 - \surd 3} \right)}} \approx 2.375$
Hence, Option C. 3.75, 2.375 is a correct answer.
Note: Equilateral triangle: - An equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides are equal. It is also known as Equiangular in Euclidean geometry that all the three angles are also congruent to each other and are each\[60^\circ \].
The second derivative test is used to determine the local extrema of a function under certain conditions. If a function has a critical point for which $f'(x) = 0$and the second derivative at this point is negative, then f has a local maximum here, whereas if the second derivative is positive then f has a local minimum here.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given: Perimeter of the window is 16m
To find Dimensions of the window i.e. length and width.
Let ABCD be a rectangle and let CDE be an equilateral triangle described on the side CD of the rectangle.

Let AB $ = $ x and BC $ = $ y
Perimeter of given window is 16m
\[ \Rightarrow \]$3{\text{x}} + 2{\text{y}} = 16$
\[ \Rightarrow \] ${\text{y}} = \dfrac{{16 - 3{\text{x}}}}{2}$ (A)
Let the area of a given figure is A.
∴ A Area of an equilateral triangle Area of a rectangle
\[ \Rightarrow \] A$ = \dfrac{{\surd 3}}{4}{{\text{x}}^2} + {\text{xy}}$ $\left( {{\text{area of equiletaral triangle}} = \dfrac{{\surd 3}}{4}{x^2}\& {\text{ }}area{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}rectangle = xy} \right)$
\[ \Rightarrow \] A$ = \dfrac{{\surd 3}}{4}{{\text{x}}^2} + {\text{x}}\left( {\dfrac{{16 - 3{\text{x}}}}{2}} \right)$ \[ \ldots \] $\left( 1 \right)$
Now, differentiating the above equation $\left( 1 \right)$ with respect to x
We get,
\[ \Rightarrow \]$\dfrac{{{\text{dA}}}}{{{\text{dx}}}} = \dfrac{{\text{d}}}{{{\text{dx}}}}\left( {\dfrac{{\surd 3}}{4}{{\text{x}}^2} + \left( {\dfrac{{16{\text{x}} - 3{{\text{x}}^2}}}{2}} \right)} \right)$
\[ \Rightarrow \]$\dfrac{{{\text{dA}}}}{{{\text{dx}}}} = \dfrac{{\surd 3}}{4}\left( {2{\text{x}}} \right) + \left( {\dfrac{{16 - 6{\text{x}}}}{2}} \right)$
\[ \Rightarrow \]$\dfrac{{{\text{dA}}}}{{{\text{dx}}}} = \dfrac{{\surd 3}}{2}\left( {\text{x}} \right) + 8 - 3{\text{x}}$ \[ \ldots \] (2) \[\]
For maximum or minimum we have,
$\dfrac{{dA}}{{dx}} = $0
On substituting the value of $\dfrac{{dA}}{{dx}}$from (2) we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \]$\dfrac{{\surd 3}}{2}\left( {\text{x}} \right) + 8 - 3{\text{x}} = $0
Taking the terms of x together and simplifying further we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \] $x\left( {3 - \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2}} \right) = 8$
\[ \Rightarrow \] $x\left( {\dfrac{{6 - \surd 3}}{2}} \right) = 8$
\[ \Rightarrow \] $x\left( {6 - \surd 3} \right) = 16$
\[ \Rightarrow \] $x = \dfrac{{16}}{{\left( {6 - \surd 3} \right)}}$
Again differentiating equation (2) with respect to x
We get,
$\dfrac{{{{\text{d}}^2}{\text{A}}}}{{{\text{d}}{x^2}}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} - 3$
Now as $\dfrac{{{{\text{d}}^2}{\text{A}}}}{{{\text{d}}{x^2}}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{2} - 3$<0 , Hence the area is maximum when ${\text{x}} = \dfrac{{16}}{{6 - \surd 3}}$
Now we substitute the value of x in equation (A), we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \]${\text{y}} = \dfrac{{16 - 3\left( {\dfrac{{16}}{{6 - \surd 3}}} \right)}}{2}$
On further simplification we get,
\[ \Rightarrow \]$y = \dfrac{{16 - \dfrac{{48}}{{6 - \surd 3}}}}{2}$
\[ \Rightarrow \]${\text{y}} = \dfrac{{16\left( {6 - \surd 3} \right) - 48}}{{2\left( {6 - \surd 3} \right)}}$
\[ \Rightarrow \]${\text{y}} = \dfrac{{96 - 16\surd 3 - 48}}{{2\left( {6 - \surd 3} \right)}}$
\[ \Rightarrow \]${\text{y}} = \dfrac{{48 - 16\surd 3}}{{2\left( {6 - \surd 3} \right)}}$
\[ \Rightarrow \]\[{\text{y}} = \dfrac{{24 - 8\surd 3}}{{\left( {6 - \surd 3} \right)}}\]
Hence, the breadth of a window $x = \dfrac{{16}}{{\left( {6 - \surd 3} \right)}} \approx 3.75$ and length of a window is ${\text{y}} = \dfrac{{24 - 8\surd 3}}{{\left( {6 - \surd 3} \right)}} \approx 2.375$
Hence, Option C. 3.75, 2.375 is a correct answer.
Note: Equilateral triangle: - An equilateral triangle is a triangle in which all three sides are equal. It is also known as Equiangular in Euclidean geometry that all the three angles are also congruent to each other and are each\[60^\circ \].
The second derivative test is used to determine the local extrema of a function under certain conditions. If a function has a critical point for which $f'(x) = 0$and the second derivative at this point is negative, then f has a local maximum here, whereas if the second derivative is positive then f has a local minimum here.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




