
The reaction of 4 – bromobenzyl chloride with NaCN in ethanol leads to:
A.4 – bromobenzyl cyanide
B.4 – cyanobenzyl chloride
C.4 – cyanobenzyl cyanide
D.4 – bromo -2 – cyanobenzyl chloride
Answer
589.8k+ views
Hint: The \[S{N^2}\] reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction where a bond is broken and another is formed synchronously. Two reacting species are involved in the rate determining step of the reaction.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
Let us first understand the molecular structures of the compounds that we would be using as reactants and catalysts.
The main reactant that has been given to us is of 4 – bromobenzyl chloride. But before we make the molecular structure of this compound, let us understand how to step by step decode the IUPAC name to form the molecular structure. The parent chain in this form of 4 – bromobenzyl chloride is evidently benzyl chloride. The molecular structure for the benzyl group is basically a benzene with a methyl group at position 1 of the ring. Hence, benzyl chloride is formed when a chlorine atom gets attached on the methyl group of the benzyl molecule. Now, 4 – bromobenzyl chloride is formed when a bromine atom is bonded with a carbon atom at position 4 in the benzene ring. Hence, the molecular structure of 4 – bromobenzyl chloride can be given as:
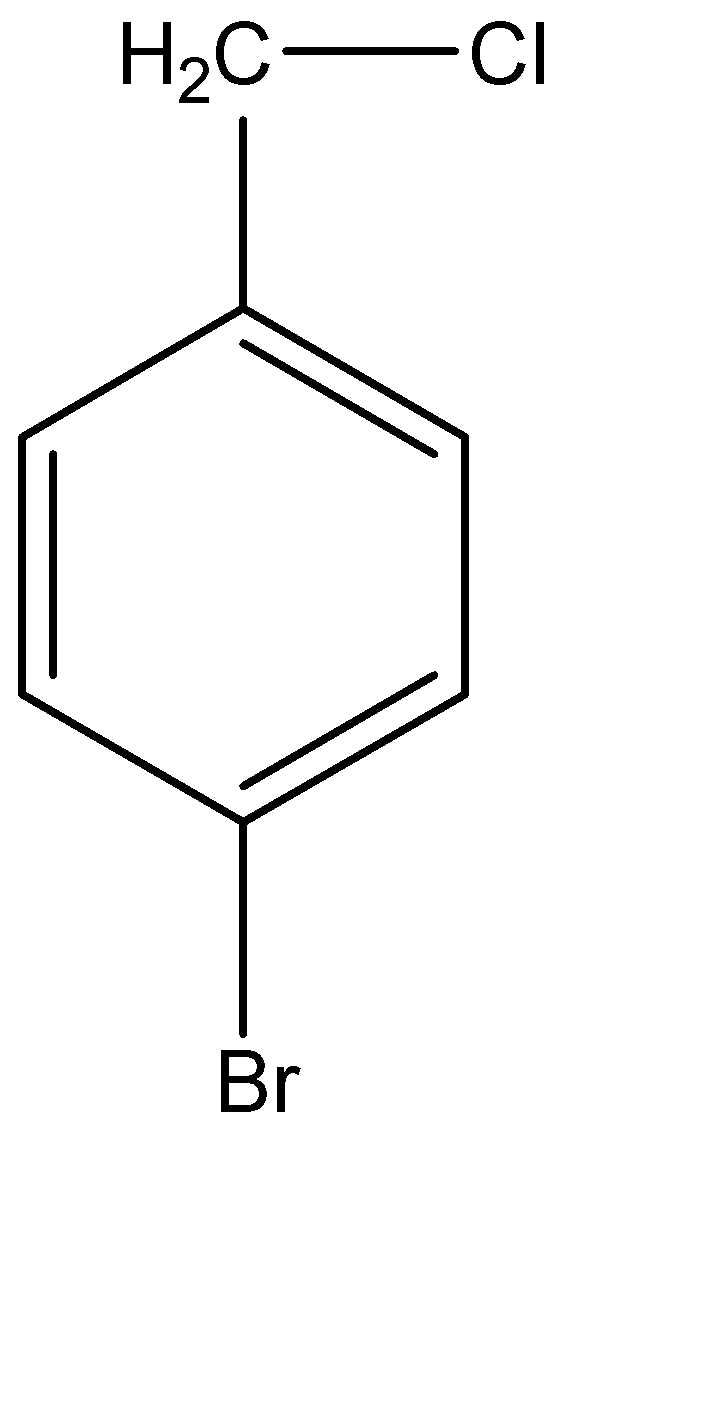
Now this compound is made to react with a compound known as sodium cyanide or NaCN. Another compound used here is ethanol or ethyl alcohol. Ethyl alcohol is a polar aprotic compound, which means that it does not give away its hydrogen atom when dissolved in a solvent. On the other hand, sodium cyanide is a nucleophilic compound. This means that \[C{N^ - }\] acts like the nucleophile.
This Chlorine present on the benzyl chloride molecule will acta s a leaving group and this results in the substitution of \[C{l^ - }\] with \[C{N^ - }\] . This reaction proceeds with \[S{N^2}\] substitution reaction. hence, the chemical reaction can be given as:
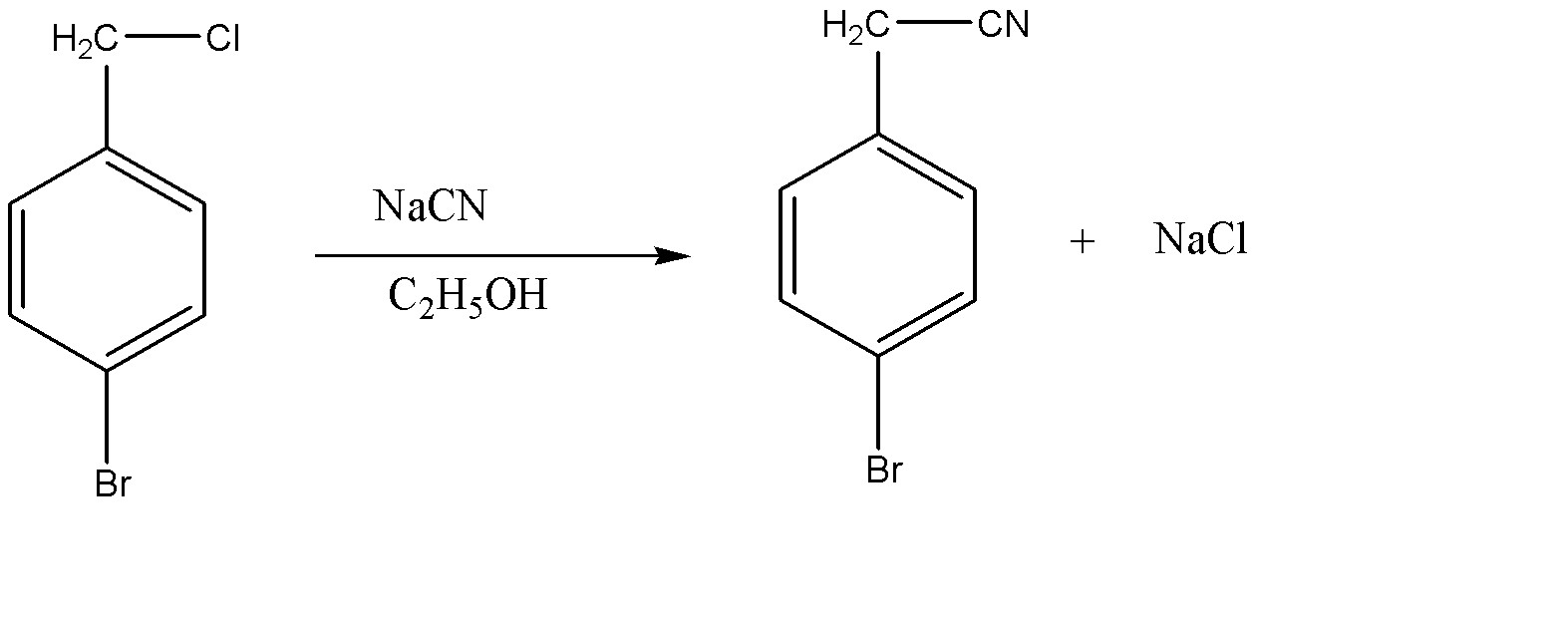
Hence the product formed is 4 – bromobenzyl cyanide
Hence, Option A is the correct option
Note: Now, Bromo group is considered to be an excellent leaving group. But as we can observe, the bromo group has direct bonding with the benzene ring. This allows it to readily participate in the resonance structures and this results in the formation of a pseudo double bond. This does not happen in the case of chlorine. Hence, the \[C - Br\] bond over here is much stronger than the \[C - Cl\] bond.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
Let us first understand the molecular structures of the compounds that we would be using as reactants and catalysts.
The main reactant that has been given to us is of 4 – bromobenzyl chloride. But before we make the molecular structure of this compound, let us understand how to step by step decode the IUPAC name to form the molecular structure. The parent chain in this form of 4 – bromobenzyl chloride is evidently benzyl chloride. The molecular structure for the benzyl group is basically a benzene with a methyl group at position 1 of the ring. Hence, benzyl chloride is formed when a chlorine atom gets attached on the methyl group of the benzyl molecule. Now, 4 – bromobenzyl chloride is formed when a bromine atom is bonded with a carbon atom at position 4 in the benzene ring. Hence, the molecular structure of 4 – bromobenzyl chloride can be given as:

