
The reaction of chloroform with alcoholic ${\text{KOH}}$ and p-toluidine forms:
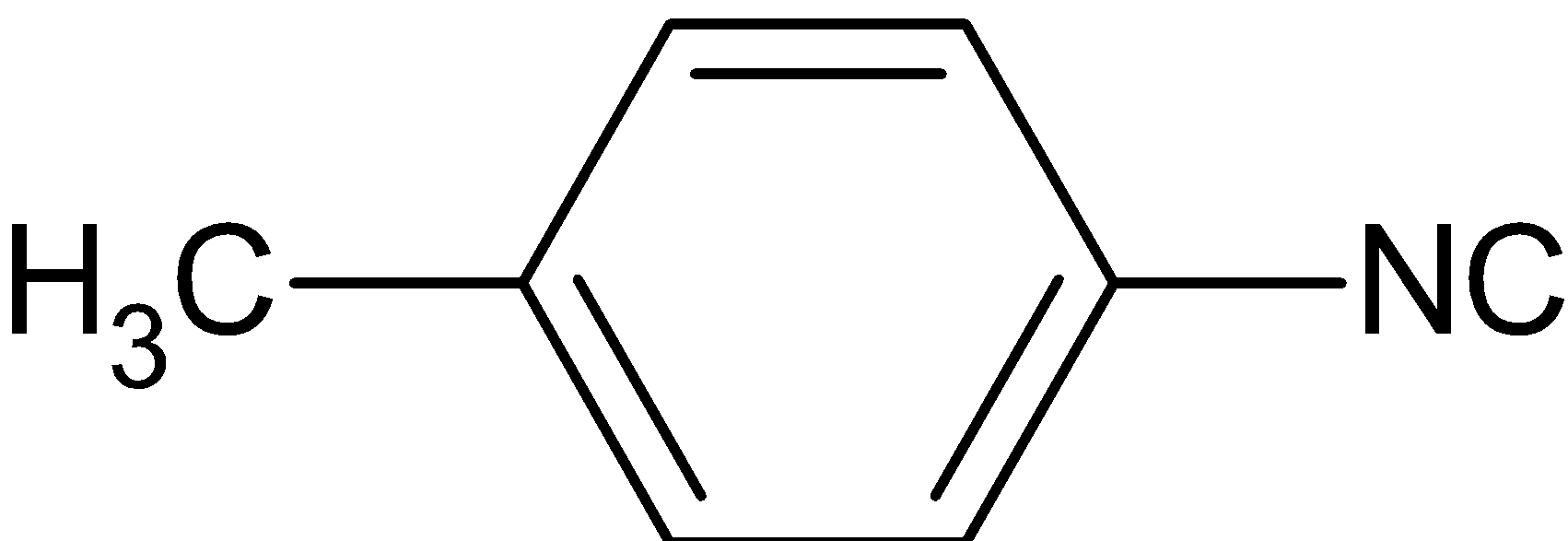
A.
B.
C.
D.




Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint:Chloroform and alcoholic potassium hydroxide are used to carry out the carbylamine reaction. It is a reaction shown only by primary amines, both aliphatic and aromatic. The attacking group is a carbene.
Complete answer:
Chloroform is tri- chloro methane and is given by the formula $CHC{l_3}$. The chemical structure of para- toluidine can be drawn as
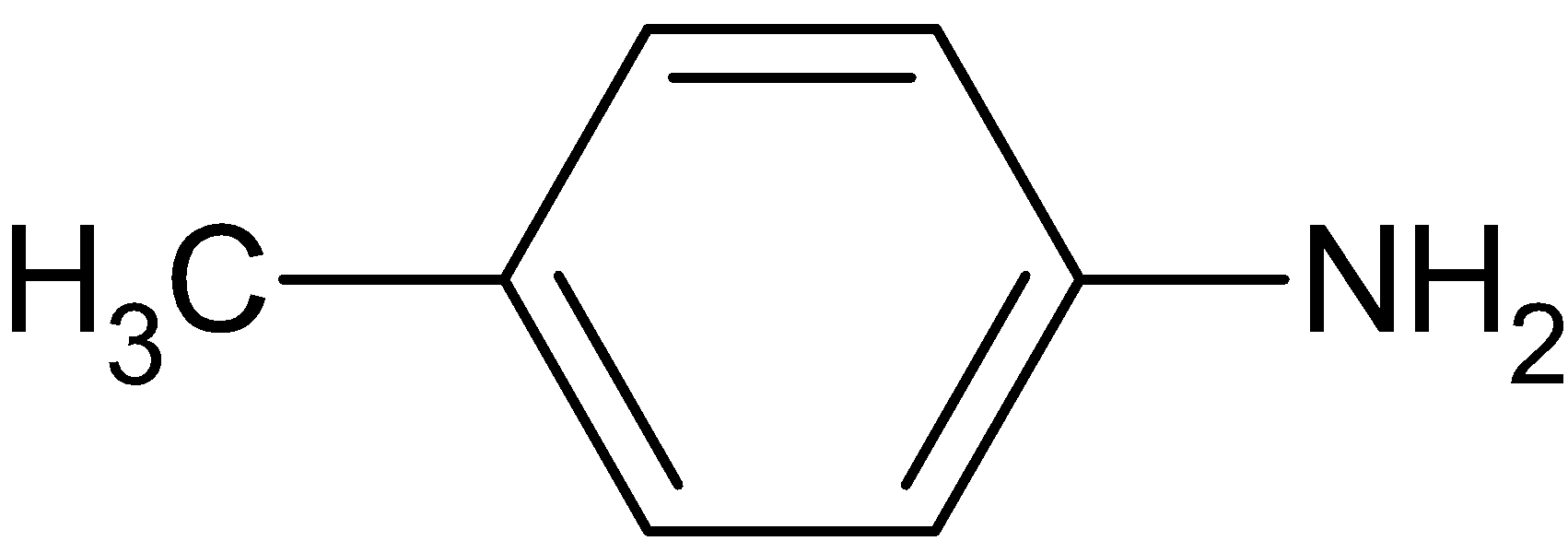
The reaction of primary amines with chloroform in the presence of alcoholic solution of an alkali is known as Hofmann isocyanide synthesis of carbylamine reaction. We know that alcoholic solution of ${\text{KOH}}$ causes dehydrohalogenation in alkyl halides and thus chloroform is converted into dichlorocarbene. Dichlorocarbene is a neutral but electron deficient species. The electrophilic carbene group attacks the nucleophilic nitrogen of the amine. Further dehydrohalogenation of the compound formed yields isocyanide.
The product formed is
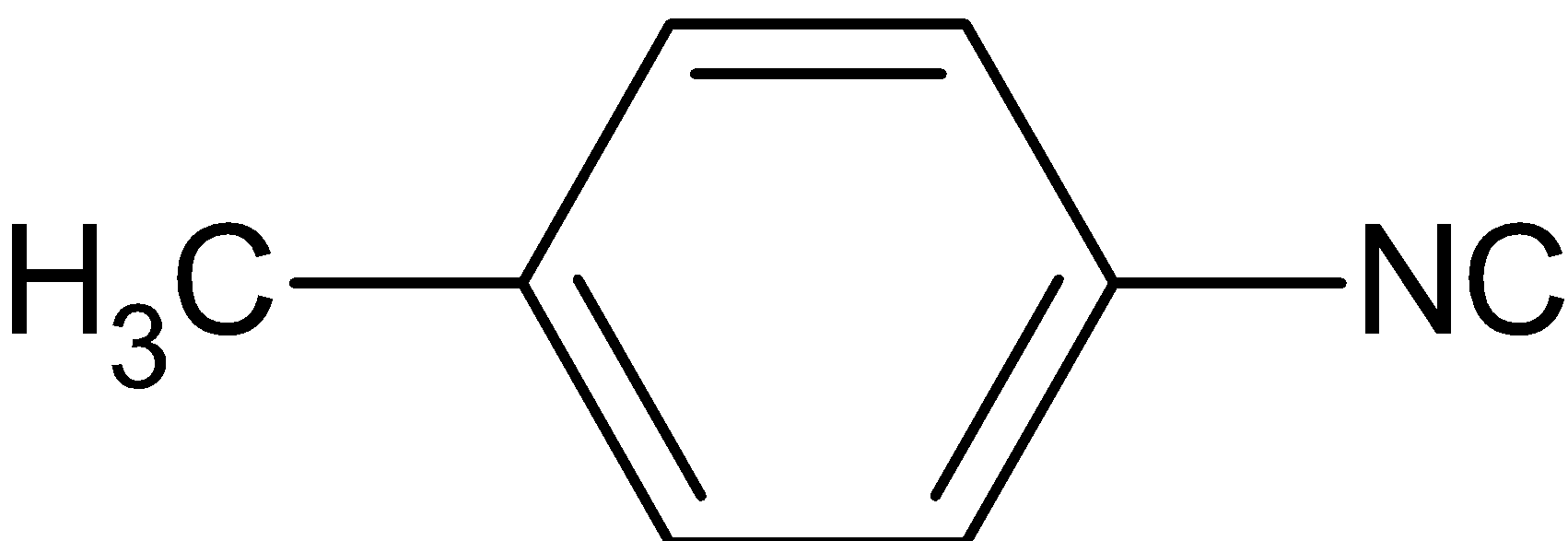
Thus, the correct answer is A.
Additional Information:
This reaction is shown only by primary amines and not by secondary or tertiary amines. Hence, this reaction can be used to detect the presence of primary amines. For the test, the amine is heated in the test tube with chloroform and alcoholic potassium hydroxide. If the compound contains primary amine, isocyanide is formed thus, imparting a foul smell.
Note:
When we use an alcoholic solution of ${\text{KOH}}$, the attacking species formed is different. In alcoholic solution ${\text{KOH}}$ forms an alkoxide ion, which is a strong base. The alkoxide ion extracts a proton from the $\beta $- carbon atom of the alkyl chloride while the chlorine atom leaves as chloride ion. Hence, if the solution used was alcoholic ${\text{KOH}}$, then the compound would have undergone dehydrohalogenation reaction twice forming an alkyne.
Complete answer:
Chloroform is tri- chloro methane and is given by the formula $CHC{l_3}$. The chemical structure of para- toluidine can be drawn as

