
The region close to the p-n junction which is depleted of mobile charge carriers is called the ___________ region.
Answer
509.1k+ views
Hint: A p-n junction is formed when one side of a single crystal of pure semiconductor is doped with acceptor impurity atoms and the other side is doped with donor impurity atoms. A semiconductor that contains no impurity is called an intrinsic semiconductor. We are going to discuss the function of the p-n junction and to find the name of the region close to the p-n junction which is depleted of mobile charge carriers.
Complete step by step answer:
Firstly, we are going to discuss the semiconductor types and about p-n junction diodes. A semiconductor can be classified into two types: Intrinsic semiconductor and Extrinsic semiconductor.
A semiconductor that contains no impurity is called an intrinsic semiconductor. It contains the same number of holes and free electrons. An extrinsic semiconductor contains an impurity with a valency higher or lower than the valency of the pure semiconductor added.
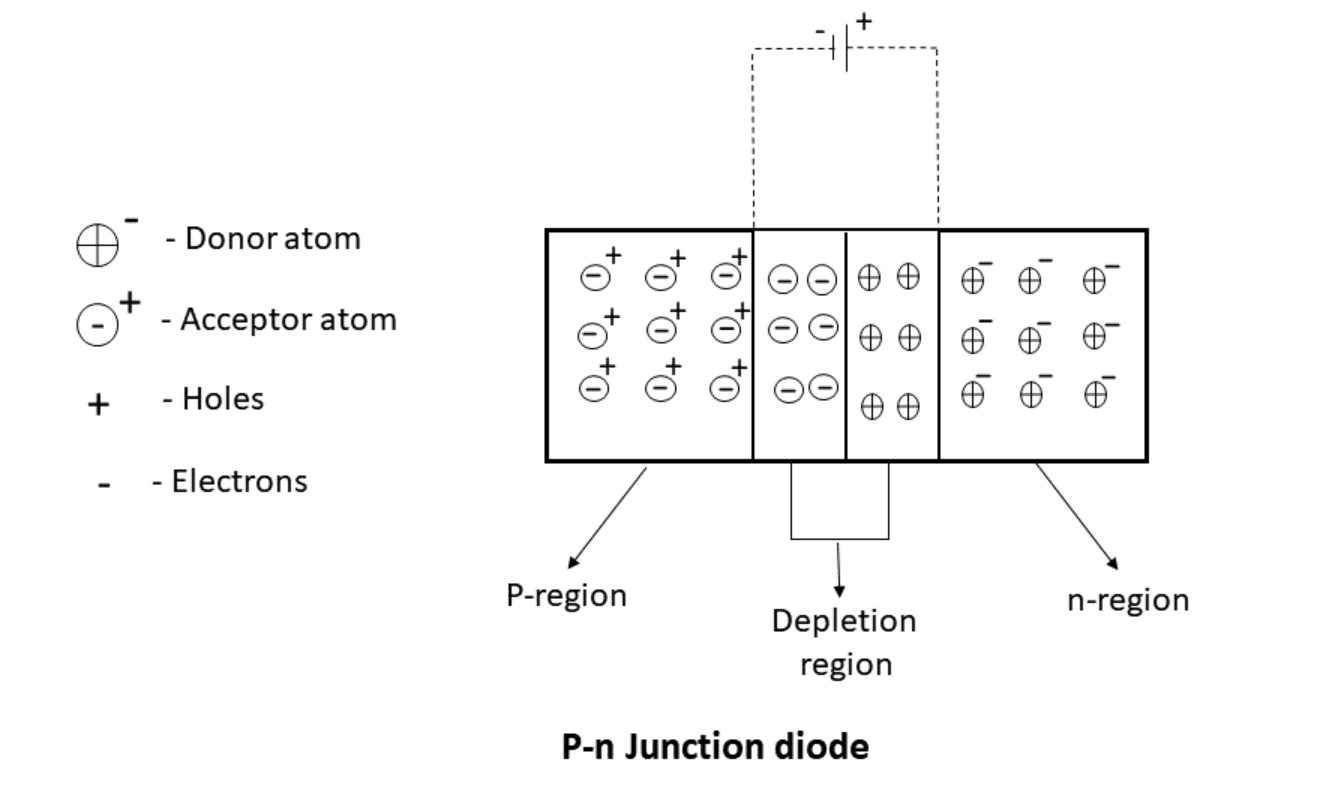
The junction is formed by the free electrons and holes cross through the junction by the process of diffusion. In the p-n junction diode, the holes cross the junction from the P-region into the N-region that recombine with the electrons very close to the N-region.
The Region does not have mobile charges on both the p-type and n-type and acts as a barrier to the flow of electrons and holes. This region contains immobile charge carriers called the depletion region.
Therefore, the region close to the p-n junction which is depleted of mobile charge carriers is called the depletion region.
Note: The depletion region acts as a barrier to the flow of electrons across the junction. As the applied voltage is increased, the current flows across the junction when it reaches the barrier potential. The potential barrier voltages of Germanium, Germanium Arsenide, and silicon are $0.3eV$,$1.1eV$ and $0.7eV$ respectively. The depletion region is also called the depletion zone and the Depletion layer.
Complete step by step answer:
Firstly, we are going to discuss the semiconductor types and about p-n junction diodes. A semiconductor can be classified into two types: Intrinsic semiconductor and Extrinsic semiconductor.
A semiconductor that contains no impurity is called an intrinsic semiconductor. It contains the same number of holes and free electrons. An extrinsic semiconductor contains an impurity with a valency higher or lower than the valency of the pure semiconductor added.

The junction is formed by the free electrons and holes cross through the junction by the process of diffusion. In the p-n junction diode, the holes cross the junction from the P-region into the N-region that recombine with the electrons very close to the N-region.
The Region does not have mobile charges on both the p-type and n-type and acts as a barrier to the flow of electrons and holes. This region contains immobile charge carriers called the depletion region.
Therefore, the region close to the p-n junction which is depleted of mobile charge carriers is called the depletion region.
Note: The depletion region acts as a barrier to the flow of electrons across the junction. As the applied voltage is increased, the current flows across the junction when it reaches the barrier potential. The potential barrier voltages of Germanium, Germanium Arsenide, and silicon are $0.3eV$,$1.1eV$ and $0.7eV$ respectively. The depletion region is also called the depletion zone and the Depletion layer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




