
The radii of two concentric circles are 13cm and 8cm. AB is a diameter of the bigger circle and BD is a tangent to the smaller circle touching at D and intersecting the larger circle at P on produced. Find the length of AP.
Answer
531.2k+ views
Hint – In this particular question use the concept that any tangent on the circle from any point makes an angle 90 degree with the radius of the circle and in any circle if the hypotenuse of the triangle is the diameter than the triangle inscribed in the circle always be a right angle triangle so use these concepts to reach the solution of the question.
Complete step-by-step answer:
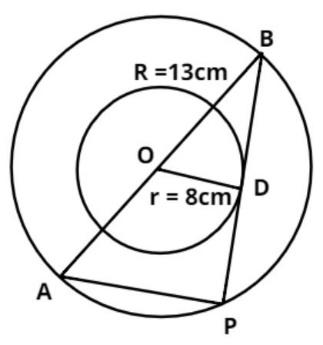
The pictorial representation of the given problem is shown above in the figure.
Let O be the center of the two concentric circles as shown in the figure.
The radii of the bigger circle is 13cm and the lower circle is 8cm.
Therefore, OB = R = 13cm and OD = r = 8cm.
And AB is the diameter of the bigger circle so it is equal to the double the radius of the bigger circle so we have,
Therefore, AB = D = 2R = 2(13) = 26cm.
Now as we know that any tangent on the circle from any point makes an angle 90 degree with the radius of the circle.
Therefore, $\angle BDO = {90^o}$
Now we extend this tangent so that it intersects the bigger circle at point P, now join the point A and P.
If the hypotenuse of the triangle is the diameter then the triangle inscribed in the circle always be a right angle triangle.
So it also makes a 90 degree at point P.
Now consider the triangle OBD and ABP we have,
$\angle OBD = \angle ABP$ (Common)
$\angle ODB = \angle APB = {90^o}$
$\angle DOB = \angle PAB$ (Alternate angle)
So by AAA congruence, these two triangles are congruent.
So in congruent triangles the respective side ratio is always equal.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{OB}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{{OD}}{{AP}} = \dfrac{{DB}}{{PB}}$
So we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{OB}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{{OD}}{{AP}}$
Now substitute the values we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{13}}{{26}} = \dfrac{8}{{AP}}$
Now simplify this we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{8}{{AP}}$
$ \Rightarrow AP = 2\left( 8 \right) = 16$cm.
So the length of the AP is 16cm.
So this is the required answer.
Note – We can also solve this type of question by using Pythagoras’ theorem in triangle OBD and ABP, i.e. ${\left( {{\text{hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^2}$,so by using this theorem in triangle OBD first find out the distance BD, then the distance BP is double the distance of BD, then again apply Pythagoras theorem in triangle ABP and find the distance AP, which is the required answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:

The pictorial representation of the given problem is shown above in the figure.
Let O be the center of the two concentric circles as shown in the figure.
The radii of the bigger circle is 13cm and the lower circle is 8cm.
Therefore, OB = R = 13cm and OD = r = 8cm.
And AB is the diameter of the bigger circle so it is equal to the double the radius of the bigger circle so we have,
Therefore, AB = D = 2R = 2(13) = 26cm.
Now as we know that any tangent on the circle from any point makes an angle 90 degree with the radius of the circle.
Therefore, $\angle BDO = {90^o}$
Now we extend this tangent so that it intersects the bigger circle at point P, now join the point A and P.
If the hypotenuse of the triangle is the diameter then the triangle inscribed in the circle always be a right angle triangle.
So it also makes a 90 degree at point P.
Now consider the triangle OBD and ABP we have,
$\angle OBD = \angle ABP$ (Common)
$\angle ODB = \angle APB = {90^o}$
$\angle DOB = \angle PAB$ (Alternate angle)
So by AAA congruence, these two triangles are congruent.
So in congruent triangles the respective side ratio is always equal.
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{OB}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{{OD}}{{AP}} = \dfrac{{DB}}{{PB}}$
So we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{OB}}{{AB}} = \dfrac{{OD}}{{AP}}$
Now substitute the values we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{13}}{{26}} = \dfrac{8}{{AP}}$
Now simplify this we have,
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} = \dfrac{8}{{AP}}$
$ \Rightarrow AP = 2\left( 8 \right) = 16$cm.
So the length of the AP is 16cm.
So this is the required answer.
Note – We can also solve this type of question by using Pythagoras’ theorem in triangle OBD and ABP, i.e. ${\left( {{\text{hypotenuse}}} \right)^2} = {\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^2} + {\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^2}$,so by using this theorem in triangle OBD first find out the distance BD, then the distance BP is double the distance of BD, then again apply Pythagoras theorem in triangle ABP and find the distance AP, which is the required answer.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Which Country is Called "The Land of Festivals"?

What type of cell is found in the Seminiferous tub class 10 biology CBSE

What are the public facilities provided by the government? Also explain each facility




