
The reaction of propene with $HOCl$ proceeds via the addition of:
(A) $C{{l}^{+}}$ and $O{{H}^{-}}$ in a single step
(B) $C{{l}^{+}}$in the first step
(C) ${{H}^{+}}$ in the first step
(D) $O{{H}^{-}}$in the first step
Answer
585k+ views
Hint: Propene is a member of group alkene in which a double bond is present. The alkenes undergo Electrophilic Addition reaction, in which the first step is the attack of an electrophile or atom/molecule with a positive charge.
Complete step by step solution:
Propene is a compound of group alkene in which a double bond is present at terminal carbon and its formula is$C{{H}_{3}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$. The alkenes show an Electrophilic Addition reaction, which means that the double bond gets converted into a single bond by the addition of electrophiles to the carbon atoms of the double bond.
So, $HOCl$is called hypochlorous acid in which the hydroxyl is the negative part and the chloride ion is the positive part, this is due to the higher electronegativity of the oxygen than chlorine.
The reaction takes place as the chlorine reacts with water to form hypochlorous acid. Now, this hypochlorous acid splits into two ions and these two ions get attached with the double bond in the propene forming 1-Chloropropan-2-ol. The reactions are given below:
$C{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O\to HOCl+HCl$
$C{{H}_{3}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}+HOCl\to C{{H}_{3}}-CH(OH)-C{{H}_{2}}(Cl)+HCl$
The reaction occurs in two steps. In the first step, the chlorine adds slowly to the double bond, and in the second step rapid nucleophile attack by${{H}_{2}}O$. The mechanism is given below:
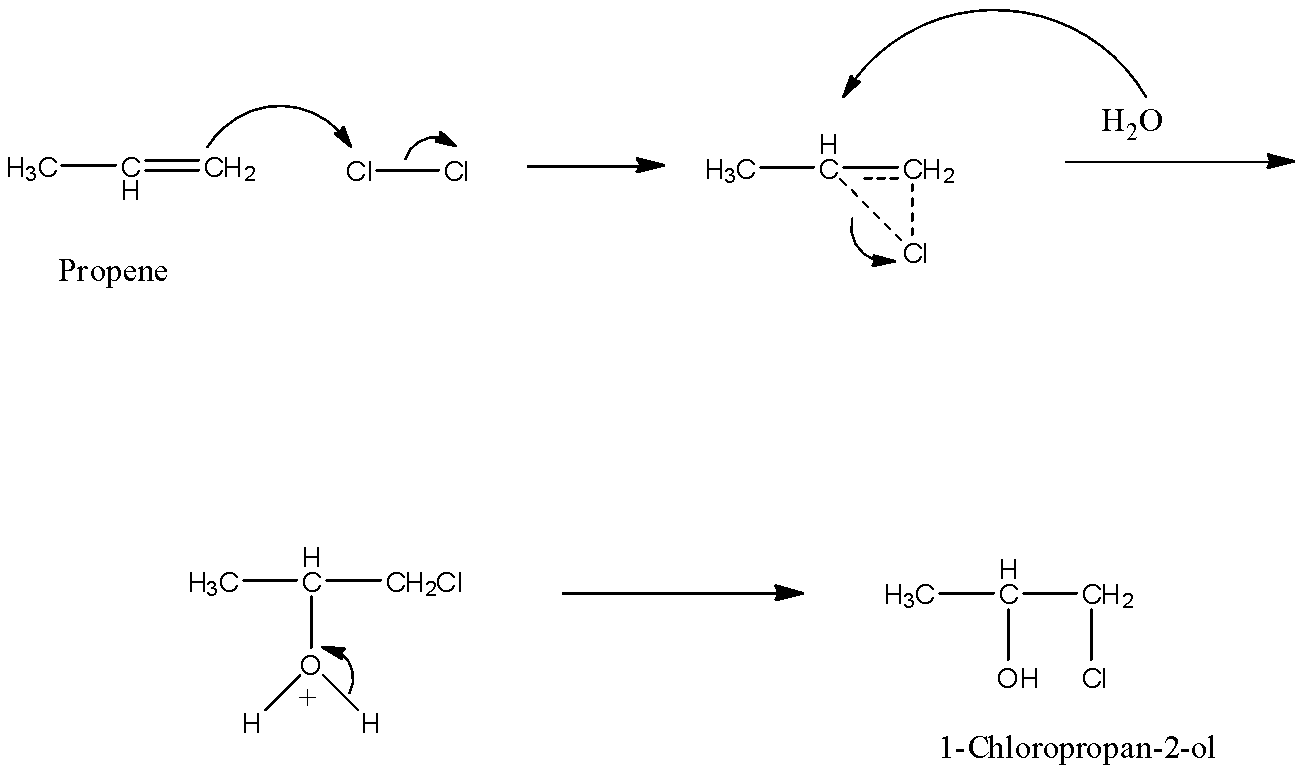
So, the correct answer is an option (B)- $C{{l}^{+}}$ in the first step.
Note: Fluorine doesn't give this reaction. And the reactivity of the halogen towards this reaction decreases as we move down the group, i.e., chlorine > bromine > iodine. Mostly chlorine and bromine give this reaction.
Complete step by step solution:
Propene is a compound of group alkene in which a double bond is present at terminal carbon and its formula is$C{{H}_{3}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}$. The alkenes show an Electrophilic Addition reaction, which means that the double bond gets converted into a single bond by the addition of electrophiles to the carbon atoms of the double bond.
So, $HOCl$is called hypochlorous acid in which the hydroxyl is the negative part and the chloride ion is the positive part, this is due to the higher electronegativity of the oxygen than chlorine.
The reaction takes place as the chlorine reacts with water to form hypochlorous acid. Now, this hypochlorous acid splits into two ions and these two ions get attached with the double bond in the propene forming 1-Chloropropan-2-ol. The reactions are given below:
$C{{l}_{2}}+{{H}_{2}}O\to HOCl+HCl$
$C{{H}_{3}}-CH=C{{H}_{2}}+HOCl\to C{{H}_{3}}-CH(OH)-C{{H}_{2}}(Cl)+HCl$
The reaction occurs in two steps. In the first step, the chlorine adds slowly to the double bond, and in the second step rapid nucleophile attack by${{H}_{2}}O$. The mechanism is given below:

So, the correct answer is an option (B)- $C{{l}^{+}}$ in the first step.
Note: Fluorine doesn't give this reaction. And the reactivity of the halogen towards this reaction decreases as we move down the group, i.e., chlorine > bromine > iodine. Mostly chlorine and bromine give this reaction.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