The reaction of primary amines with chloroform in the presence of alcoholic solution of an alkali is known as Hofmann isocyanide synthesis of carbylamine reaction. We know that alcoholic solution of ${\text{KOH}}$ causes dehydrohalogenation in alkyl halides and thus chloroform is converted into dichlorocarbene. Dichlorocarbene is a neutral but electron deficient species. The electrophilic carbene group attacks the nucleophilic nitrogen of the amine. Further dehydrohalogenation of the compound formed yields isocyanide.
The product formed is

Thus, the correct answer is A.
Additional Information:
This reaction is shown only by primary amines and not by secondary or tertiary amines. Hence, this reaction can be used to detect the presence of primary amines. For the test, the amine is heated in the test tube with chloroform and alcoholic potassium hydroxide. If the compound contains primary amine, isocyanide is formed thus, imparting a foul smell.
Note:
When we use an alcoholic solution of ${\text{KOH}}$, the attacking species formed is different. In alcoholic solution ${\text{KOH}}$ forms an alkoxide ion, which is a strong base. The alkoxide ion extracts a proton from the $\beta $- carbon atom of the alkyl chloride while the chlorine atom leaves as chloride ion. Hence, if the solution used was alcoholic ${\text{KOH}}$, then the compound would have undergone dehydrohalogenation reaction twice forming an alkyne.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw ray diagrams each showing i myopic eye and ii class 12 physics CBSE

Giving reasons state the signs positive or negative class 12 physics CBSE

Explain esterification reaction with the help of a class 12 chemistry CBSE

What is defined as a solenoid Depict a diagram with class 12 physics CBSE




