
The ratio (R) of output resistance ${{r}_{0}}$, and the input resistance ${{r}_{i}}$ in measurements of input and output characteristics of a transistor is typically in the range :
$\begin{align}
& a). {{10}^{2}}-{{10}^{3}} \\
& b). 1-10 \\
& c). 0.1-1.0 \\
& d). 0.1-0.001 \\
\end{align}$
Answer
576.3k+ views
Hint: Find the resistors acting as an input resistor and an output resistor in any transistor. Next, find the range of those individual resistances. As the ratio between the output and the input resistors can be found by dividing the ratios of the ranges of input and output resistors, we can easily find the ratio.
Formulas used:
$R=\dfrac{{{R}_{out}}}{{{R}_{in}}}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
In a transistor, the input resistance throughout the circuit will be ${{r}_{\pi }}$ as the current through the resistor ${{r}_{0}}$ is the only way to pass. The output resistance ill then be equal to ${{R}_{out}}={{r}_{0}}$
Therefore, the ratio between the output resistance and input resistance will be,
$Ratio=\dfrac{{{r}_{0}}}{{{r}_{\pi }}}$
The circuit diagram of a transistor is as follows:
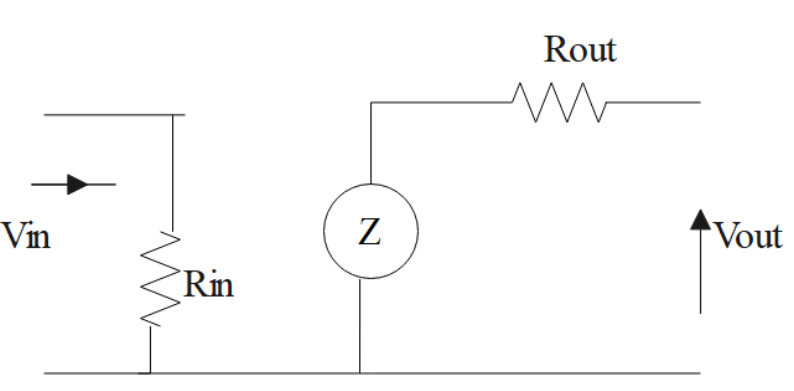
The output resistance is very large in a transistor and its range will be in the order of $100k\Omega $ and the input resistor in a transistor will be of order $1-10k\Omega $
Hence, the ratio between the output resistance and the input resistance will be of order 100-1000.
Therefore, the correct option is option a.
Additional information:
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electric power. It is composed of semiconductor material usually with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. In our day-to-day life, we come across two different types of transistors, one is the PNP transistor, the other transistor ebbing the NPN transistor. A transistor is a type of semiconductor device that can be used to both conduct and insulate electric current or voltage. A transistor basically acts as a switch and an amplifier. In simple words, we can say that a transistor is a miniature device that is used to control or regulate the flow of electronic signals.
Note: The range of input resistors and the output resistors in transistors are not the same for all. Each transistor will be having different ranges of input resistors and output resistors. In the above case, we have considered the small-signal model of a BJT circuit.
Formulas used:
$R=\dfrac{{{R}_{out}}}{{{R}_{in}}}$
Complete step-by-step solution:
In a transistor, the input resistance throughout the circuit will be ${{r}_{\pi }}$ as the current through the resistor ${{r}_{0}}$ is the only way to pass. The output resistance ill then be equal to ${{R}_{out}}={{r}_{0}}$
Therefore, the ratio between the output resistance and input resistance will be,
$Ratio=\dfrac{{{r}_{0}}}{{{r}_{\pi }}}$
The circuit diagram of a transistor is as follows:

The output resistance is very large in a transistor and its range will be in the order of $100k\Omega $ and the input resistor in a transistor will be of order $1-10k\Omega $
Hence, the ratio between the output resistance and the input resistance will be of order 100-1000.
Therefore, the correct option is option a.
Additional information:
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electric power. It is composed of semiconductor material usually with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. In our day-to-day life, we come across two different types of transistors, one is the PNP transistor, the other transistor ebbing the NPN transistor. A transistor is a type of semiconductor device that can be used to both conduct and insulate electric current or voltage. A transistor basically acts as a switch and an amplifier. In simple words, we can say that a transistor is a miniature device that is used to control or regulate the flow of electronic signals.
Note: The range of input resistors and the output resistors in transistors are not the same for all. Each transistor will be having different ranges of input resistors and output resistors. In the above case, we have considered the small-signal model of a BJT circuit.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




