
The runs scored by two teams A and B on the first 60 balls in a cricket match are given below. Represent the data of both the teams on the same graph by frequency polygons.
Number of balls Team A Team B $1 - 6$ 2 5 \[7 - 12\] 1 6 \[13 - 18\] 8 2 \[19 - 24\] 9 10 \[25 - 30\] 4 5 \[31 - 36\] 5 6 \[37 - 42\] 6 3 \[43 - 48\] 10 4 \[49 - 54\] 6 8 \[55 - 60\] 2 10
| Number of balls | Team A | Team B |
| $1 - 6$ | 2 | 5 |
| \[7 - 12\] | 1 | 6 |
| \[13 - 18\] | 8 | 2 |
| \[19 - 24\] | 9 | 10 |
| \[25 - 30\] | 4 | 5 |
| \[31 - 36\] | 5 | 6 |
| \[37 - 42\] | 6 | 3 |
| \[43 - 48\] | 10 | 4 |
| \[49 - 54\] | 6 | 8 |
| \[55 - 60\] | 2 | 10 |
Answer
570.9k+ views
Hint: In this question, Firstly we have to make the continuous class interval. Class interval refers to the numerical width of any class in a particular distribution. It is defined as the difference between the upper-class limit and the lower class limit.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Step1: It can be observed that the class intervals of the given data are not continuous. There is a gap of one in between them. Therefore,\[\;\dfrac{1}{2} = {\text{ }}0.5\] has to be added to the upper class limit and 0.5 has to be subtracted from the lower class limit.
Also, class mark of each interval can be found by using following formula
\[Class{\text{ }}mark{\text{ }} = \dfrac{{\left( {upper{\text{ }}class{\text{ }}limit + lower{\text{ }}class{\text{ }}limit} \right)}}{2}\]
Step2: Continuous data with class mark of each class interval can be represented as follows
Step3: by taking class marks on x axis and runs scored on y axis a frequency polygons can be constructed as
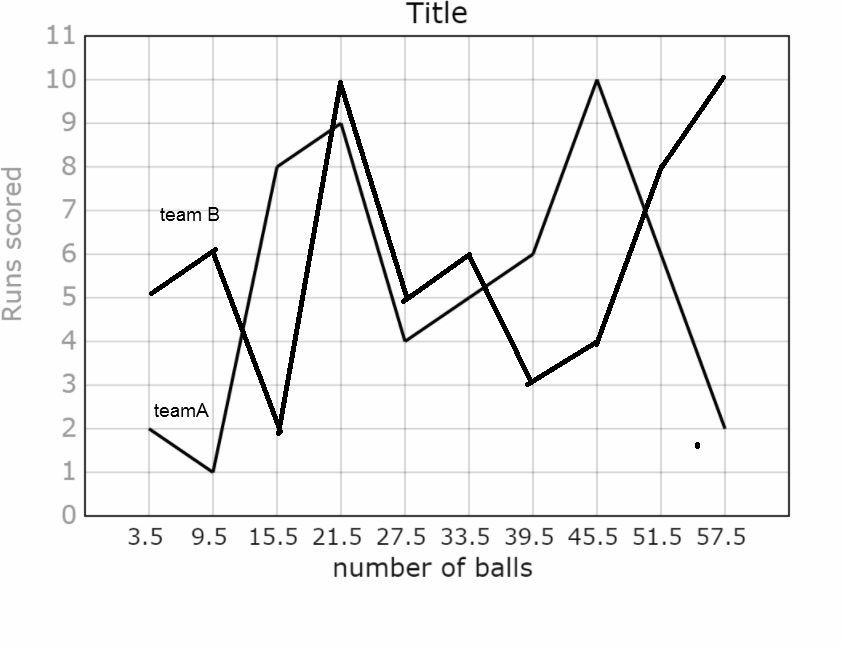
Note: Remember, In order to make class intervals continuous, you are supposed to subtract 0.5 from the lower limit and add 0.5 in the upper limit. The size of the class interval is often selected as 5, 10, 15 or 20 etc. Each class interval starts at a value that is a multiple of the size. There is yet another visual way of representing quantitative data and its frequencies is a polygon.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Step1: It can be observed that the class intervals of the given data are not continuous. There is a gap of one in between them. Therefore,\[\;\dfrac{1}{2} = {\text{ }}0.5\] has to be added to the upper class limit and 0.5 has to be subtracted from the lower class limit.
Also, class mark of each interval can be found by using following formula
\[Class{\text{ }}mark{\text{ }} = \dfrac{{\left( {upper{\text{ }}class{\text{ }}limit + lower{\text{ }}class{\text{ }}limit} \right)}}{2}\]
Step2: Continuous data with class mark of each class interval can be represented as follows
| Number of Balls | Class mark | Team A | Team B |
| \[0.5 - 6.5\] | 3.5 | 2 | 5 |
| \[6.5 - 12.5\] | 9.5 | 1 | 6 |
| \[12.5 - 18.5\] | 15.5 | 8 | 2 |
| \[24.5 - 30.5\] | 27.5 | 4 | 5 |
| \[30.5 - 36.5\] | 33.5 | 5 | 6 |
| \[36.5 - 42.5\] | 39.5 | 6 | 3 |
| \[42.5 - 48.5\] | 45.5 | 10 | 4 |
| \[48.5 - 54.5\] | 51.5 | 6 | 8 |
| \[54.5 - 60.5\] | 57.5 | 2 | 10 |
Step3: by taking class marks on x axis and runs scored on y axis a frequency polygons can be constructed as

Note: Remember, In order to make class intervals continuous, you are supposed to subtract 0.5 from the lower limit and add 0.5 in the upper limit. The size of the class interval is often selected as 5, 10, 15 or 20 etc. Each class interval starts at a value that is a multiple of the size. There is yet another visual way of representing quantitative data and its frequencies is a polygon.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




