
The protein part of the enzyme is known as
A Holoenzyme
B Apoenzyme
C Isoenzyme
D All of the above
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint:Enzymes are the bio-catalyst. They are made up of protein. The function of the enzyme is to speed up the reaction without being utilized. Essential biological reactions such as respiration, photosynthesis, digestion, protein synthesis are catalyzed by enzymes.
Complete answer:
Enzymes are large molecules. Only a small part of a large enzyme has an affinity to bind with the substrate. This small region is known as the active site. Enzymes are specific i.e. they bind to a specific substrate. Example RuBisCo is specific for RUDP. The enzyme converts the substrate molecule into the product.
Enzymes are made up of protein. Enzymes are not fully active. Enzymes show a specific site for binding of Co-factor. Cofactors are non-protein, usually inorganic molecules. Which binds to the inactive enzyme and makes it active for substrate binding.
The protein part i.e. inactive part of the enzyme is called Apoenzyme.
When the cofactor binds to Apoenzyme it becomes active it is called Holoenzyme.
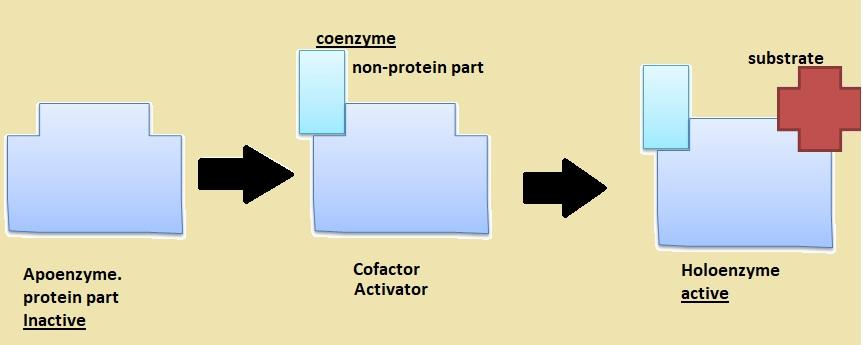
Cofactor when loosely attached to apoenzyme it is called a coenzyme. When the cofactor is firmly bound to the apoenzyme it is called a Prosthetic group.
Isoenzyme is the enzyme which differs in amino acid sequence but catalyzes the same biochemical reaction.
So the correct answer to the given question is option B) Apoenzyme
Note: Apoenzyme is inactive and Holoenzyme is active. A molecule that works with an enzyme is called a substrate. The substrate binds to a specific site known as an active site for substrate binding.
Complete answer:
Enzymes are large molecules. Only a small part of a large enzyme has an affinity to bind with the substrate. This small region is known as the active site. Enzymes are specific i.e. they bind to a specific substrate. Example RuBisCo is specific for RUDP. The enzyme converts the substrate molecule into the product.
Enzymes are made up of protein. Enzymes are not fully active. Enzymes show a specific site for binding of Co-factor. Cofactors are non-protein, usually inorganic molecules. Which binds to the inactive enzyme and makes it active for substrate binding.
The protein part i.e. inactive part of the enzyme is called Apoenzyme.
When the cofactor binds to Apoenzyme it becomes active it is called Holoenzyme.

Cofactor when loosely attached to apoenzyme it is called a coenzyme. When the cofactor is firmly bound to the apoenzyme it is called a Prosthetic group.
Isoenzyme is the enzyme which differs in amino acid sequence but catalyzes the same biochemical reaction.
So the correct answer to the given question is option B) Apoenzyme
Note: Apoenzyme is inactive and Holoenzyme is active. A molecule that works with an enzyme is called a substrate. The substrate binds to a specific site known as an active site for substrate binding.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




