
The rod of weight \[W\] is supported by two parallel knife edges \[A\] and \[B\] is in equilibrium in horizontal position. The knives are at a \[d\] distance d from each other. The center of the mass of a rod is at distance \[x\] from the \[A\]. The normal reaction on \[A\] is,
(A) \[\dfrac{W(d-x)}{x}\]
(B) \[\dfrac{W(d-x)}{d}\]
(C) \[\dfrac{Wx}{d}\]
(D) \[\dfrac{Wd}{x}\]
Answer
587.1k+ views
Hint: The rod is supported by two identical knives edges. Here the position of the center of mass is also given. The system is in equilibrium therefore all the forces are balanced and torque at all points is zero. So the question will be solved by a combination of Newton’s third law of motion and torque acting on the given system.
Formula used:
\[{{F}_{x}}(\uparrow )={{F}_{x}}(\downarrow )\]
And \[\tau =r\times f\]
Complete answer:
The rod of weight \[W\] is supported by two parallel knife edges \[A\] and \[B\] is in equilibrium in horizontal position, the knives are at a \[d\] distance d from each other, the center of the mass of a rod is at distance \[x\] from the \[A\], are as shown in figure.
The forces of the system is in equilibrium in \[x\] direction,
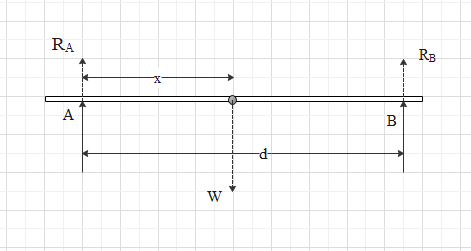
From the Newton’s third law of motion
\[{{R}_{A}}+{{R}_{B}}=W\] \[.....(1)\]
And for that torque about \[B\]knife is zero,
\[(d-x)W+d{{R}_{A}}=0\] \[.....(2)\]
\[\therefore {{R}_{A}}=\dfrac{(d-x)W}{d}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
Torque is the measure of the force which can rotate the body about any particular axis and torque is the cause of angular acceleration. Hence here the system is in equilibrium therefore no angular acceleration in any part of the system. So the torque by knife \[A\] is zero.
Formula used:
\[{{F}_{x}}(\uparrow )={{F}_{x}}(\downarrow )\]
And \[\tau =r\times f\]
Complete answer:
The rod of weight \[W\] is supported by two parallel knife edges \[A\] and \[B\] is in equilibrium in horizontal position, the knives are at a \[d\] distance d from each other, the center of the mass of a rod is at distance \[x\] from the \[A\], are as shown in figure.
The forces of the system is in equilibrium in \[x\] direction,

From the Newton’s third law of motion
\[{{R}_{A}}+{{R}_{B}}=W\] \[.....(1)\]
And for that torque about \[B\]knife is zero,
\[(d-x)W+d{{R}_{A}}=0\] \[.....(2)\]
\[\therefore {{R}_{A}}=\dfrac{(d-x)W}{d}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note:
Torque is the measure of the force which can rotate the body about any particular axis and torque is the cause of angular acceleration. Hence here the system is in equilibrium therefore no angular acceleration in any part of the system. So the torque by knife \[A\] is zero.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




