
The reaction of the given compound with HBr gives:
A.
B.
C.
D.





Answer
373.8k+ views
Hint: The addition of hydrogen bromide to an alkene is an electrophilic addition reaction. This reaction takes place according to Markownikoff’s rule. It states that when HBr is added to a carbon-carbon double bond of an alkene, the negative part of the reagent is added to the more substituted carbon atom.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
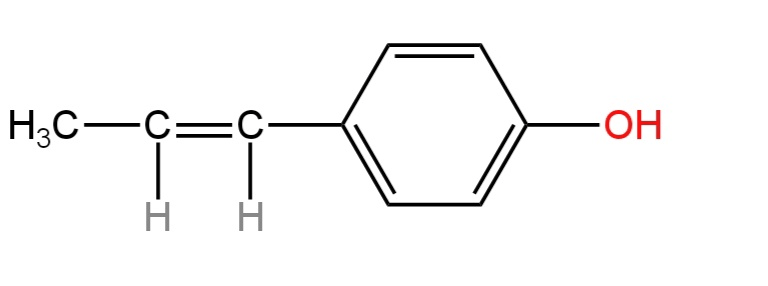
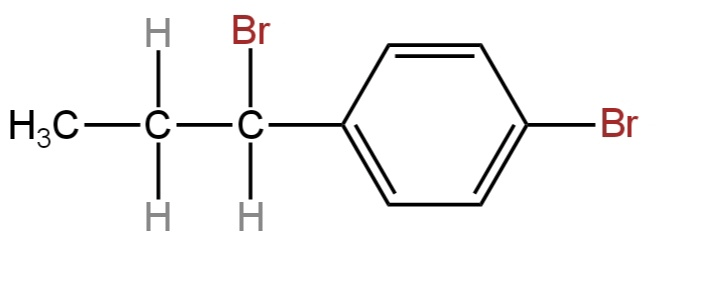
The given compound has the following structure.
Its IUPAC name is 4-(1-Prop-1-enyl)phenol.
It contains an aliphatic portion comprising three carbon atoms and an aromatic portion comprising a benzene ring.
The aliphatic part has a three-membered carbon chain including a carbon-carbon double bond.
This reaction happens in three steps.
Proton from HBr is contributed to a double-bonded alkene group forming a secondary carbocation.
This secondary carbonation undergoes rearrangement to form a more stable benzyl carbocation through a 1,2-hydride shift.
Due to the formation of this carbocation, the positive charge on the carbon atom gets delocalized due to resonance.
The mechanism is as follows:
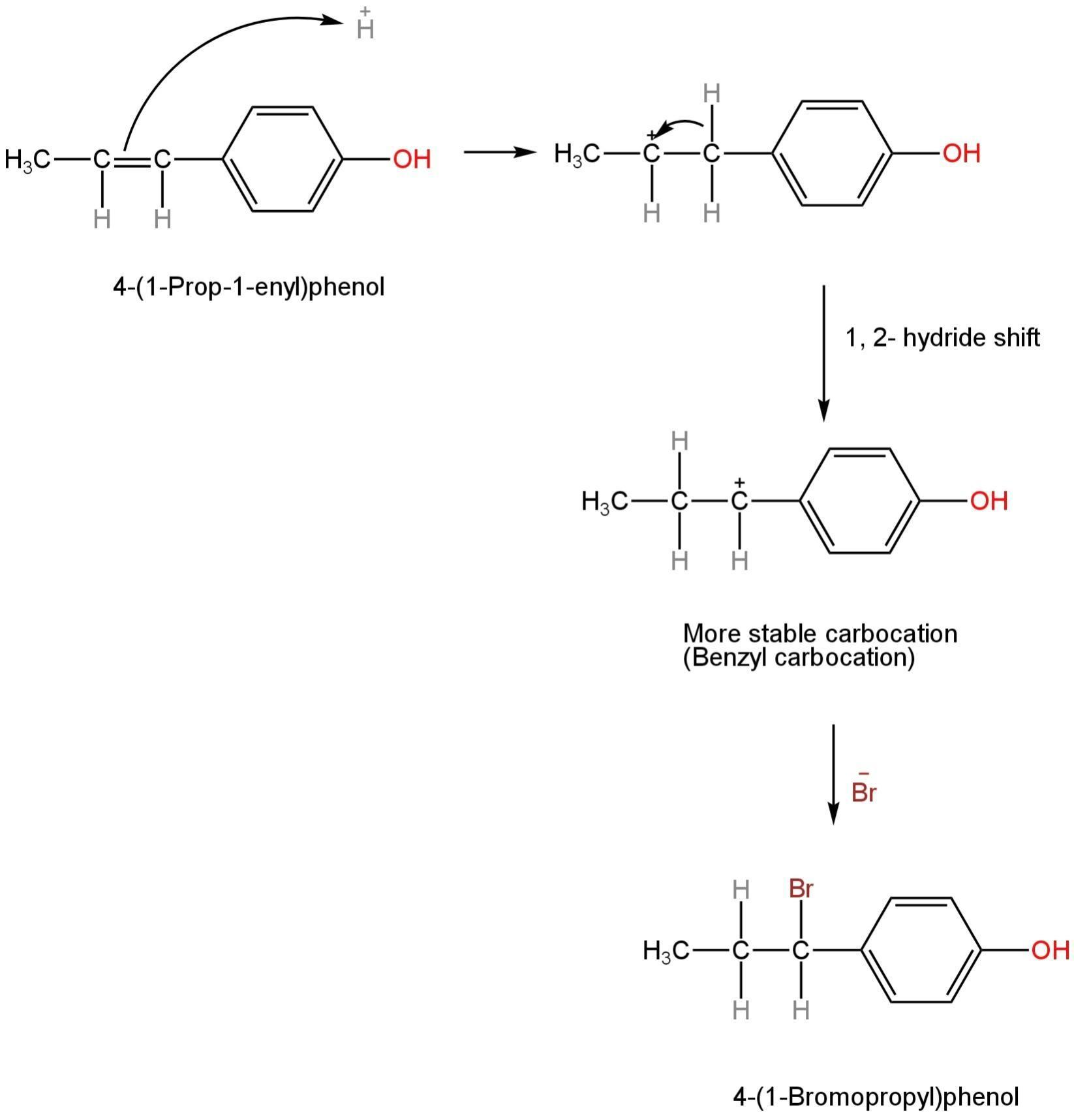
Image: Mechanism of formation of 4-(1-Bromopropyl)phenol.
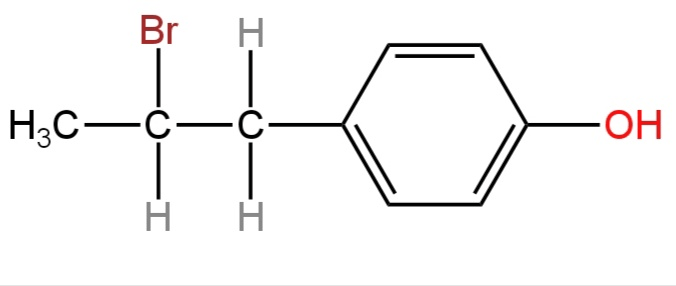
This stable benzyl carbocation then takes a bromide ion to form 4-(1-Bromopropyl)phenol.
4-(1-Prop-1-enyl)phenol on reaction with HBr forms 4-(1-Bromopropyl)phenol
as a major product.
The structure of 4-(1-Bromopropyl)phenol is represented by option C.
So, option C is correct.
Note: Benzyl and allyl carbocations are the most stable carbocation followed by tertiary, secondary, primary, and methyl. 1,2 Hydride Shift is a change in configuration reaction in which hydrogen shifts from one carbon atom to another carbon in a chemical compound. This tendency of movement concerns two adjacent atoms. This occurs to produce a more stable carbocation.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The given compound has the following structure.
Its IUPAC name is 4-(1-Prop-1-enyl)phenol.
It contains an aliphatic portion comprising three carbon atoms and an aromatic portion comprising a benzene ring.
The aliphatic part has a three-membered carbon chain including a carbon-carbon double bond.
This reaction happens in three steps.
Proton from HBr is contributed to a double-bonded alkene group forming a secondary carbocation.
This secondary carbonation undergoes rearrangement to form a more stable benzyl carbocation through a 1,2-hydride shift.
Due to the formation of this carbocation, the positive charge on the carbon atom gets delocalized due to resonance.
The mechanism is as follows:

Image: Mechanism of formation of 4-(1-Bromopropyl)phenol.
This stable benzyl carbocation then takes a bromide ion to form 4-(1-Bromopropyl)phenol.
4-(1-Prop-1-enyl)phenol on reaction with HBr forms 4-(1-Bromopropyl)phenol
as a major product.
The structure of 4-(1-Bromopropyl)phenol is represented by option C.
So, option C is correct.
Note: Benzyl and allyl carbocations are the most stable carbocation followed by tertiary, secondary, primary, and methyl. 1,2 Hydride Shift is a change in configuration reaction in which hydrogen shifts from one carbon atom to another carbon in a chemical compound. This tendency of movement concerns two adjacent atoms. This occurs to produce a more stable carbocation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What is BLO What is the full form of BLO class 8 social science CBSE

The value of 6 more than 7 is A 1 B 1 C 13 D 13 class 7 maths CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell




