
The relationship between the dissociation energy of \[{N_2}\] and \[{N_2}^ + \] is :
(A) Dissociation energy of \[{N_2}\]= Dissociation energy of \[{N_2}^ + \]
(B) Dissociation energy of \[{N_2}\] can neither be higher or lower than dissociation energy of \[{N_2}^ + \]
(C) Dissociation energy of \[{N_2}\]> Dissociation energy of \[{N_2}^ + \]
(D) Dissociation energy of \[{N_2}^ + \]> Dissociation energy \[{N_2}\]
Answer
594k+ views
Hint:
We can say that higher the bond order of the bond, the stronger the bond will be. We will require more energy to break stronger bonds. Dissociation energy is the energy required to break a bond.
Complete answer:
Dissociation energy stands for the energy required to break the bond. To compare the energy required to break the bonds in \[{N_2}\] and\[{N_2}^ + \], we can find their bond orders and then can calculate their respective bond strength and from this, we can relate their bond dissociation energies.
So, let’s see the MO diagram of \[{N_2}\] to find its bond order.
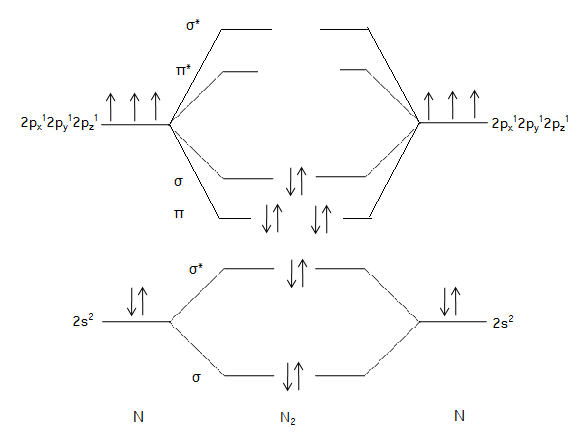
Now, bond order of \[{N_2}\] = \[\dfrac{{Numbers{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}electrons{\text{ }}in{\text{ }}BMO{\text{ }} - {\text{ }}Numbers{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}electrons{\text{ }}in{\text{ }}ABMO}}{2}\]= \[\dfrac{{8 - 2}}{2}\] = 3
Bond order of \[{N_2}\] is 3.
Now, in case of \[{N_2}^ + \], one electron from the valence sigma orbital is removed and hence its bond order will be,
Bond order of \[{N_2}^ + \] = \[\dfrac{{Numbers{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}electrons{\text{ }}in{\text{ }}BMO{\text{ }} - {\text{ }}Numbers{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}electrons{\text{ }}in{\text{ }}ABMO}}{2}\]
= \[\dfrac{{7 - 2}}{2}\]
= 3.5
So, bond order of \[{N_2}^ + \] is 3.5
Now we know that higher the bond order of the bond, higher will be its strength and more strong the bond, more energy it will be required to break it.
So, from the above discussion, we can say that dissociation energy of \[{N_2}^ + \] is lower than that of \[{N_2}\].
So, correct answer is (C) Dissociation energy of \[{N_2}\]> Dissociation energy of \[{N_2}^ + \]
Additional Information:
In such cases like \[{N_2}^ + \], it is possible that the bond order of a species is fractional.
- Bond order between two compounds shows the bond multiplicity as well as the bond strength. As the bond multiplicity increases, the sharing of electrons also increases and therefore the strength increases.
- As the bond order of any bond increases, the bond length decreases, that means bond length and bond strength is inversely proportional.
Note:
Remember here that breaking of all three bonds in both the molecules is assumed. We cannot obtain the energy required to break the single bond of the triple bond between the two nitrogen atoms by just bond order calculations.
We can say that higher the bond order of the bond, the stronger the bond will be. We will require more energy to break stronger bonds. Dissociation energy is the energy required to break a bond.
Complete answer:
Dissociation energy stands for the energy required to break the bond. To compare the energy required to break the bonds in \[{N_2}\] and\[{N_2}^ + \], we can find their bond orders and then can calculate their respective bond strength and from this, we can relate their bond dissociation energies.
So, let’s see the MO diagram of \[{N_2}\] to find its bond order.

Now, bond order of \[{N_2}\] = \[\dfrac{{Numbers{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}electrons{\text{ }}in{\text{ }}BMO{\text{ }} - {\text{ }}Numbers{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}electrons{\text{ }}in{\text{ }}ABMO}}{2}\]= \[\dfrac{{8 - 2}}{2}\] = 3
Bond order of \[{N_2}\] is 3.
Now, in case of \[{N_2}^ + \], one electron from the valence sigma orbital is removed and hence its bond order will be,
Bond order of \[{N_2}^ + \] = \[\dfrac{{Numbers{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}electrons{\text{ }}in{\text{ }}BMO{\text{ }} - {\text{ }}Numbers{\text{ }}of{\text{ }}electrons{\text{ }}in{\text{ }}ABMO}}{2}\]
= \[\dfrac{{7 - 2}}{2}\]
= 3.5
So, bond order of \[{N_2}^ + \] is 3.5
Now we know that higher the bond order of the bond, higher will be its strength and more strong the bond, more energy it will be required to break it.
So, from the above discussion, we can say that dissociation energy of \[{N_2}^ + \] is lower than that of \[{N_2}\].
So, correct answer is (C) Dissociation energy of \[{N_2}\]> Dissociation energy of \[{N_2}^ + \]
Additional Information:
In such cases like \[{N_2}^ + \], it is possible that the bond order of a species is fractional.
- Bond order between two compounds shows the bond multiplicity as well as the bond strength. As the bond multiplicity increases, the sharing of electrons also increases and therefore the strength increases.
- As the bond order of any bond increases, the bond length decreases, that means bond length and bond strength is inversely proportional.
Note:
Remember here that breaking of all three bonds in both the molecules is assumed. We cannot obtain the energy required to break the single bond of the triple bond between the two nitrogen atoms by just bond order calculations.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