Now this compound is made to react with a compound known as sodium cyanide or NaCN. Another compound used here is ethanol or ethyl alcohol. Ethyl alcohol is a polar aprotic compound, which means that it does not give away its hydrogen atom when dissolved in a solvent. On the other hand, sodium cyanide is a nucleophilic compound. This means that \[C{N^ - }\] acts like the nucleophile.
This Chlorine present on the benzyl chloride molecule will acta s a leaving group and this results in the substitution of \[C{l^ - }\] with \[C{N^ - }\] . This reaction proceeds with \[S{N^2}\] substitution reaction. hence, the chemical reaction can be given as:

Hence the product formed is 4 – bromobenzyl cyanide
Hence, Option A is the correct option
Note: Now, Bromo group is considered to be an excellent leaving group. But as we can observe, the bromo group has direct bonding with the benzene ring. This allows it to readily participate in the resonance structures and this results in the formation of a pseudo double bond. This does not happen in the case of chlorine. Hence, the \[C - Br\] bond over here is much stronger than the \[C - Cl\] bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Chemistry: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

Chemical formula of Bleaching powder is A Ca2OCl2 B class 11 chemistry CBSE

Name the part of the brain responsible for the precision class 11 biology CBSE

The growth of tendril in pea plants is due to AEffect class 11 biology CBSE

One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE




