
The relationship between mean, median and mode for a moderately skewed distribution is
A. $\text{Mode=2Median-3Mean}$
B. $\text{Mode=Median+2Mean}$
C. $\text{Mode=3Median-Mean}$
D. $\text{Mode=3Median-2Mean}$
Answer
522.6k+ views
Hint: To find the relationship between mean, median and mode for a moderately skewed distribution, we should express this relationship by Karl Pearson’s formula. It is defined as the distance between the mean and the median is about one-third the distance between the mean and the mode. We can write this as \[\text{Mean}-\text{Median=}\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\left( \text{Mean}-\text{Mode} \right)\] . When solving this, we will get the required solution.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We need to find the relationship between mean, median and mode for a moderately skewed distribution. Let us see what skewed distribution is.
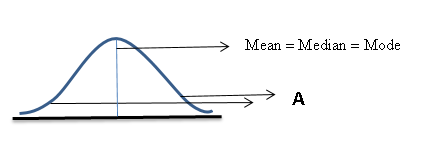
The above figure shows normal distribution. ‘A’ is known as the tail. In this distribution, we can see that $\text{Mean}=\text{Median}=\text{Mode}$ . If one tail is longer than another, the distribution becomes skewed. These are sometimes called asymmetric or asymmetrical distributions.
Let us see the types of skew distribution. There are 2 types –positive and negative.
Negatively-skewed distributions have a long left tail. They are also called negatively-skewed distributions. We can represent it as follows:
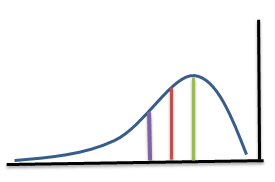
In the above figure, green colour indicates mode, red is median and violet is mean. From the figure, we can get the following relation
$\text{Mode}>\text{Median}>\text{Mean}$
Now, let us see the positively-skewed distribution.
Positive-skew distributions have a long right tail. They are also called right-skewed distributions. We can represent it as follows:
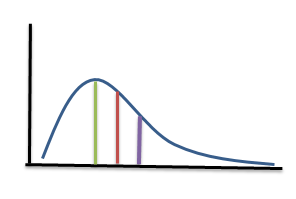
From the above figure, we can observe that
$\text{Mode}<\text{Median}<\text{Mean}$
Now, let us see what moderately-skewed distribution is.
Highly skewed: Skewness is less than -1 or greater than 1
Moderately skewed: Skewness between -1 and -0.5 or between 0.5 and 1.
Approximately symmetric: Skewness is between -0.5 and 0.5.
We can express the relationship between mean, median and mode by Karl Pearson’s formula. It is defined as the distance between the mean and the median is about one-third the distance between the mean and the mode.
\[\text{Mean}-\text{Median=}\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\left( \text{Mean}-\text{Mode} \right)\]
Let us now solve this. We will get
\[\text{Mode}=\text{Mean}-3\left( \text{Mean}-\text{Median} \right)\]
Let us now simplify the RHS. We will get
\[\text{Mode}=\text{Mean}-3\text{Mean+}3\text{Median}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \text{Mode}=-2\text{Mean+}3\text{Median} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{Mode}=3\text{Median}-2\text{Mean} \\
\end{align}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: You may make an error when writing the formula \[\text{Mean}-\text{Median=}\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\left( \text{Mean}-\text{Mode} \right)\] as \[\text{Mean}-\text{Mode=}\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\left( \text{Mean}-\text{Median} \right)\] . Do all the calculations carefully, else the required solution will not be reached. The relation \[\text{Mode}=3\text{Median}-2\text{Mean}\] is used for moderate skewed distribution only.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We need to find the relationship between mean, median and mode for a moderately skewed distribution. Let us see what skewed distribution is.

The above figure shows normal distribution. ‘A’ is known as the tail. In this distribution, we can see that $\text{Mean}=\text{Median}=\text{Mode}$ . If one tail is longer than another, the distribution becomes skewed. These are sometimes called asymmetric or asymmetrical distributions.
Let us see the types of skew distribution. There are 2 types –positive and negative.
Negatively-skewed distributions have a long left tail. They are also called negatively-skewed distributions. We can represent it as follows:

In the above figure, green colour indicates mode, red is median and violet is mean. From the figure, we can get the following relation
$\text{Mode}>\text{Median}>\text{Mean}$
Now, let us see the positively-skewed distribution.
Positive-skew distributions have a long right tail. They are also called right-skewed distributions. We can represent it as follows:

From the above figure, we can observe that
$\text{Mode}<\text{Median}<\text{Mean}$
Now, let us see what moderately-skewed distribution is.
Highly skewed: Skewness is less than -1 or greater than 1
Moderately skewed: Skewness between -1 and -0.5 or between 0.5 and 1.
Approximately symmetric: Skewness is between -0.5 and 0.5.
We can express the relationship between mean, median and mode by Karl Pearson’s formula. It is defined as the distance between the mean and the median is about one-third the distance between the mean and the mode.
\[\text{Mean}-\text{Median=}\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\left( \text{Mean}-\text{Mode} \right)\]
Let us now solve this. We will get
\[\text{Mode}=\text{Mean}-3\left( \text{Mean}-\text{Median} \right)\]
Let us now simplify the RHS. We will get
\[\text{Mode}=\text{Mean}-3\text{Mean+}3\text{Median}\]
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \text{Mode}=-2\text{Mean+}3\text{Median} \\
& \Rightarrow \text{Mode}=3\text{Median}-2\text{Mean} \\
\end{align}\]
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: You may make an error when writing the formula \[\text{Mean}-\text{Median=}\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\left( \text{Mean}-\text{Mode} \right)\] as \[\text{Mean}-\text{Mode=}\dfrac{1}{3}\text{ }\left( \text{Mean}-\text{Median} \right)\] . Do all the calculations carefully, else the required solution will not be reached. The relation \[\text{Mode}=3\text{Median}-2\text{Mean}\] is used for moderate skewed distribution only.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




